Disc osteophyte complex is a spinal ailment caused due to the formation of osteophytes in the spine affecting the intervertebral disc. Osteophytes (also called bone spurs) are the bony outgrowths that can develop as a result of your body's natural reaction to any damage or irritation caused to the bones or ligaments in the spine. What is a Disc Osteophyte Complex? By A. Mendelson, MD October 9, 2023 Please read the disclaimer Back pain can be a perplexing issue, often caused by underlying factors like the Disc Osteophyte Complex. This condition not only brings discomfort but also leaves a distinctive mark on imaging.

Disc Osteophyte Complex Causes, Symptoms & Treatment Bonati
Disc osteophyte complex (also known as disc osteophyte bar) is a term used on MRI of the cervical spine to denote the presence of disc protrusion and/or marginal endplate osteophytes resulting in narrowing of the cervical canal. The term Disc Osteophyte Complex is given to a pathological condition where multiple spinal vertebrae intervertebral discs get affected by formation of Bone Spurs or Osteophytes. Disc osteophyte complex is the development of osteophytes (bone spurs) affecting more than one intervertebral disk or spinal vertebrae. Osteophytes or bone spurs develop in the musculoskeletal system due to normal wear and tear as you age. The term "disc-osteophyte complex" generally refers to abnormal extension of intervertebral disc material that accompanies immediately adjacent osteophyte formation at the vertebral body margin (see the below figure). It is important to note (as shown in the illustrations) that the disc almost always extends further than the osteophytes.
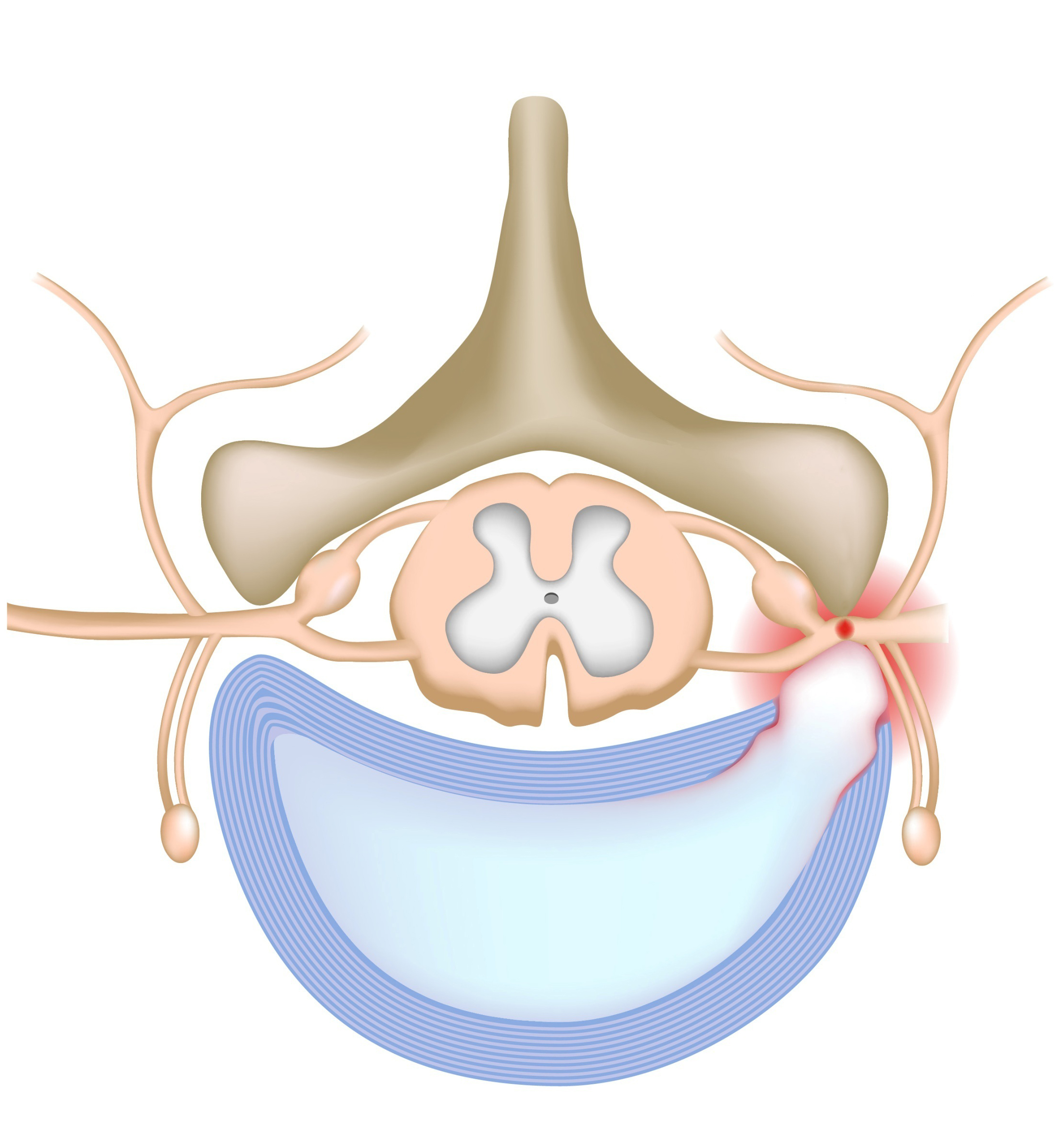
Disc Osteophyte Complex Causes, Symptoms & Treatment Bonati
Overview Cervical spondylosis is a general term for age-related wear and tear affecting the spinal disks in your neck. As the disks dehydrate and shrink, signs of osteoarthritis develop, including bony projections along the edges of bones (bone spurs). Cervical spondylosis is very common and worsens with age. Disc osteophyte complex should not be used in the lumbar spine. The pathophysiology is different, so stick to using the standard nomenclature of bulge, osteophyte, and disc herniation. DOC should not be used to the exclusion of the terms "osteophyte" and "disc herniation" (protrusion, extrusion) when they are obvious in the cervical spine. Spondylosis is a natural aging process of the spine. characterized by degeneration of the disc and the four joints of the cervical motion segment which include. two facet joints. two uncovertebral joints of Luschka) Degenerative cycle includes. disc degeneration. disc desiccation, loss of disc height, disc bulging, and possible disc herniation. Mimics of disc herniation must also be kept in mind when reviewing magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) studies: these include disc osteophyte complex, epidural haematoma, facet joint cyst, and tumours such as meningioma, nerve sheath tumours, and metastases. Introduction

