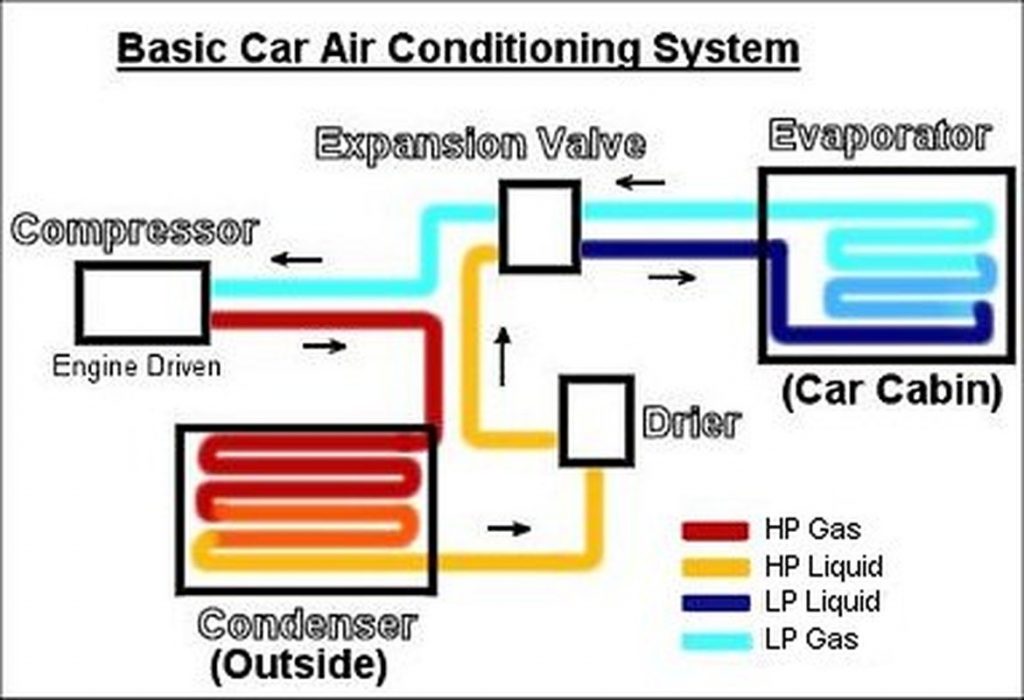
Free Shipping Available. Buy on ebay. Money Back Guarantee! All automotive air conditioning systems are (nearly) closed loops with a high-pressure side and low-pressure side. We'll start with the high-pressure side as it leads from the engine to the passenger compartment:. Compressor: The compressor is a pump driven by a belt attached to the engine's crankshaft. When the refrigerant is drawn into the compressor, it is in a low-pressure gaseous form.
How does your car airconditioning work? ABC Services Cheltenham
The air conditioning system is made up of the following components: compressor, condenser, evaporator, orifice tube (or expansion valve), and an accumulator (or receiver-drier). Each of these components serves a different purpose. Learn more about the repetitive cycle of the system from the list of air conditioner components and the AC parts. Automotive air conditioning (A/C) systems have become more complex, making DIY repair more difficult. Strict environmental regulations also make repairs more costly and complicated. The most common air conditioning parts are the compressor, condenser, evaporator, orifice tube, thermal expansion valve, receiver-driver, and accumulator. The automobile air conditioner must be capable of removing all the heat inputs. Heat load on the air conditioner for customary units is expected to be as high as 18000 Btu/hr, which is equivalent to 1.5 tons of air conditioning. About half of this heatis conducted through the body metal and Step 2: Condenser. Example of a car A/C condenser. When the refrigerant gets to the condenser, it is hot because of the pressure. Its purpose is to collect this heat and move it out of the AC system. You can imagine this as a small radiator, where the gas releases the heat as it goes through. Air is also flowing around the condenser, which.
An effective guide to car air conditioning system repair CSY
The air-conditioning system in a car works by manipulating refrigerant between a liquid and a gaseous state. As the refrigerant changes states, it absorbs heat and humidity from the vehicle and allows the system to give off cool, dry air. To change the refrigerant between a liquid and a gaseous state, the air-conditioning system works to. The system drew in more outside air than contemporary systems; thus, reducing the staleness associated with automotive air conditioning at the time. Instead of plastic tubes mounted on the rear window package shelf as on GM cars, small ducts directed cool air toward the ceiling of the car where it filtered down around the passengers instead of blowing directly on them, a feature that modern. Step 1: Turn the engine off and install the gauge set. Step 2: Restart the engine and turn on the air conditioning. Step 3: Observe the pressure readings. Though every air conditioning system will vary, you want to see the high side pressure around 20 psi and the low side around 40 psi. How Car Air Conditioning Systems Work.As with the air conditioning you have at home or work, your car's A/C is made up of three main components: the compressor, evaporator, and condenser. The compressor is a pump that is attached by a belt to your car's engine crankshaft. The unit's refrigerant (R-134a or HFC-134a) is drawn into the.

Rowleys Tires & Automotive Services Complete Auto Repair Bay City Tires Air Conditioning
Air conditioning has two main purposes: Cools the air entering the passenger compartment. Removes the moisture from the air so it feels more comfortable inside the vehicle. In many makes, air conditioning cycles automatically when the defrost setting is chosen. It pulls the humidity from the windshield to improve your visibility. The Vapir 3 - S Compact Climate Control System is similar to the Vapir 2 -S but with a new distribution duct design to give you independent adjustability between dash, defrost and floor modes. The Vapir 3 - S A/C system was designed to install on a smooth firewall with our multi-mount system.
The air conditioning system is made up of two distinct sides, which include high-pressure and low-pressure components. Types of A/C Systems. There are two main types of automotive A/C systems: Thermal Expansion Valve systems (TEV, TXV, or TX) and Clutch-Cycling Orifice Tube systems (CCOT). Both of these are closed systems, meaning that. Here's a basic summary of how each part produces these phase changes and keeps the cabin cool. Compressor: The air conditioning compressor, driven by a belt or electric motor, circulates refrigerant in the system. Compressed refrigerant moves through tubes and hoses to the drier and condenser. Condenser: Usually mounted forward of the.

The history of the Automotive Air Conditioning System
Topic Discussed:how an Automotive Air Conditioning System works, along with the different parts and functions of different components of an Automotive Air Co. 8. Use the Fresh Air Vent, But Only Occasionally. 9. Intermittently Run Your Air in Defrost Mode. 10. Keep the A/C on the Coldest Setting. 1. Watch High Engine Temperatures on Steep Grades. If you.




