Bunsen Burner is a kind of gas burner that creates a safe, smokeless, hot, and non-luminous flame which can be used for various scientific experiments and research. In 1857, German scientist Robert Bunsen and his lab assistant Peter Desaga invented the Bunsen burner and named it after his surname. A Bunsen burner, named after Robert Bunsen, is a kind of ambient air gas burner used as laboratory equipment; it produces a single open gas flame, and is used for heating, sterilization, and combustion. [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] The gas can be natural gas (which is mainly methane) or a liquefied petroleum gas, such as propane, butane, or a mixture.
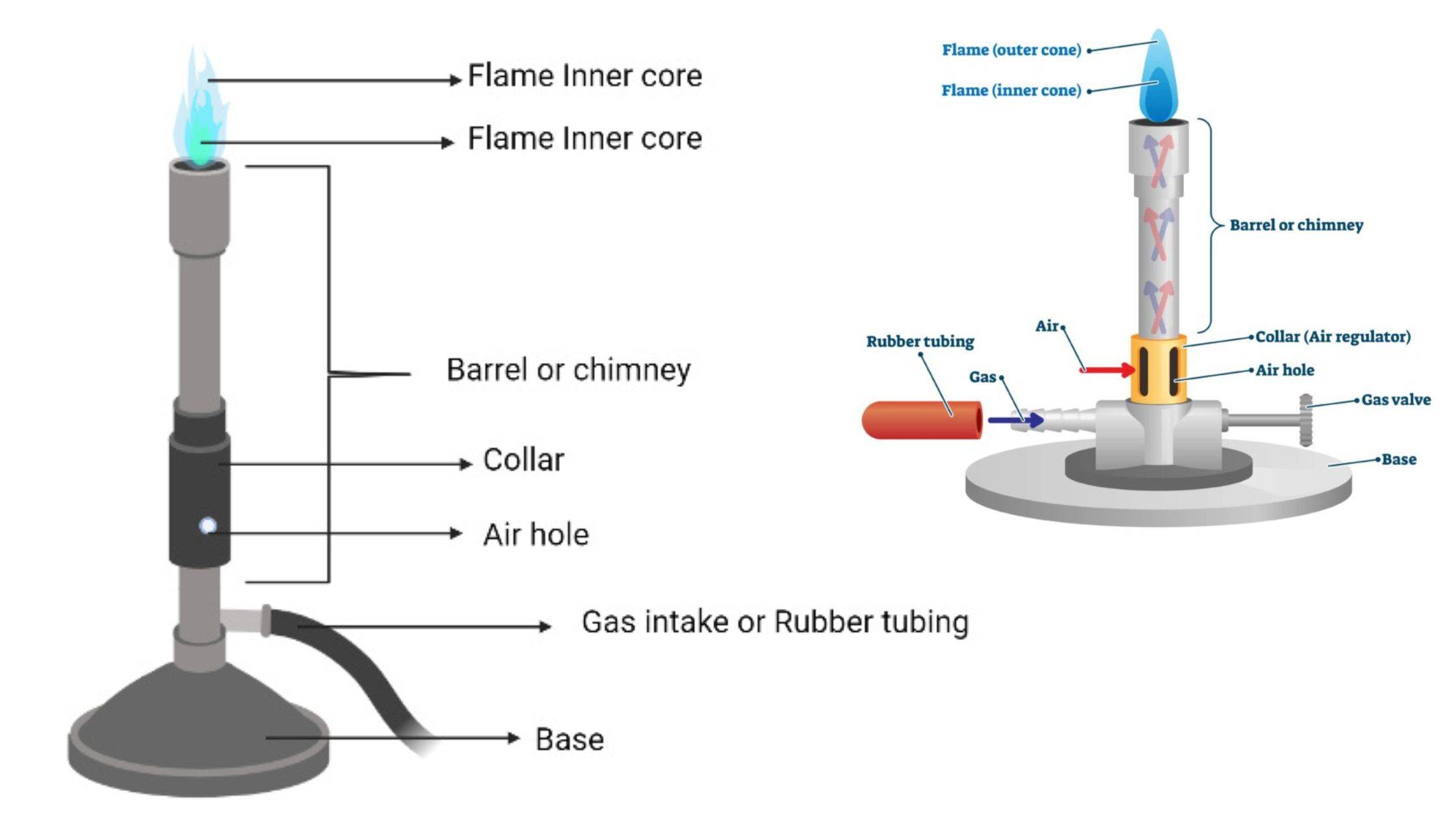
Bunsen Burner Definition, Principle, Parts, Functions
The Bunsen burner flame diagram shows the different zones of a flame that can be obtained from a Bunsen burner. These zones include the inner blue cone, the outer blue cone, and the luminous zone. Each zone has different characteristics and temperatures, making them suitable for different purposes in scientific experiments and other. A Bunsen burner is a type of gas burner that is used in