Atoms are tiny particles that form the basic building blocks of all matter in the universe, whether solid, liquid, or gas. All living organisms and nonliving objects found on Earth are made of trillions and trillions of atoms. The smaller particles that make up an atom are known as subatomic particles. Parts of an Atom Diagram Because the sum of the numbers of protons and neutrons equals the mass number, 127, the number of neutrons is 74 (127 − 53 = 74). Since the iodine is added as a 1− anion, the number of electrons is 54 [53 - (1-) = 54]. Exercise 2.2.1 2.2. 1. An ion of platinum has a mass number of 195 and contains 74 electrons.

Learn the Parts of an Atom
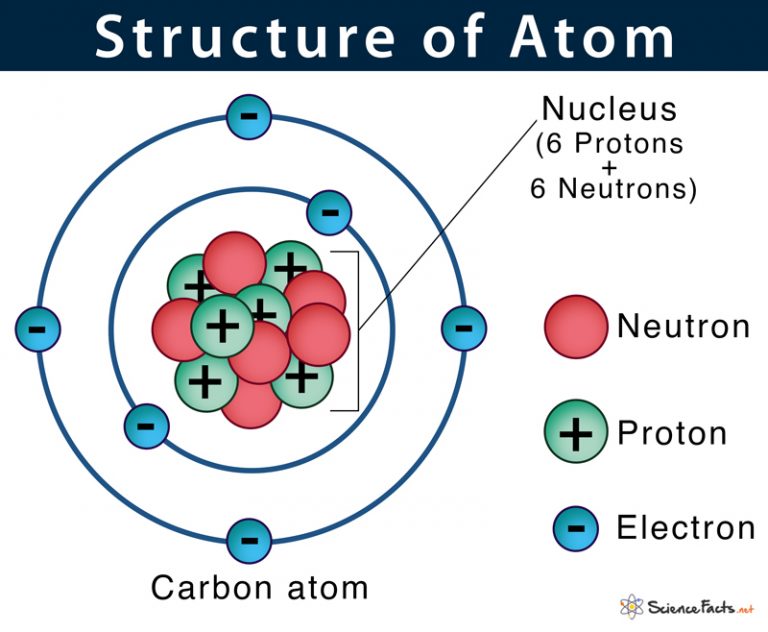
Most of the atom is empty space. The rest consists of three basic types of subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons.The protons and neutrons form the atom's central nucleus. (The ordinary hydrogen atom is an exception; it contains one proton but no neutrons.) As their names suggest, protons have a positive electrical charge, while neutrons are electrically neutral—they carry. Devised by Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev (1834-1907) in 1869, the table places elements into columns— groups —and rows— periods —that share certain properties. These properties determine an element's physical state at room temperature—gas, solid, or liquid—as well as its chemical reactivity, the ability to form chemical bonds with other atoms. An ion of an atom is one in which the number of protons and electrons is not the same. If there are more protons than electrons, an atomic ion has a positive charge and is called a cation. If there are more electrons than protons, the ion has a negative charge and is called an anion. While protons and neutrons are located inside the nucleus at the center of the atom, electrons are located outside the nucleus in what is often called the electron cloud. Figure 4.4.1 4.4. 1: Electrons are much smaller than protons or neutrons. If an electron was the mass of a penny, a proton or a neutron would have the mass of a large bowling.
atom diagram to label
Atom Diagram [/caption]The image on the left is a basic atom diagram. This one shows the protons, neutrons, and electrons of a carbon atom. Each is in a group of six. That makes the atom. An atom that gains one or more electrons will exhibit a negative charge and is called an anion. Positively charged atoms called cations are formed when an atom loses one or more electrons. For example, a neutral sodium atom (Z = 11) has 11 electrons. If this atom loses one electron, it will become a cation with a 1+ charge (11 − 10 = 1+). You can see that each part of the atom is labeled with a "+", "-", or a "0." Those symbols refer to the charge of the particle. Have you ever heard about getting a shock from a socket, static electricity, or lightning? Those are all related to electric charges. Charges are also found in tiny particles of matter. Relative charge. -1. The number of electrons in an atom is always the same as the number of protons, so atoms are electrically. neutral. overall. Atoms can lose or gain electrons. When they do.
