This Osmosis High-Yield Note provides an overview of Gas Exchange essentials. All Osmosis Notes are clearly laid-out and contain striking images, tables, and diagrams to help visual learners understand complex topics quickly and efficiently. Find more information about Gas Exchange: Osmosis Gas Exchange high-yield notes offers clear overviews. Gas exchange is the 'swapping' of gasses - absorbing oxygen into the blood and removing carbon dioxide from the blood. Diffusion close diffusion The overall movement of particles of gas or.
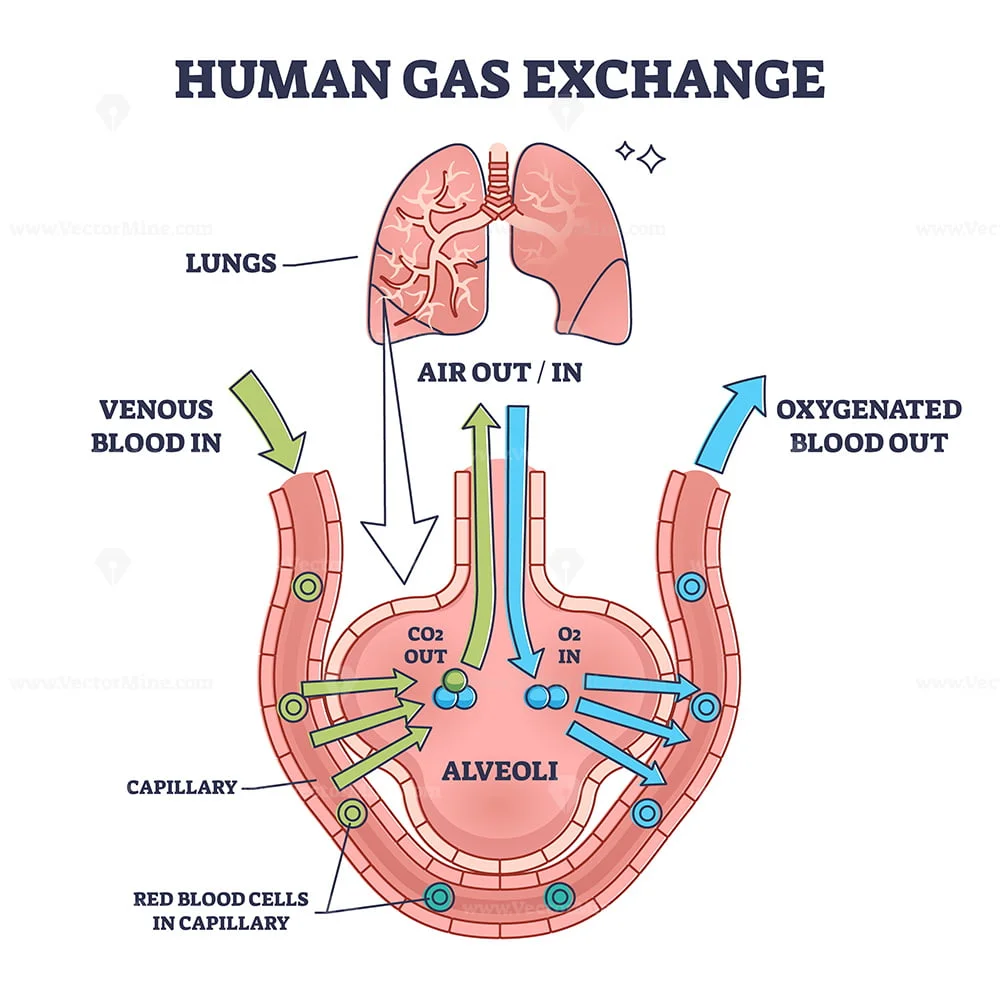
Human gas exchange process with oxygen cycle explanation outline diagram VectorMine
13.4 Summary. Gas exchange. is the biological process through which gases are transferred across cell membranes to either enter or leave the blood. Gas exchange takes place continuously between the blood and cells throughout the body, and also between the blood and the air inside the lungs. Gas exchange in the lungs takes place in. Internal respiration is gas exchange that occurs at the level of body tissues ( Figure 22.4.3 ). Similar to external respiration, internal respiration also occurs as simple diffusion due to a partial pressure gradient. However, the partial pressure gradients are opposite of those present at the respiratory membrane. Gas exchange is the physical process by which gases move passively by diffusion across a surface. For example,. the operations and effects of a cocurrent and a countercurrent flow exchange system is depicted by the upper and lower diagrams respectively. In both it is assumed (and indicated) that red has a higher value (e.g. of temperature or. Gas exchange is the process by which oxygen and carbon dioxide move between the bloodstream and the lungs. This is the primary function of the respiratory system and is essential for ensuring a constant supply of oxygen to tissues. This article will discuss the principles of gas exchange, factors affecting the rate of exchange and relevant clinical conditions.