many chemistry procedures in a laboratory setting. It is used to heat substances, to combust substances, and to sterilize objects on high. It burns with a pale blue flame, the primary flame, seen as a small inner cone, and a secondary, almost colourless flame, seen as a larger, outer cone, which results when the remaining gas is completely oxidized by the surrounding air. cone of a Bunsen burner flame CH4 + 2O2 Equation 1 CH4 + O2 CO2 + 2H2O + heat C + 2H2O + heat Equation 2a CH4 + 3⁄2O2 → CO + 2H2O + heat Equation 2b The modern Bunsen burner has changed very little from Robert Bunsen's original design.
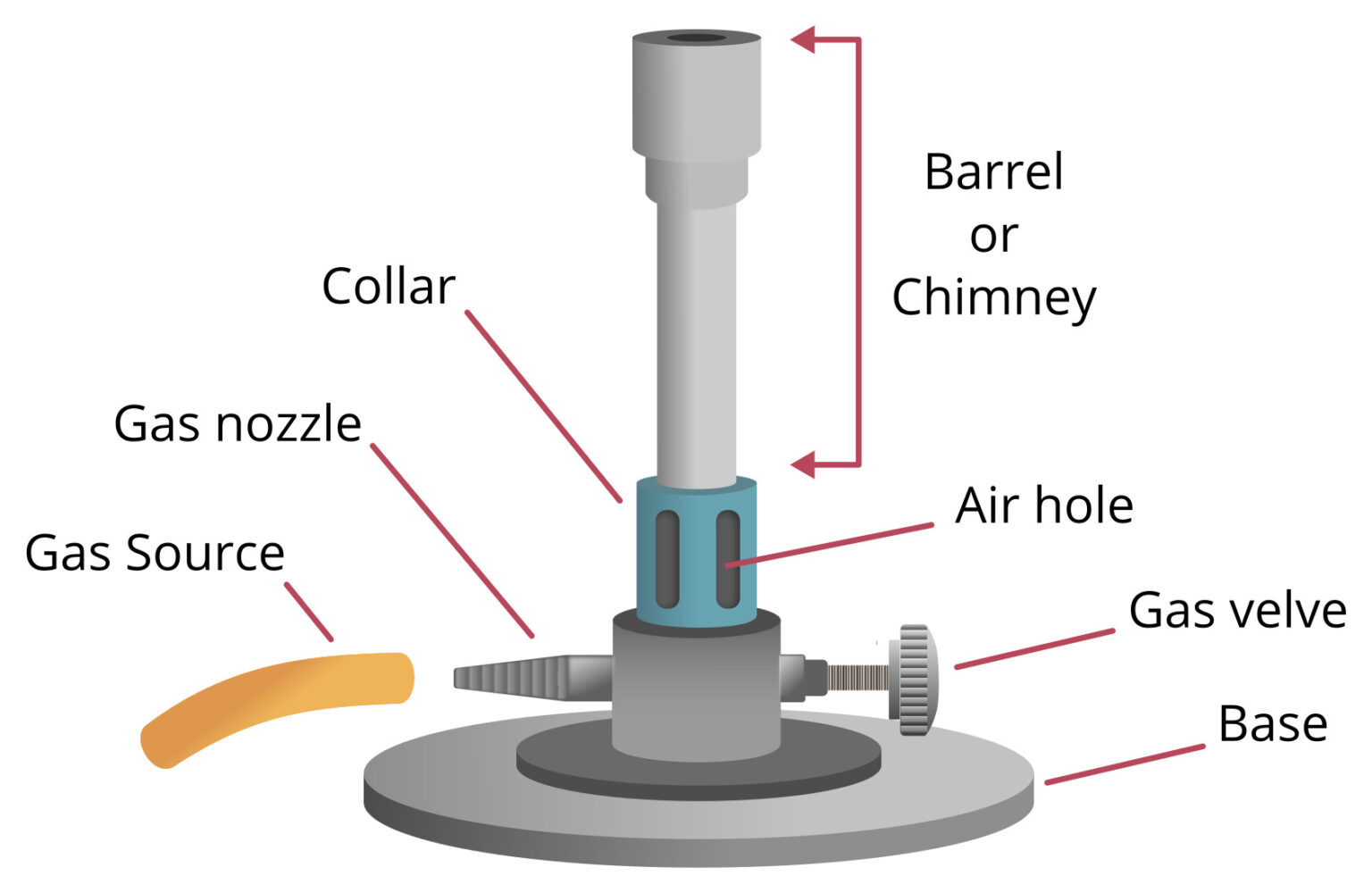
Bunsen Burner Definition, Principle, Parts, Functions
Bunsen burner is a gas burner that produces smokeless, nonluminous flame used for heating, sterilizing, and combustion purposes in laboratory experiments. It was named after Robert Bunsen, a German scientist who designed it in 1857. A.D. Bunsen burner ignites by the fusion of fuel and air (oxygen). The Bunsen burner is the object most frequently associated with a chemistry laboratory. In this lab, it will serve as the primary heat source. The burner operates