Forest Food Chain and Web: Examples and Who's on Top Advertisement Every forest in the world is full of diverse plants and animal species, which create a complex ecosystem. The food chains and web are at the heart of this ecosystem, determining which animals eat what. The rainforest food chain structure is a multi-layered and intricate web. Here's a simplified overview: Producers: Plants and algae that convert sunlight into energy. Primary Consumers: Herbivores that feed on producers. Secondary Consumers: Carnivores that feed on primary consumers.
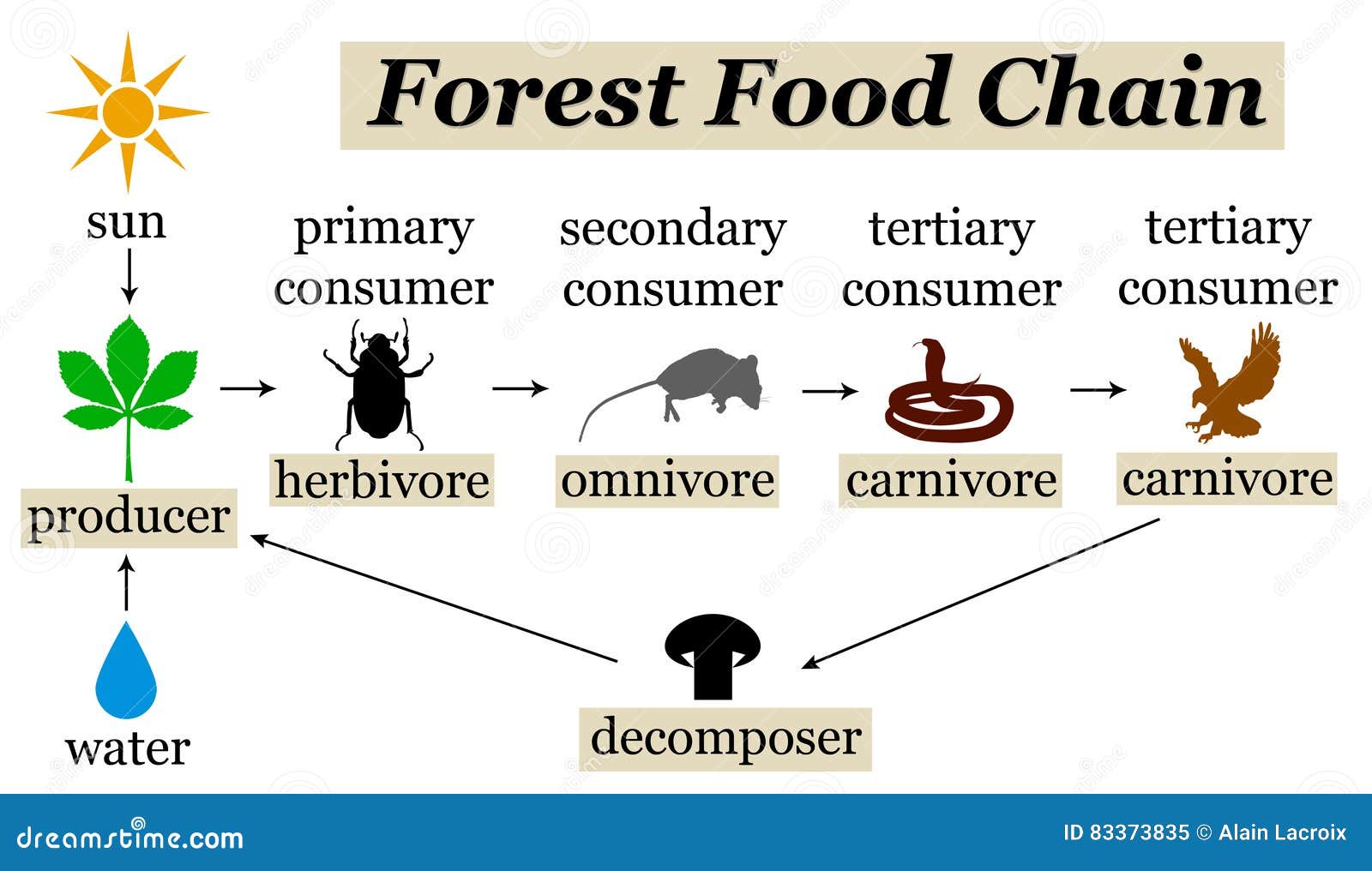
Forest food chain stock illustration. Illustration of mouse 83373835
The food chain within the deciduous forest comprises "producers," "consumers" and "decomposers. " At the beginning of the chain is the sun, which turns plants into producers. In a forest Food Web, many different organisms contribute to the ecosystem's overall health. Here is a list of 20 different organisms that play a role in a forest Food Web: 1. **Producers**: The green architects that capture sunlight and convert it into energy. 2. **Primary Consumers**: The herbivores that graze on the producers. 3. The food chain describes who eats whom in the wild. Every living thing—from one-celled algae to giant blue whales ( Balaenoptera musculus )—needs food to survive. Each food chain is a possible pathway that energy and nutrients can follow through the ecosystem. For example, grass produces its own food from sunlight. A rabbit eats the grass. In ecology, a food chain is a series of organisms that eat one another so that energy and nutrients flow from one to the next. For example, if you had a hamburger for lunch, you might be part of a food chain that looks like this: grass → cow → human. But what if you had lettuce on your hamburger?

