Transform Your Marks Into Grade-A Achievements With Osmosis's Unique Study Tools. Osmosis helps train your brain with resources designed to lock in key info for good. Find the deal you deserve on eBay. Discover discounts from sellers across the globe. No matter what you love, you'll find it here. Search A-fork and more.

Child With Dinner Fork Deformity Annals of Emergency Medicine
A dinner fork deformity, also known as a bayonet deformity, occurs as the result of a malunited distal radial fracture, usually a Colles fracture. The distal fragment is dorsally angulated, displaced and often also impacted. The term is descriptive, as the lateral view of the wrist is similar to the shape of a fork, seen from the side, tines down. A Colles Fracture is a complete fracture of the radius bone of the forearm close to the wrist resulting in an upward (posterior) displacement of the radius and obvious deformity. It is commonly called a "broken wrist" in spite of the fact that the distal radius is the location of the fracture, not the carpal bones of the wrist. [1] The clinical presentation of Colles fracture is frequently described as a dinner fork deformity - distal fracture of the radius causes posterior displacement of the distal fragment, causing the forearm to be angled posteriorly just proximal to the wrist. INTRODUCTION :- ⇒ Dinner fork deformity is due to colle's fracture in which the fracture of the distal radius in forearm with dorsal (posterior) and radial displacmentof the wristand hand. ⇒ Dinner fork also called "bayonet" deformity due to the shape of the forearm. CAUSE:- ⇒ Wrist fracture. ⇒ Over stretched hand (common in child)
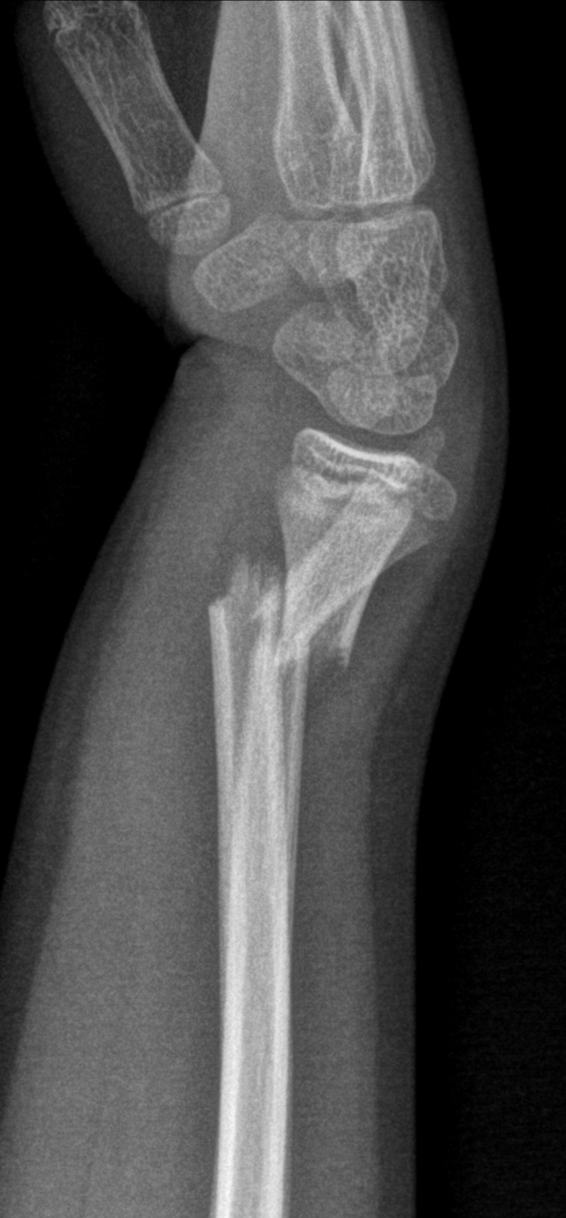
Colles fracture dinner fork deformity Image
Overview A Colles' wrist fracture occurs when the radius bone in your forearm breaks. It's also known as a distal radius fracture, transverse wrist fracture, or a dinner-fork deformity of. A Colles' fracture is a type of fracture of the distal forearm in which the broken end of the radius is bent backwards. [2] Symptoms may include pain, swelling, deformity, and bruising. [2] Complications may include damage to the median nerve. [1] It typically occurs as a result of a fall on an outstretched hand. [2] Objectives: Identify the etiology and epidemiology of Colles fractures. Outline the appropriate history, physical, and evaluation of a patient with a Colles fracture. Review the treatment and management options available for Colles fractures. Colles' fracture Due to the dorsal displacement of the distal fragment, Colles' type fractures are often said to have a "dinner fork" appearance. Graphic 78559 Version 2.0

Child With Dinner Fork Deformity Annals of Emergency Medicine
Dinner fork deformity is a term used to describe the appearance of the wrist on a lateral radiograph in cases of distal radial fracture with associated dorsal displacement and impaction, as seen in cases of Colles fracture. The mechanism of injury is usually a fall on an outstretched hand. Deformity of the wrist, sometimes called a "dinner fork deformity," which causes it to look crooked and bent. To diagnose a broken wrist, your doctor will give you a thorough physical exam .
If dorsal angulation is severe enough, a dinner fork deformity may be described.There is also usually impaction with resultant shortening of the radius. An associated ulnar styloid fracture is present in up to 50% of cases. A pronator quadratus sign is generally seen. Report checklist Displaced fractures usually present with a 'dinner fork' deformity and require closed reduction and possible surgical fixation. Successfully reduced fractures can be treated non-surgically with immobilisation and radiographic monitoring.
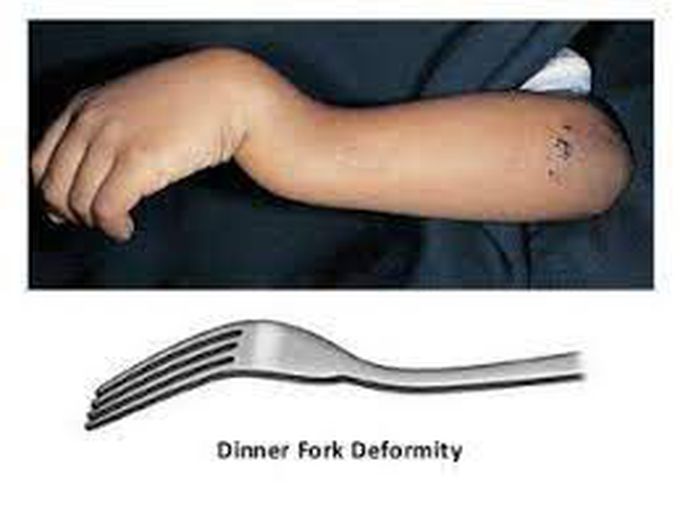
Dinner Fork Deformity MEDizzy
A dinner fork deformity also identifies as a bayonet deformity, happens as the result of a malunited distal radial fracture, generally a Colles fracture. The distal fragment is dorsally angulated, displaced, and often also impacted. What are the Causes of Dinner fork deformity? Wrist fracture mainly after colle's fracture The deformity that results from the Colles' fracture is described as a "dinner fork" deformity because of depression at the fracture site, dorsal angulation, and dorsal displacement of the distal radius. History-taking should focus on the mechanism of injury and amount of energy involved.




