The calculation of fluid balance involves measuring the amount of fluid entering the body and comparing it to the amount of fluid leaving the body. The purpose is to determine whether there is a deficit or an excess of fluid ( Bannerman, 2018 ). Understanding a patient's fluid status can give an indication of overall health. Fluid balance charts are of particular importance when a patient is on intravenous (IV) fluids and it is a key recommendation in National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) guidelines that patients have regular monitoring of fluid balance over each 24-hour period. 1 As well as those patients on intravenous fluids, monitoring fluid b.

24hr Fluid Balance ADULT Chart_v3 (1) Medical Specialties Health Sciences
The regulation of body fluid balance is a key concern in health and disease and comprises three concepts. The first concept pertains to the relationship between total body water (TBW) and total effective solute and is expressed in terms of the tonicity of the body fluids. This systematic review aimed to investigate and describe the quality of fluid balance monitoring in medical, surgical and intensive care units, with an emphasis on the completeness of charting data, calculation errors and accuracy, and to evaluate methods used to improve fluid balance charting. Materials and methods Reviewing fluid balance charts is a simple and effective method of assessing and monitoring the hydration status of patients. Several articles report that these charts are often either inaccurately or incompletely filled thereby limiting their usefulness in clinical practice. Effectiveness of daily fluid balance charting in comparison to the measurement of body weight when used in guiding fluid therapy for critically ill adult patients: a systematic review protocol : JBI Evidence Synthesis You may be trying to access this site from a secured browser on the server. Please enable scripts and reload this page. Log in or
10 Best Printable Fluid Intake Charts PDF for Free at Printablee
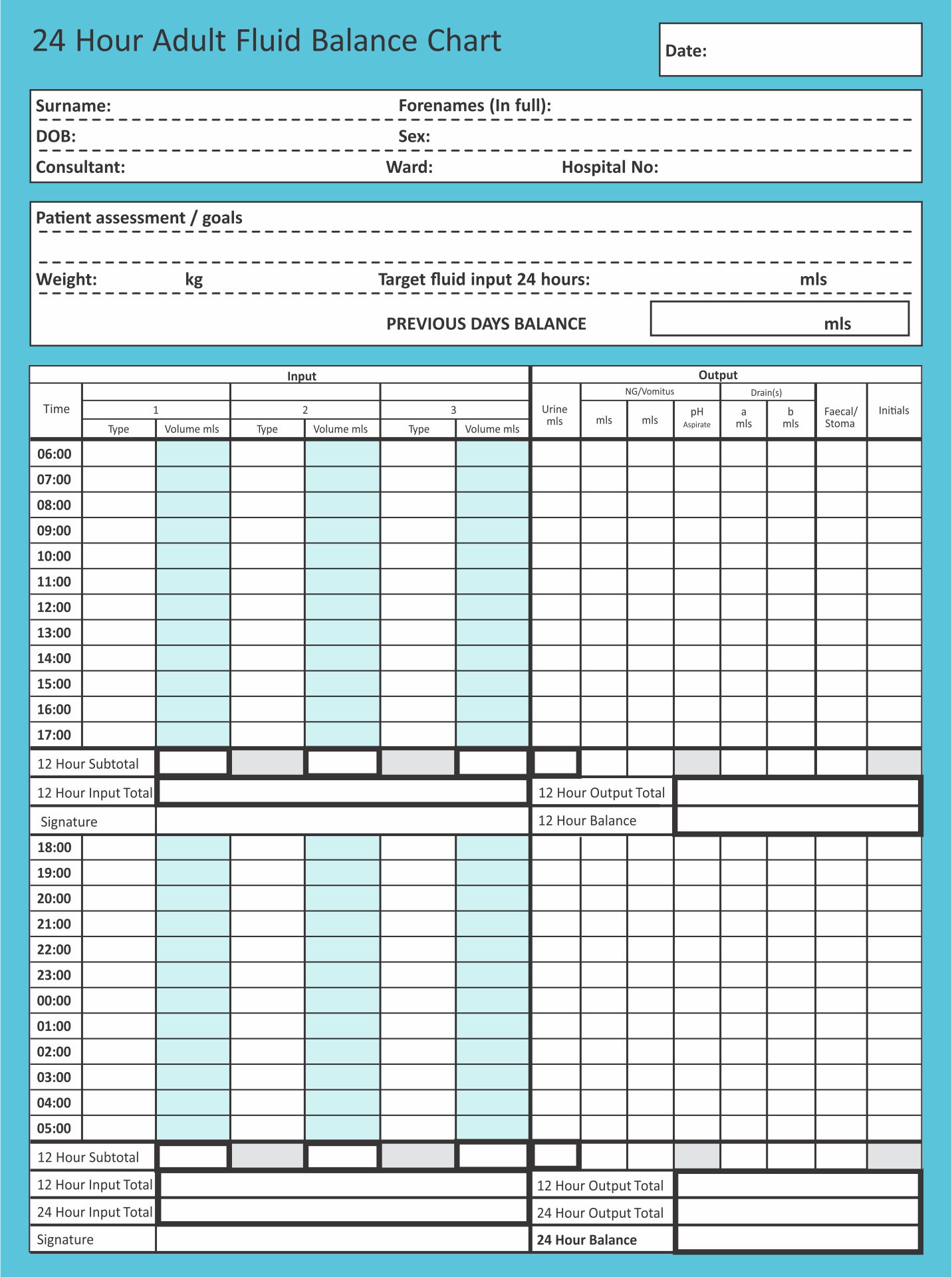
Fluid balance, also known as fluid homeostasis, describes the balancing of the body's fluid input and output levels to prevent the fluid concentration from changing. Indications for commencing a Fluid balance chart. 2.4.1. Fluid balance charts must be completed for the following patients unless a decision has been made otherwise by a medical practitioner or a senior registered nurse. • NEWS score >3 and/or risk of level 2 or 3 care. • Patients with sepsis. An accurate fluid balance chart is important as it allows medical teams to monitor patient input and output. Fluid balance charts are of particular importance when a patient is on intravenous (IV) fluids and it is a key recommendation in National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) guidelines that patients have regular monitoring of. The fluid balance chart is used as a non-invasive tool to assess the surgical patient's hydration status. Surgical trainees prescribe fluids on a daily basis, an essential part of patient fluid management. A good understanding of these charts is important, as inaccurate interpretation can have a detrimental effect on patient outcome.