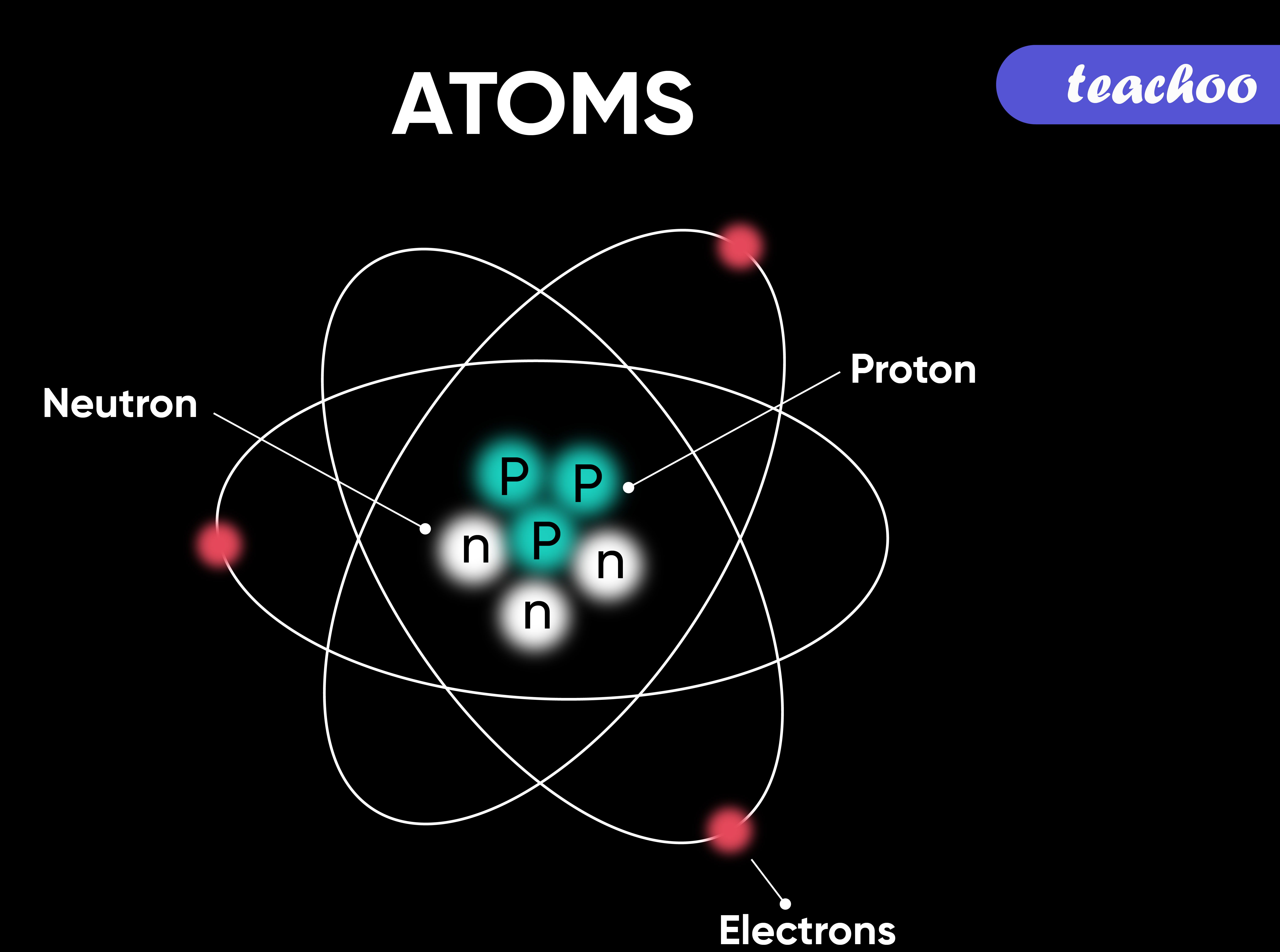
What is Atom? How does it Exist? and it's Symbols Teachoo
Chemical Symbols. A chemical symbol is an abbreviation that we use to indicate an element or an atom of an element. For example, the symbol for mercury is Hg (Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\)). We use the same symbol to indicate one atom of mercury (microscopic domain) or to label a container of many atoms of the element mercury (macroscopic domain). Key Takeaways: Model of the Atom. An atom is a building block of matter that cannot be broken apart using any chemical means. Nuclear reactions can alter atoms. The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged). Protons and neutrons form the atomic nucleus.
Mass: The majority of an atoms' mass comes from the protons and neutrons that make up its nucleus. Electrons are the least massive of an atom's constituent particles, with a mass of 9.11 x 10-31. And while ancient magi and philosophers conceived of a world composed of four or five elements - earth, air, water, fire (and metal, or consciousness) - by classical antiquity, philosophers began.

Energy Mind Map
The Structure of an Atom Explained With a Labeled Diagram - Science Struck The Structure of an Atom Explained With a Labeled Diagram An atom is the basic unit of matter. The following article provides you with diagrams that will help you understand the structure of an atom better. This entry was posted on January 20, 2017 by Anne Helmenstine (updated on November 19, 2023) The three main parts of an atom are protons, neutrons, and electrons. The atom is the basic building block of matter. Atoms combine to form pure elements, compounds, and complex forms like computers and phones. Atoms are the smallest particle of matter.




