Functions Female anatomy includes the internal and external structures of the reproductive and urinary systems. Reproductive anatomy plays a role in sexual pleasure, getting pregnant, and breastfeeding. The urinary system helps rid the body of toxins through urination (peeing). The female reproductive system functions to produce gametes and reproductive hormones, just like the male reproductive system; however, it also has the additional task of supporting the developing fetus and delivering it to the outside world.
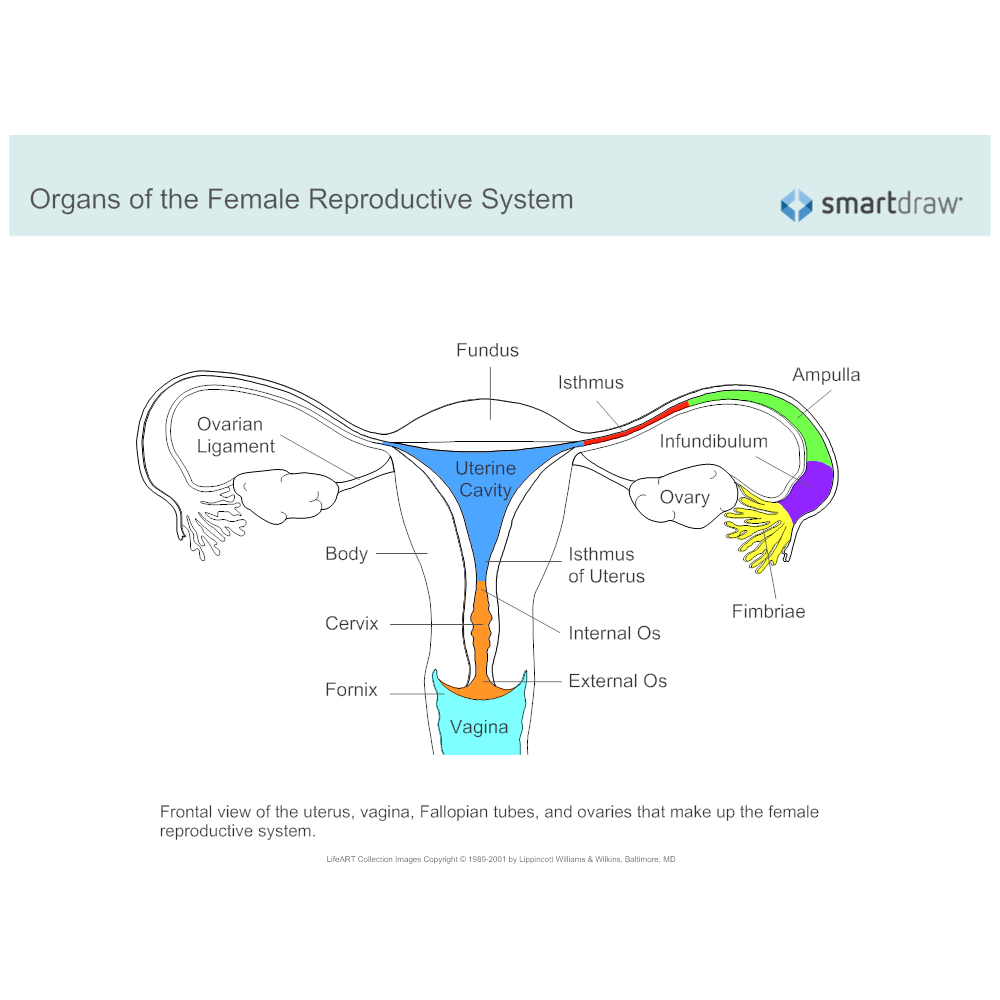
Female Reproductive System Diagram
The female reproductive system is one of the most vital parts of the human reproductive process. The major organs of the female reproductive system include the vagina, uterus, ovaries,. The female reproductive system is a group of organs that work together to enable reproduction, pregnancy, and childbirth. It also produces female sex hormones, including estrogen and. Osmosis Female reproductive system high-yield notes offers clear overviews with striking illustrations, tables, and diagrams. Make learning more manageable. Toggle Anatomy System. The female reproductive system includes the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, vulva, mammary glands and breasts. These organs are involved in the production and transportation of gametes and the production of sex hormones. The female reproductive system also facilitates the fertilization of ova by sperm and.

Female reproductory system anatomy chart — Stock Vector © Sudowoodo 178166266
The female reproductive system is made up of internal and external organs that function to produce haploid gametes called eggs (or oocytes), secrete sex hormones (such as estrogen), and carry and give birth to a fetus. As shown in Figure 22.6.2 22.6. 2, the internal reproductive organs include the vagina, uterus, Fallopian (uterine) tubes, and. Synonyms: none The female sex organs consist of both internal and external genitalia. Together they comprise the female reproductive system, supporting sexual and reproductive activities. The external genital organs, or vulva, are held by the female perineum. In humans, female and male reproductive systems work together to reproduce. There are two kinds of sex cells — sperm and eggs. When a sperm meets an egg, it can fertilize it and create a zygote. This zygote eventually becomes a fetus. Both a sperm and an egg are needed for human reproduction. An female's internal reproductive organs are the vagina, uterus, fallopian tubes, cervix, and ovary. External structures include the mons pubis, pudendal cleft, labia majora and minora, vulva, Bartholin's gland, and the clitoris. The female reproductive system contains two main parts: the uterus, which hosts the developing fetus, produces.