Illustration of discosteophyte complex size measurement. Download Scientific Diagram
by Spine Info Editor • Last updated November 18, 2022. An osteophyte discal complex is the development of osteophytes (bone overgrowth aka bone spurs) that involve more than one disc or vertebrae. definition, osteophyte. Conditions: The authoritative spine information, definition, treatment and causes source. Read more about:Osteophyte Discal. Disc osteophyte complex is a term sometimes used by medical professionals when spinal disc problems and osteophytes, also called bone spurs, are both present in the spinal column, especially the upper region. These issues commonly develop as a result of the natural deterioration of the spine as we age.
Bone spurs (osteophytes) often form where bones meet each other — in your joints. They can also form on the bones of your spine. The main cause of bone spurs is the joint damage associated with osteoarthritis. Most bone spurs cause no symptoms and can go undetected for years. They might not require treatment. Neck stiffness The neck is likely sore and has reduced mobility, especially if experiencing increased pain when turning from side to side. See Stiff Neck Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Headaches Cervicogenic headaches may occur when an osteophyte compresses a nerve root in the neck.

Lumbar disc showing degenerated by osteophyte formation
Cervical osteophyte formation typically occurs when ligaments and tendons around the cervical spine's bones and joints are damaged or inflamed. This process usually happens with wear and tear over time. The inflamed or damaged tissue that stimulates cervical osteophyte growth is often caused by cervical osteoarthritis, a degradation in the. On sagittal imaging at L5-S1, a disk osteophyte complex extends posteriorly and obliterates the inferior portion of the neural foramen, resulting in compression of the L5 nerve (arrow). Note the lack of normal fat (circumferential to the nerve), which is obliterated in both the anteroposterior or superoinferior dimensions. At L4-5, one.




