Electron micrograph of a chloroplast The inner membrane system of the chloroplast is called the thylakoid membranes and the matrix surrounding the thylakoids is called the stroma. Stacks of thylakoids are termed the grana, while the membranes connecting the grana are called the stroma thylakoids. Figure 23 (a) Electron micrograph of a chloroplast. A: double outer membrane or envelope (the outer and inner membranes are labelled separately in (b)); B, stroma; C, stroma lamellae; D, granum, composed of a stack of thylakoids. (b) Schematic diagram of chloroplast structure. Show description Figure 23

Electron micrograph of a chloroplast in a fieldcollected Elysia... Download Scientific Diagram
Chloroplasts are found only in plants and photosynthetic algae. (Humans and other animals do not have chloroplasts.). Electron micrograph of a mitochondrion, showing matrix, cristae, outer membrane, and inner membrane. _Image credits: upper image, "Eukaryotic cells: Figure 7," by OpenStax College, Biology . Modification of work by Matthew. The chloroplast organelle in mesophyll cells of higher plants represents a sunlight-driven metabolic factory that eventually fuels life on our planet. Knowledge of the ultrastructure and the dynamics of this unique organelle is essential to understanding its function in an ever-changing and challenging environment. Chloroplasts, the organelles responsible for photosynthesis, are in many respects similar to mitochondria.. (Electron micrograph . Despite this greater complexity, the membranes of chloroplasts have clear functional similarities with those of mitochondria—as expected, given the role of both organelles in the chemiosmotic generation of ATP. Serial-Block-Face Scanning Electron Microscopy (SBF-SEM) associated with biomolecular analysis show that chloroplast differentiation proceeds by distinct 'structure establishment' and 'chloroplast proliferation' phases, each with differential protein and lipid regulation.

Electron micrograph of chloroplasts (C) inside cells lining the... Download Scientific Diagram
Through light and electron microscopy analyses of Bienertia chloroplasts, we delineated the assembly process of thylakoid membranes in a growing chloroplast, observed the gradual gain of grana. The thylakoid architecture of such morphologically variable chloroplasts is confirmed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The method of monitoring structural variation by light microscopy in combination with electron microscopy is described. Keywords: Light microscopy, TEM, Chloroplast, Thylakoid membrane, Arabidopsis thaliana Go to: As reviewed by Staehelin in 2003, the study of chloroplast structure has advanced with enhancements in light and electron microscopy from two-dimensional transmission electron microscopy (TEM) imaging to three-dimensional (3D) electron tomography (ET) and with improvements in sample preservation from chemically preservation to freeze-fracture to. As reviewed by Staehelin in 2003, the study of chloroplast structure has advanced with enhancements in light and electron microscopy from two-dimensional transmission electron microscopy (TEM) imaging to three-dimensional (3D) electron tomography (ET) and with improvements in sample preservation from chemically preservation to freeze-fracture to.

TEM of chloroplast from Coleus blumei Stock Image B110/0067 Science Photo Library
Although the German botanist Hugo von Mohl ( 1837) is generally credited with the discovery and definitive description of the "Chlorophyllkörner"—chloroplast granules, the first reports of green granules were published much earlier. Chloroplasts in C4 plants exhibit structural dimorphism because thylakoid architectures vary depending on energy requirements. Advances in electron microscopy imaging capacity and sample preparation technologies allowed characterization of thylakoid structures and their macromolecular arrangements with unprecedented precision mostly in C3 plants.
Download scientific diagram | Electron micrograph of a chloroplast in a field-collected Elysia clarki. The thylakoids (TH) are arranged in bands of two to six lamellae all running in the same. The schematic diagram in (b) shows the chloroplast bounded by an outer membrane immediately beneath which is the inner membrane. This membrane encloses the stroma, within which are the cylindrical grana, connected by membranes called stroma lamellae. The enlargement shows the internal structure of a single granum: stacks of flat membranous sacs.
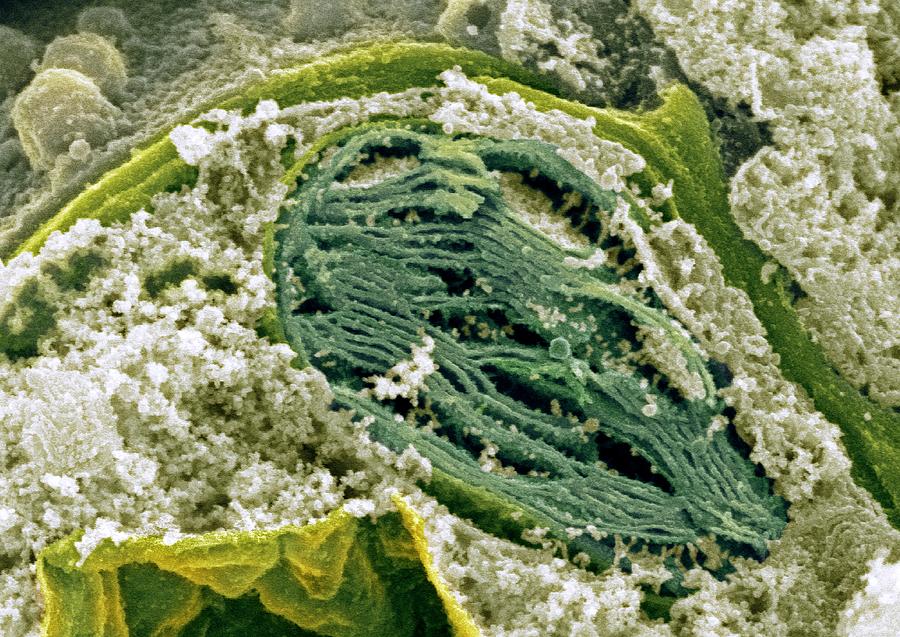
Chloroplast, Sem Photograph by Dr David Furness, Keele University Fine Art America
Chloroplasts The sketch of the chloroplast above was made from an electron micrograph of a chloroplast from a higher order plant (Levy).. both photosystems are used in an electron transport process that yields energy in the form of ATP and reduced coenzymes to the stroma of the chloroplast to be used in the synthesis of carbohydrates. Chloroplast nucleoids are thought to be the functional unit for various processes, including DNA replication, repair, recombination, inheritance, and transcription, and are often compared with.