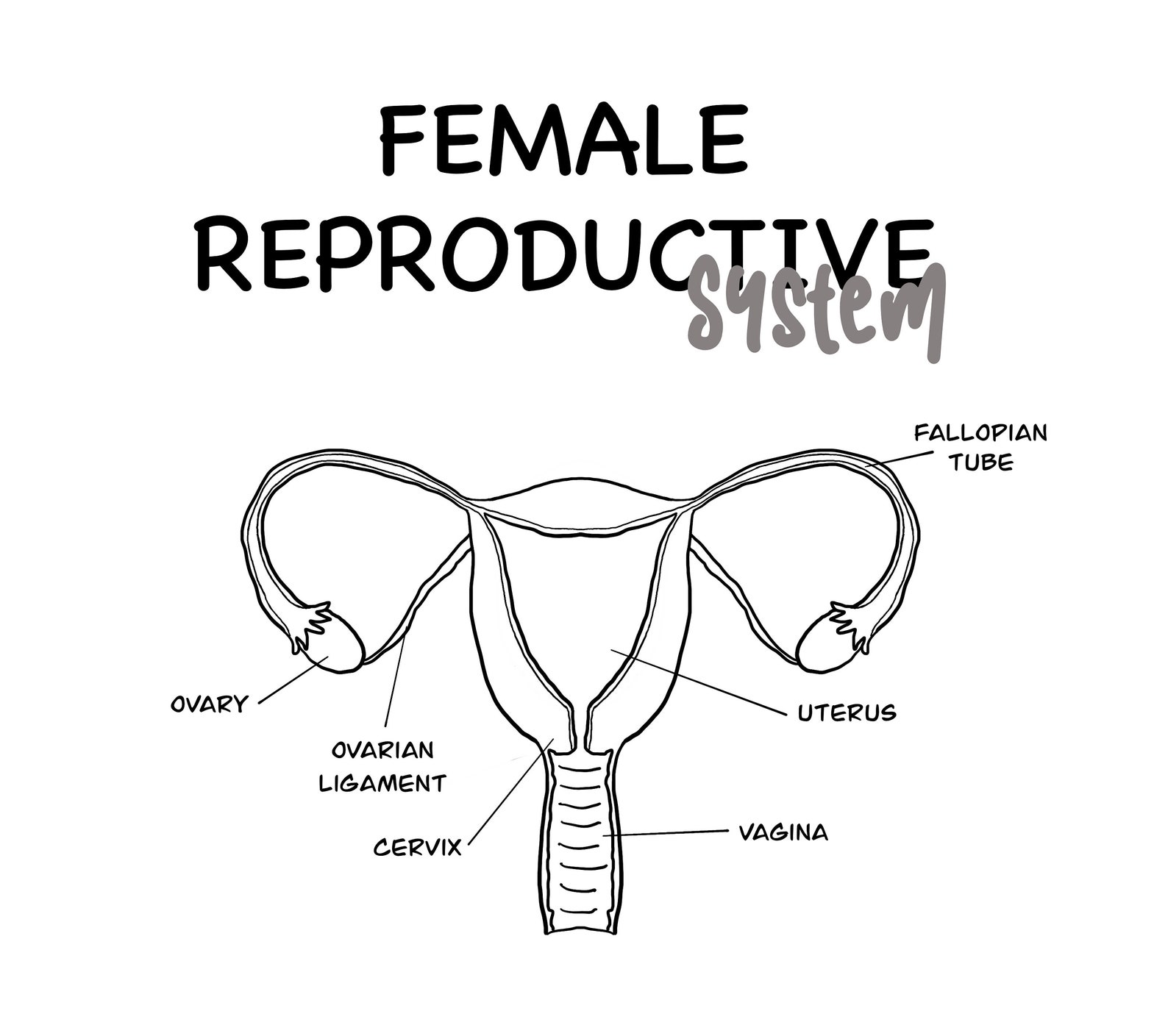
Female Reproductive System Educational Printable Etsy
Female anatomy includes the external genitals, or the vulva, and the internal reproductive organs. This article looks at female body parts and their functions, and it provides an interactive diagram. Female reproductive system labeled Learn faster with quizzes Sources + Show all Male and female reproductive system: Parts and functions As mentioned, the male and female reproductive systems, and therefore their parts and functions, are very different. In this section, we'll give you an overview. The male reproductive system
Learn about the female reproductive system's anatomy through diagrams and detailed facts. Our experts describe the functions of female reproduction, including ovulation, fertilization, and menopause. Find more on the female reproductive organs, the menstrual cycle, and more. Male reproductive gland that produces sperm and male hormones. Ovaries. Female reproductive gland that produces eggs and female hormones. Menstrual cycle. Pattern of events in females involving the development and release of an egg. Fertilization. The process in sexual reproduction in which a male gamete and female gamete fuse to form a new cell.
