Element Sodium (Na), Group 1, Atomic Number 11, s-block, Mass 22.990. Sources, facts, uses, scarcity (SRI), podcasts, alchemical symbols, videos and images. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable isotope is 23 Na. The free metal does not occur in nature and must be prepared from compounds. Sodium is the sixth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and exists in numerous minerals such as feldspars, sodalite, and halite (NaCl).
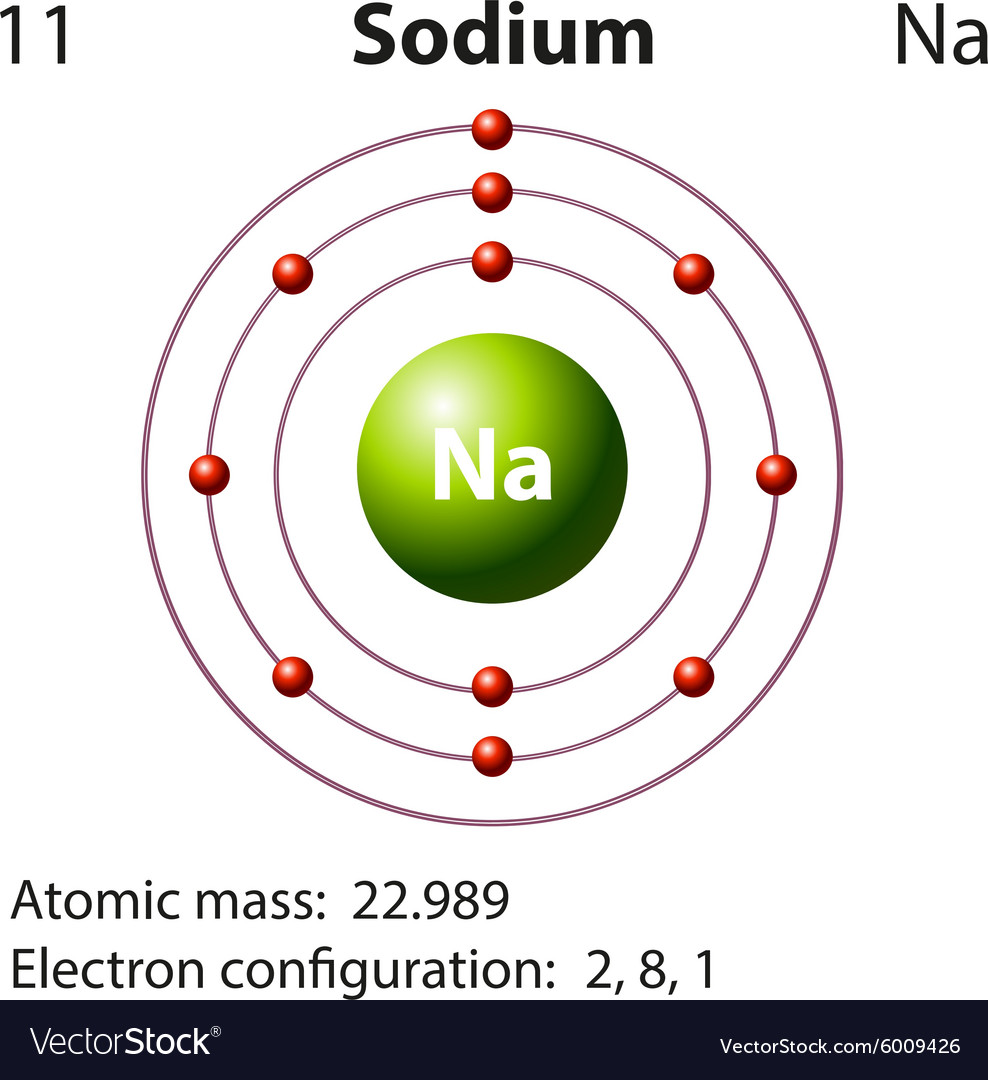
Diagram representation of the element sodium Vector Image
Atomic Structure of the Sodium Atom (Na) 28,372 views 294 The Sodium atom (Na) is commonly used for examples and practice problems in chemistry. In this video we'll look at the atomic. Atomic no. Element Shorthand Electron Configuration Full Electron Configuration Electron shell arrangement; 1: Electron configuration of Hydrogen (H) 1s 1: 1s 1: 1: 2: Electron configuration of Helium (He) 1s 2: 1s 2: 2: 3: Electron configuration of Lithium (Li) [He] 2s 1: 1s 2 2s 1: 2, 1: 4: Electron configuration of Beryllium (Be) [He] 2s 2. Periodic Table element Summary Sodium Sodium is a chemical element with symbol Na and atomic number 11. Classified as a n alkali metal, Sodium is a solid at room temperature. 11 Na Sodium View All Properties H He Li Be B C N O F Ne Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar K Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Figure 2.2.1 2.2. 1: The Structure of the Atom. Atoms have protons and neutrons in the center, making the nucleus, while the electrons orbit the nucleus. The modern atomic theory states that atoms of one element are the same, while atoms of different elements are different.

Atom Sodium Model Stock Illustration Download Image Now iStock
sodium (Na), chemical element of the alkali metal group (Group 1 [Ia]) of the periodic table. Sodium is a very soft silvery-white metal. Sodium is the most common alkali metal and the sixth most abundant element on Earth, comprising 2.8 percent of Earth's crust. Molecular Formula Na Synonyms 7440-23-5 Na Sodium Natrium Sodio View More. Molecular Weight 22.9897693 g/mol Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14) Element Name Sodium Dates Create: 2004-09-16 Modify: 2023-12-23 Description Sodium appears as a silvery soft metal that becomes grayish white upon exposure to air. Sodium is a chemical element with atomic number 11 which means there are 11 protons and 11 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Sodium is Na. Sodium is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. The chemical abbreviation for sodium was first published by Jöns Jakob Berzelius in his system of atomic symbols. It is a contraction of the element's new Latin name natrium, which refers to the Egyptian natron, a natural mineral salt primarily made of hydrated sodium carbonate. In 1807, Sir Humphry Davy isolated sodium for the first time by electrolysis of dried sodium hydroxide, which had.
