Explore Skin Diagram with BYJU'S. Diagram of the skin is illustrated in detail with neat and clear labelling. Also available for free download Skin that has four layers of cells is referred to as "thin skin.". From deep to superficial, these layers are the stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, and stratum corneum. Most of the skin can be classified as thin skin. "Thick skin" is found only on the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet.
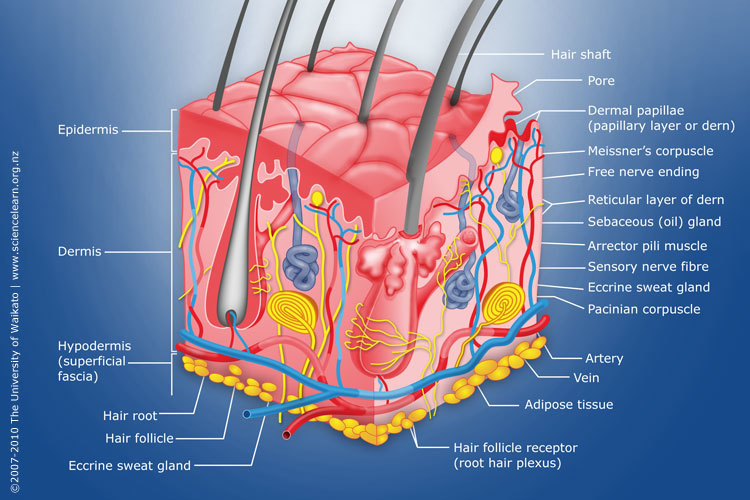
Diagram of human skin structure — Science Learning Hub
Dandruff Eczema Melanoma It is made up of the following five layers. Stratum Corneum The stratum corneum is the top layer of the epidermis. Its jobs are to: Helps your skin retain moisture Keep unwanted substances out of your body It is made of dead, flattened cells called keratinocytes that are shed approximately every two weeks. Introduction Skin is the largest organ in the body and covers the body's entire external surface. It is made up of three layers, the epidermis, dermis, and the hypodermis, all three of which vary significantly in their anatomy and function. 1/3 Synonyms: none This article will describe the anatomy and histology of the skin. Undoubtedly, the skin is the largest organ in the human body; literally covering you from head to toe. The organ constitutes almost 8-20% of body mass and has a surface area of approximately 1.6 to 1.8 m2, in an adult. Figure 1. Layers of Skin. The skin is composed of two main layers: the epidermis, made of closely packed epithelial cells, and the dermis, made of dense, irregular connective tissue that houses blood vessels, hair follicles, sweat glands, and other structures.