Basic Principles of Gas Exchange TaylortaroAdams
Gas exchange occurs at two sites in the body: in the lungs, where oxygen is picked up and carbon dioxide is released at the respiratory membrane, and at the tissues, where oxygen is released and carbon dioxide is picked up. External respiration is the exchange of gases with the external environment, and occurs in the alveoli of the lungs. 16.2D: Gas Exchange in Plants. Page ID. John W. Kimball. Tufts University & Harvard. In order to carry on photosynthesis, green plants need a supply of carbon dioxide and a means of disposing of oxygen. In order to carry on cellular respiration, plant cells need oxygen and a means of disposing of carbon dioxide (just as animal cells do). The smallest bronchioles end in tiny air sacs. These are called alveoli. They inflate when a person inhales and deflate when a person exhales. During gas exchange oxygen moves from the lungs to the bloodstream. At the same time carbon dioxide passes from the blood to the lungs. This happens in the lungs between the alveoli and a network of tiny. Gas exchange occurs at two sites in the body: in the lungs, where oxygen is picked up and carbon dioxide is released at the respiratory membrane, and at the tissues, where oxygen is released and carbon dioxide is picked up. External respiration is the exchange of gases with the external environment, and occurs in the alveoli of the lungs.

Exchange Of Gases Transport GCSE Biology Revision Notes
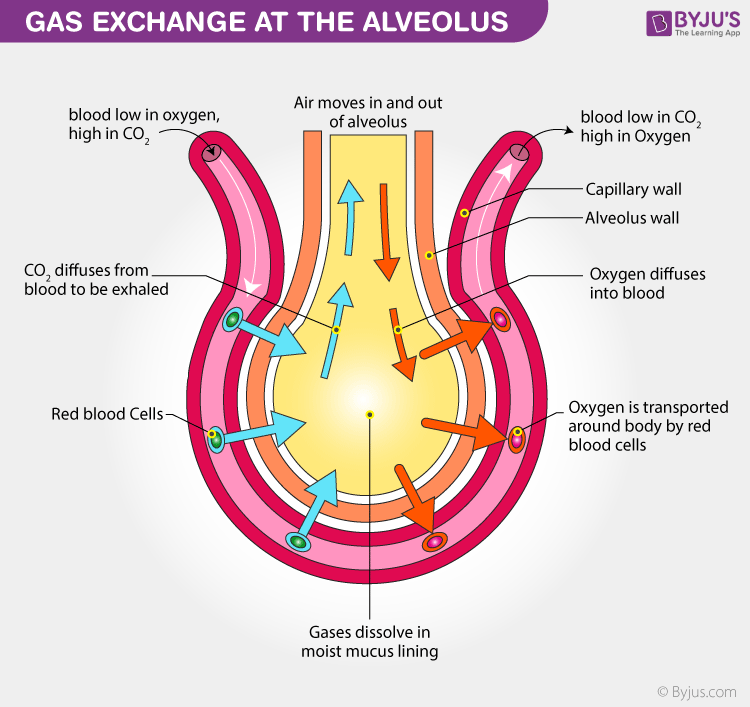
Gas exchange is the process of swapping one gas for another. It occurs in the alveoli of the lungs. Oxygen diffuses into the capillaries from the air in the alveoli and carbon dioxide diffuses out of the capillaries and into the air in the alveoli.. 6.4.4 Draw and label a diagram of the ventilation system, including trachea, lungs, bronchi. Key points. The gas exchange system is responsible for getting oxygen into the blood and removing carbon dioxide as a person breathes. Breathing is also called 'ventilation' and is the movement of.
The process of gas exchange. The gases are transferred between the organism's internal and external environments. The transfer occurs passively (no energy required), down the concentration gradient. The transfer of gases includes the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide during the respiration and photosynthesis processes. Gas exchange in birds occurs between air capillaries and blood capillaries, rather than in alveoli. Flight poses a unique challenge with respect to breathing. Flying consumes a great amount of energy; therefore, birds require a lot of oxygen to aid their metabolic processes. Birds have evolved a respiratory system that supplies them with the.

Infographic Lungs How Gas Exchange Works Carolina Biological Supply
Gas exchange only occurs in small sacs called alveoli, where a web-like arrangement of blood vessels comes into close proximity to the inhaled air. The pathway to reach the alveoli includes the trachea, the bronchi, and the bronchioles, each of which are part of the "dead space" of the lungs.. Diagram showing methods of transporting. Gas exchange occurs in the alveoli so that oxygen is loaded into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide is unloaded from the bloodstream. Afterwards, oxygen is brought to the left side of the heart via the pulmonary vein, which pumps it into systemic circulation.. Overview of cellular respiration: A diagram of cellular respiration including.