7.4 Regulation of Water Balance Medicine LibreTexts
The harmful effects of positive fluid balance and the importance of deresuscitation of discussed in Deresuscitation and positive fluid balance; METHODS OF ASSESSING FLUID STATUS. Cumulative fluid balance chart. this is what is typically referred to when assessing 'fluid balance', rather than fluid status; consists of a 24 hour chart showing. The Fluid Balance Chart provides a summary of patient's daily intake and output mainly for viewing purposes only. Blood and Blood Products, Intermittent and bolus Intravenous Therapy and Enteral Feeds are the only exceptions that get documented directly into the Fluid Balance Chart.
This systematic review aimed to investigate and describe the quality of fluid balance monitoring in medical, surgical and intensive care units, with an emphasis on the completeness of charting data, calculation errors and accuracy, and to evaluate methods used to improve fluid balance charting. Abstract Shepherd A (2011) Measuring and managing fluid balance. Nursing Times; 107: 28, early online publication. Ensuring patients are adequately

Fluid Balance Charts Nursing UK YouTube
Hypervolaemia refers to an excess of fluid in the body. Colloquially it is often referred to as fluid overload. Hypervolaemia is common in the elderly and those with renal or cardiac failure. It can be caused by excessive fluid intake or inappropriate fluid retention (e.g. heart failure, renal failure). fluid balance charts; and review of blood chemistry5 Fluid balance recording is often inadequate or inaccurate often because of staff shortages, lack of training or lack of time balance, including what fluid balance is, and how and why it is measured. It also dis-cusses the importance of measuring fluid balance accurately, and the health implica-