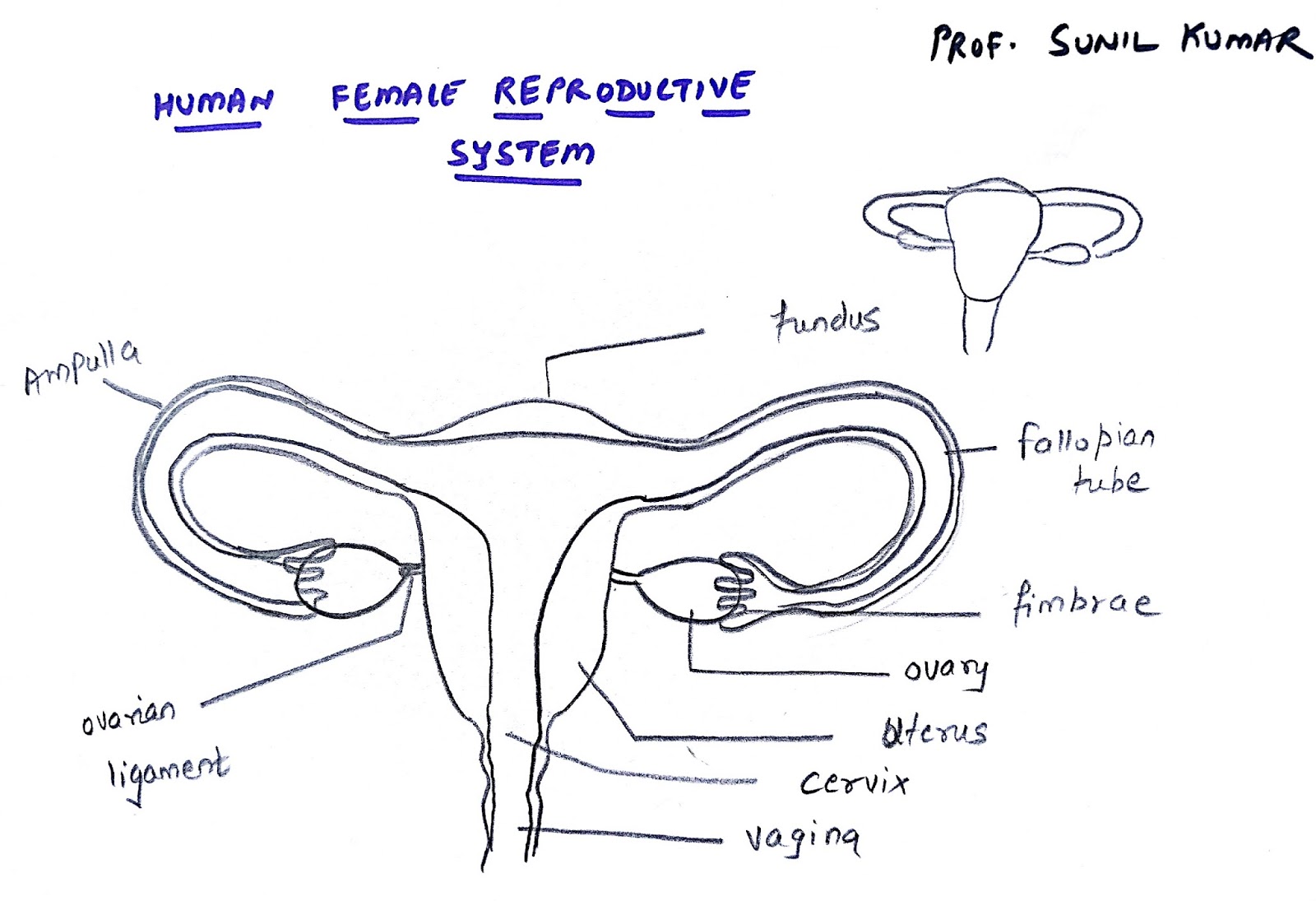
PROF. SUNIL KUMAR'S ADDABIOLOGY EASY WAY TO DRAW FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
The external female reproductive structures are referred to collectively as the vulva (Figure 23.1.2 23.1. 2 ). The mons pubis is a pad of fat that is located at the anterior, over the pubic bone. After puberty, it becomes covered in pubic hair. The labia majora (labia = "lips"; majora = "larger") are folds of hair-covered skin that. The vagina is part of the internal genitalia of the female reproductive system. The internal female sex organs form a pathway, the internal female genital tract, composed of the vagina, uterus, the paired uterine tubes and ovaries. The vagina serves a multitude of functions. It facilitates menstruation, childbirth and sexual intercourse, as it.