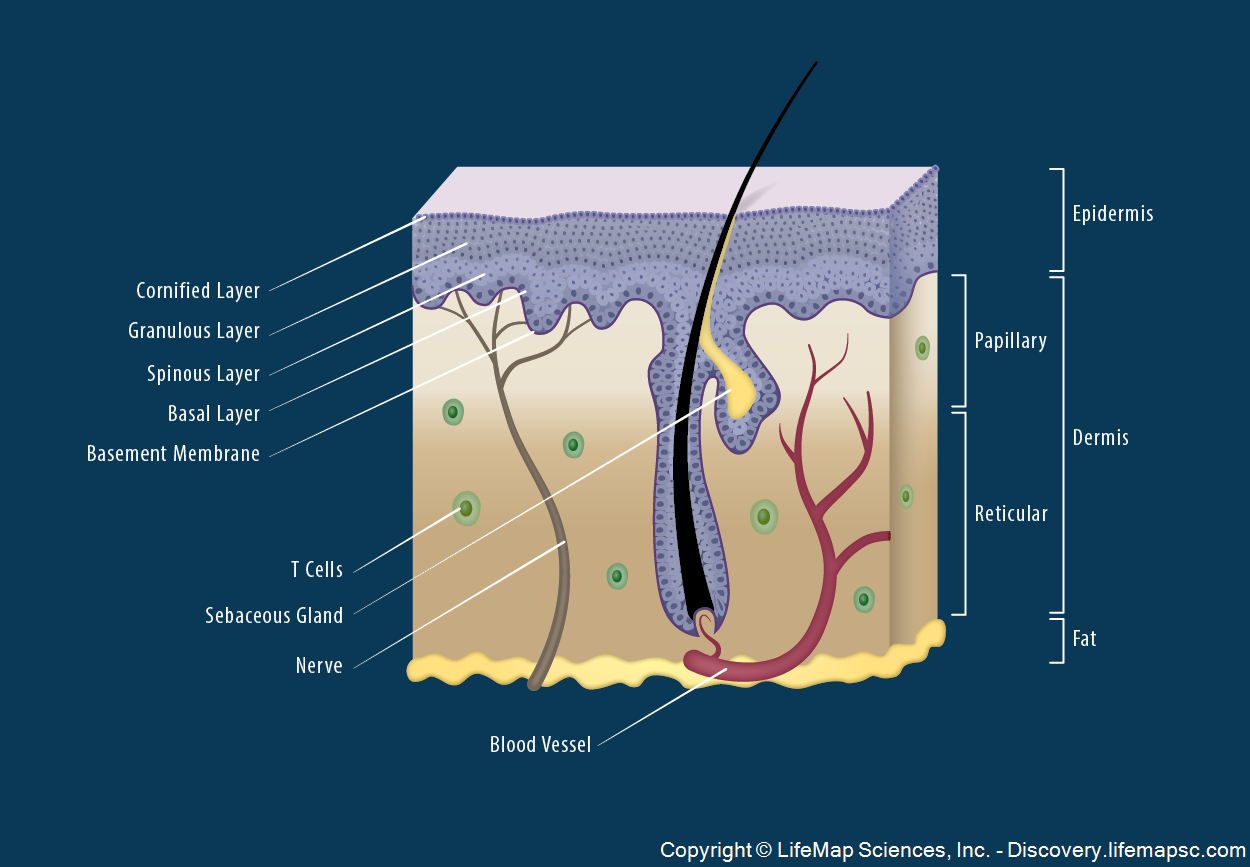
Skin Structure infographic LifeMap Discovery
Diagram of human skin structure Image Add to collection Rights: The University of Waikato Te Whare Wānanga o Waikato Published 1 February 2011 Size: 100 KB Referencing Hub media The epidermis is a tough coating formed from overlapping layers of dead skin cells. Appears in ARTICLE Touch Key facts about the integumentary system; Skin: Functions: chemical and mechanical barrier, biosynthesis, control of body temperature, sensory Layers: Epidermis (Stratum Basale, Spinosum, Granulosum, Lucidum, Corneum) and dermis (papillary, reticular) Mnemonic: British and Spanish Grannies Love Cornflakes Hair: Types: vellus and terminal Structure: Follicle and bulb (shaft, inner root sheath. The Epidermis The epidermis is composed of keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium. It is made of four or five layers of epithelial cells, depending on its location in the body. It does not have any blood vessels within it (i.e., it is avascular). Skin that has four layers of cells is referred to as "thin skin." The Layers of Your Skin. Your skin includes three layers known as epidermis, dermis, and fat. Some health issues, such as dermatitis and infections, can affect how these different layers work to.
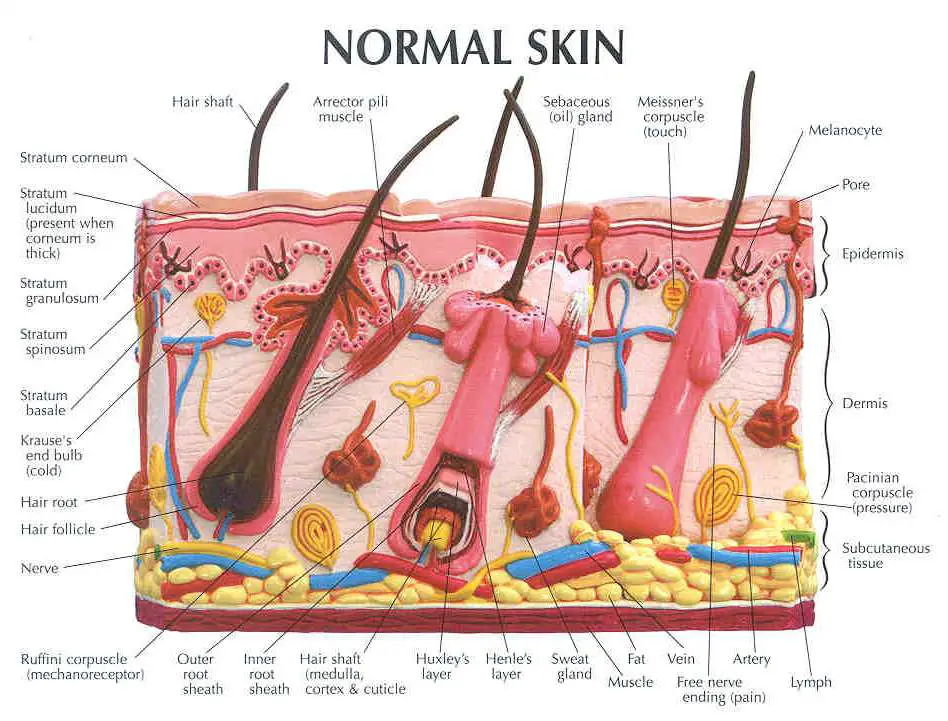
Skin diagram labeled
Skin is part of the integumentary system and considered to be the largest organ of the human body. There are three main layers of skin: the epidermis, the dermis, and the hypodermis (subcutaneous fat). The focus of this topic is on the epidermal and dermal layers of skin. Skin appendages such as sweat glands, hair follicles, and sebaceous glands are reviewed in-depth elsewhere.