Forest Ecosystem Food Pyramid
Food Web A food web consists of all the food chains in a single ecosystem. Grades 3 - 12+ Subjects Biology, Ecology Photograph Marine Food Web A Caribbean reef shark swims over a healthy coral reef in the Caribbean Sea. Sharks like this one are apex predators. Apex predators eat other consumers. They may be at the fourth or fifth trophic level. A food chain is a model that shows the relationships between all organisms in a forest ecosystem based on how they exchange energy with one another. Models are pictorial or metaphorical representations of very complex systems that make those systems easier to understand and visualize Food Webs and Food Chains | Forest Founders Learning Center Producers The first trophic level is for producers, organisms that create their own food. These organisms are also called autotrophs. They make their own food through processes like photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. The forest industry provided $4.3 billion to Ontario's overall Gross domestic product ( GDP) in 2020 with total revenues of $18 billion. Ontario's forest and wood products sector is unique in terms of having a large secondary and value-added sector, and high level of integration and dependency between mills.

Diagram showing food web in the rainforest 3177350 Vector Art at Vecteezy
The forest food chain is a practical tool for understanding energy flow and the impact of species loss or gain in the ecosystem. The rainforest food chain is a multi-layered and intricate web. The forest ecosystem is arranged from bottom to top, with producers occupying the lowest trophic level and tertiary consumers at the top. The rainforest food chain includes levels like the primary and secondary consumers, such as monkeys, ocelots and birds of prey, as well as the apex predators atop the chain, such as the jaguars, crocodiles and green anacondas. Producers, Consumers and Decomposers
Food chain, in ecology, the sequence of transfers of matter and energy in the form of food from organism to organism. A rainforest food chain represents how energy flows through the rainforest ecosystem when predators eat their prey. Rainforest is home to diverse plants and animal species.
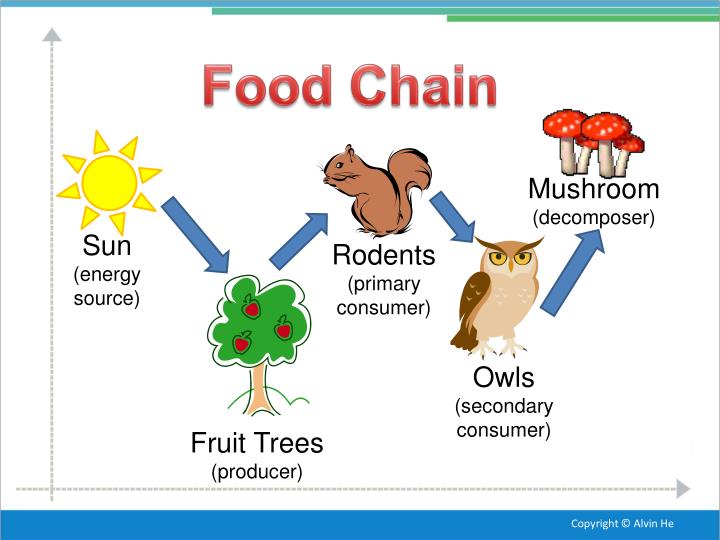
PPT Temperate Deciduous Forest PowerPoint Presentation ID2638689
1. Producers Producers are photosynthesizing organisms. Any green plant can be a producer. Green plants get their food from the sun, which they use to turn into sugar. This sugar also called glucose, is used by the plant to make many things, like wood, leaves, roots, and bark. Food Webs A forest community includes many feeding relationships. These relationships can be too complex to show with a food chain. For example, grizzly bears eat many different organisms, including berries, insects, chipmunks, and fish. Berries are eaten by bears, birds, insects, and other animals.