on natural gas,. Lighting the burner in this manner will result in a flame that is 1-2 inches tall. Normally a flame size of 3-5 inches is needed. Gas flow into the burner tube. A Bunsen burner is a laboratory device that plays a crucial role in scientific experiments and research. It was invented by German scientist Robert Bunsen in collaboration with his lab assistant Peter Desaga in 1857. The burner was named after Bunsen, recognizing his contribution to its design and development. However, one should be familiar with the different parts of a burner to handle it safely and understand how it works. An efficient Bunsen burner is purely metallic (except the gas tubing) and has five main parts: 1. Barrel or stack: It is approximately 5 inches long to raise the flame to a suitable height for heating.
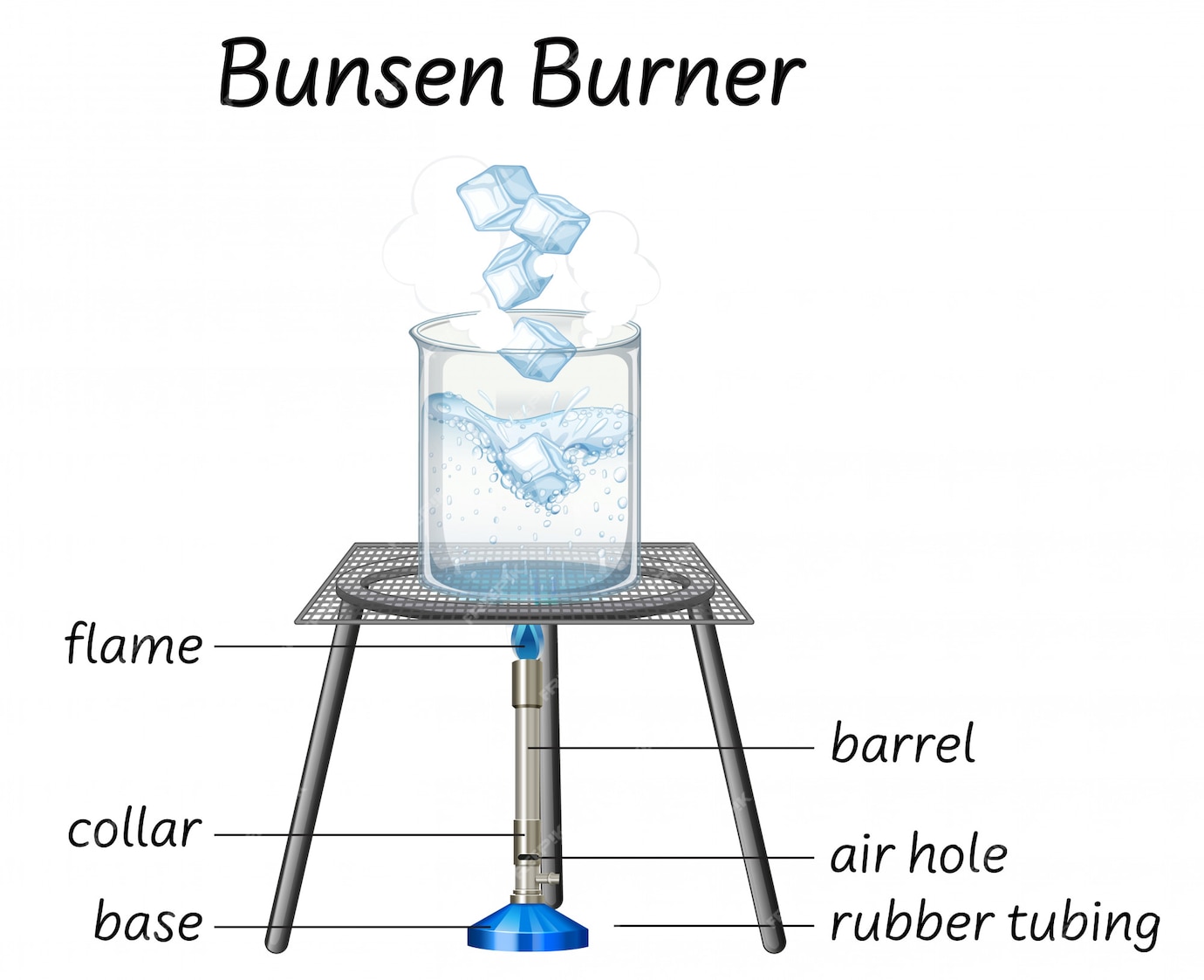
Free Vector Science bunsen burner diagram
To light a burner; Bunsen burners are generally used to rapidly heat high-boiling liquids with low flammability (such as water). Safety note: It is important to know that they can reach temperatures of approximately \(1500^\text{o} \text{C}\),\(^5\) and can easily ignite most organic compounds. If an apparatus is improperly set up, or if there is a small gap that allows organic vapors to. Diagram below the three distinct flames you can create with the Bunsen Burner: In your diagram label the different temperature regions, if necessary. Flame #1: Temp: ________________ Flame #1 Diagram Color: ________________ Observations: Flame #3 Diagram Flame #2: Temp: ________________ Color: ________________ Observations: Flame #2 Diagram
1. Get a Bunsen burner and a piece of rubber tubing for Bunsen burners. Check for any cracks or damage on the rubber tubing. Get a new piece of tubing if yours is damaged. Attach one end of the tubing to the gas source on the laboratory bench and the other end to the gas inlet on the Bunsen burner. 2. Combustion, Reactive Hazard, and Bioprocess Safety. Shijie Liu, in Bioprocess Engineering (Second Edition), 2017. 18.8.3 Diffusion Flames. When the air inlet is shut off in a Bunsen burner, the flame can still be maintained, but it switches from the blue color of a normal CH 4 flame to the yellow of a diffusion flame. This is the situation of a gas stove. Pure CH 4 flows up the tube, and the O.