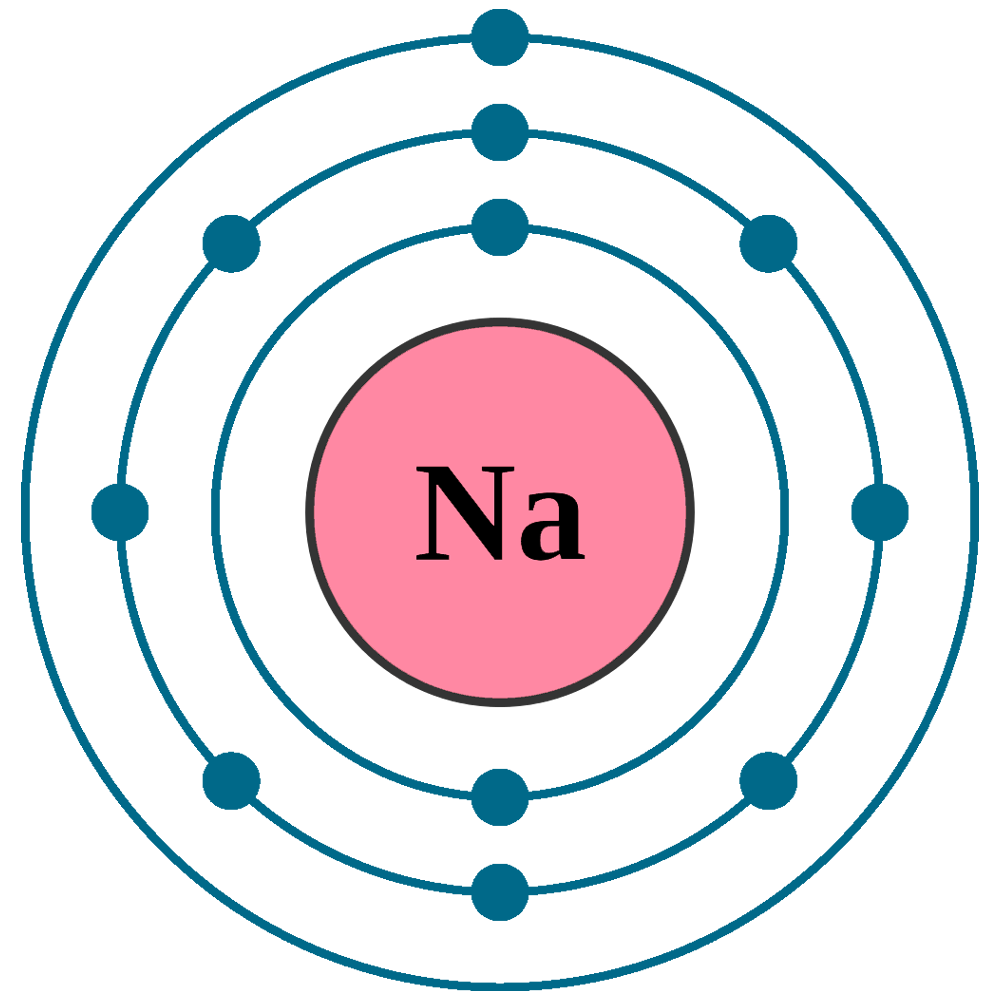
Sodium Na (Element 11) of Periodic Table NewtonDesk
Name: Sodium Symbol: Na Atomic Number: 11 Atomic Mass: 22.98977 amu Melting Point: 97.72 °C (370.87 K, 207.9 °F) Boiling Point: 883 °C (1156 K, 1621 °F) Number of Protons/Electrons: 11 Number of Neutrons: 12 Classification: Alkali Metal Crystal Structure: Cubic Density @ 293 K: 0.971 g/cm 3 Color: silvery Atomic Structure Protons and Neutrons in Sodium. Sodium is a chemical element with atomic number 11 which means there are 11 protons in its nucleus. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z.The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10-19 coulombs.
Element 11 of Periodic table is Sodium with atomic number 11, atomic weight 22.98977. Sodium, symbol Na, has a Body Centered Cubic structure and Silver color. Sodium is a Alkali Metal element. It is part of group 1 (lithium family). Sodium is a chemical element with atomic number 11 in the periodic table. It's the fourth most abundant element and comprises around 2.6% of Earth's crust. Being a member of the alkali metals family of the periodic table, this monoisotopic element has one valence electron that makes it one of the most reactive elements in the periodic table.

Sodium (Na). Diagram of the nuclear composition, electron configuration, chemical data, and
nglos324 - sodium Sodium is an alkali metal in group IA of the periodic table with atomic number 11, an atomic weight of 22.99, and a density of 0.97 Mg/m 3 . Its melting point is 97.8 C, and it boils at 892 C. The electronic configuration of Sodium is (Ne) (3s 1 ). Its atomic radius is 0.190 nm and the (+1) ionic radius is 0.95 nm. Sodium has the electronic structure 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 1. When sodium atoms come together, the electron in the 3s atomic orbital of one sodium atom shares space with the corresponding electron on a neighboring atom to form a molecular orbital - in much the same sort of way that a covalent bond is formed.