[1] Anatomy of the Skin Skin Facts about the skin The skin is the body's largest organ. It covers the entire body. It serves as a protective shield against heat, light, injury, and infection. The skin also: Regulates body temperature Stores water and fat Is a sensory organ Prevents water loss Prevents entry of bacteria
The skin is the body's largest and primary protective organ, covering its entire external surface and serving as a first-order physical barrier against the environment. Its functions include temperature regulation and protection against ultraviolet (UV) light, trauma, pathogens, microorganisms, and toxins. This diagram shows the layers found in skin. There are three main layers: the epidermis, dermis and hypodermis. There are also sweat glands, and hairs, which have sebaceous glands, and a smooth muscle called the arrector pili muscle, associated with them.
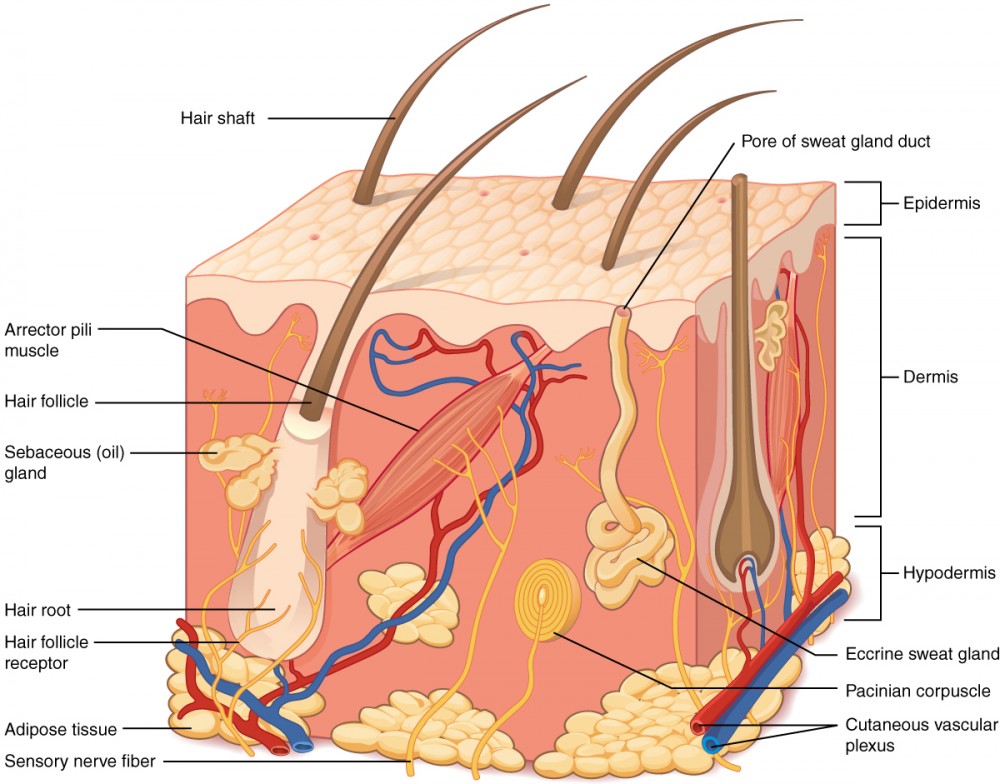
Layers of the Skin Anatomy and Physiology I
Skin also helps maintain a constant body temperature. Human skin is only about 0.07 inches (2 mm) thick. Skin is made up of two layers that cover a third fatty layer. The outer layer is called the epidermis; it is a tough protective layer that contains melanin (which protects against the rays of the sun and gives the skin its color). Overview The three layers of skin on top of muscle tissue. What is the skin? The skin is the body's largest organ, made of water, protein, fats and minerals. Your skin protects your body from germs and regulates body temperature. Nerves in the skin help you feel sensations like hot and cold.