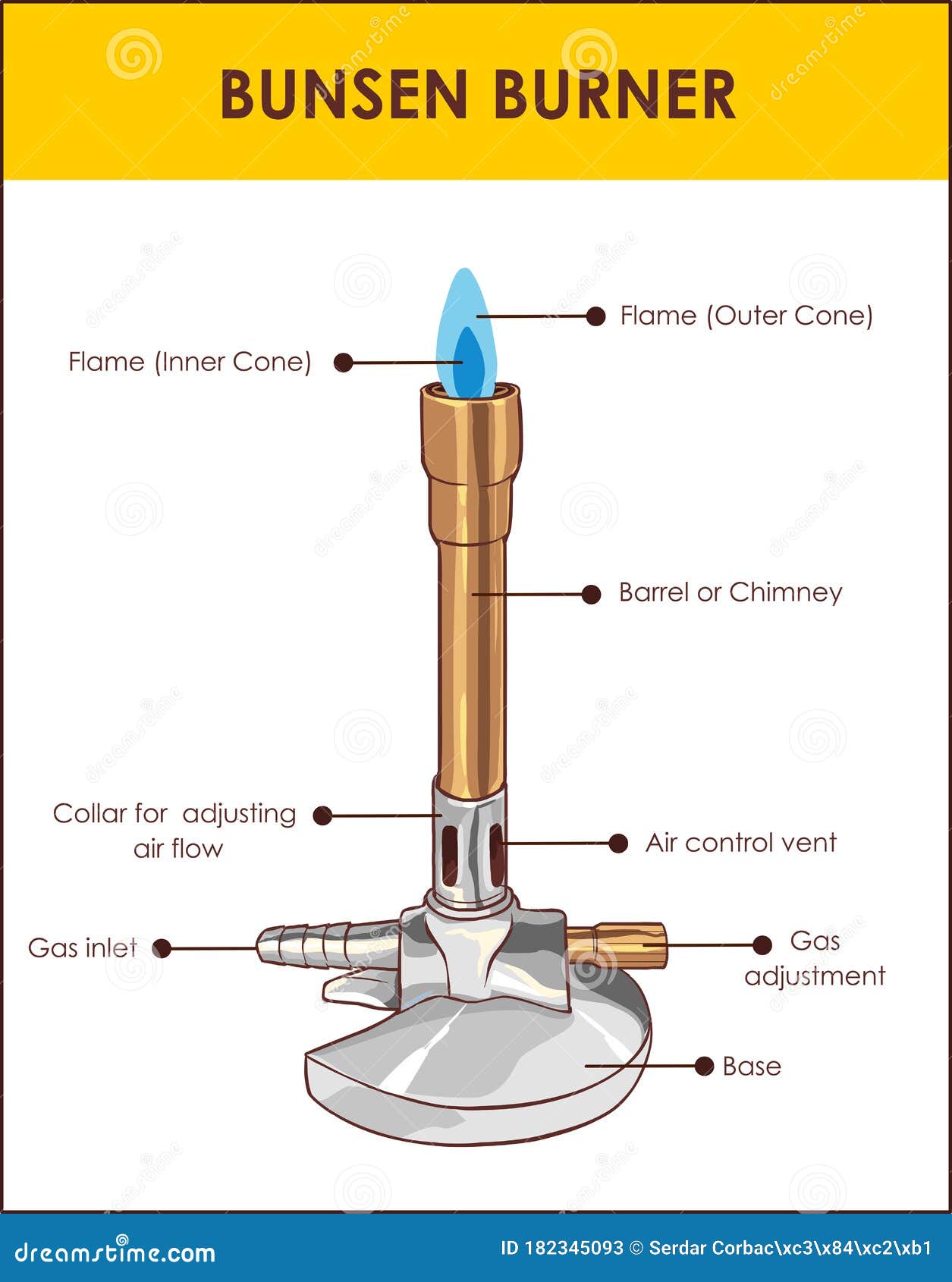
Parts Of A Bunsen Burner Diagram Images and Photos finder
A typical diagram is shown below: In this article you'll learn: What are the parts of a Bunsen burner? What is the function of a Bunsen burner? How do you use a Bunsen burner? What is the hottest part of a flame on a Bunsen burner? Let's Get Started…! Parts of Bunsen Burner and Their Functions A Bunsen burner flame sits at the mouth of the tube at the top of the equipment, and can be effective for creating a convection current. Standard natural rubber tubing has been used for many years, but you can also use tubes made from neoprene or a tube made from a polymer blend like Enduraflex.




