How does the urinary system work? The urinary system's function is to filter blood and create urine as a waste by-product. The organs of the urinary system include the kidneys, renal pelvis, ureters, bladder and urethra. The body takes nutrients from food and converts them to energy. THE KIDNEYS The kidneys sit at the back of the abdominal wall and at the start of the urinary system. These organs are constantly at work: Nephrons, tiny structures in the renal pyramids, filter gallons of blood each day. The kidneys reabsorb vital substances, remove unwanted ones, and return the filtered blood back to the body.
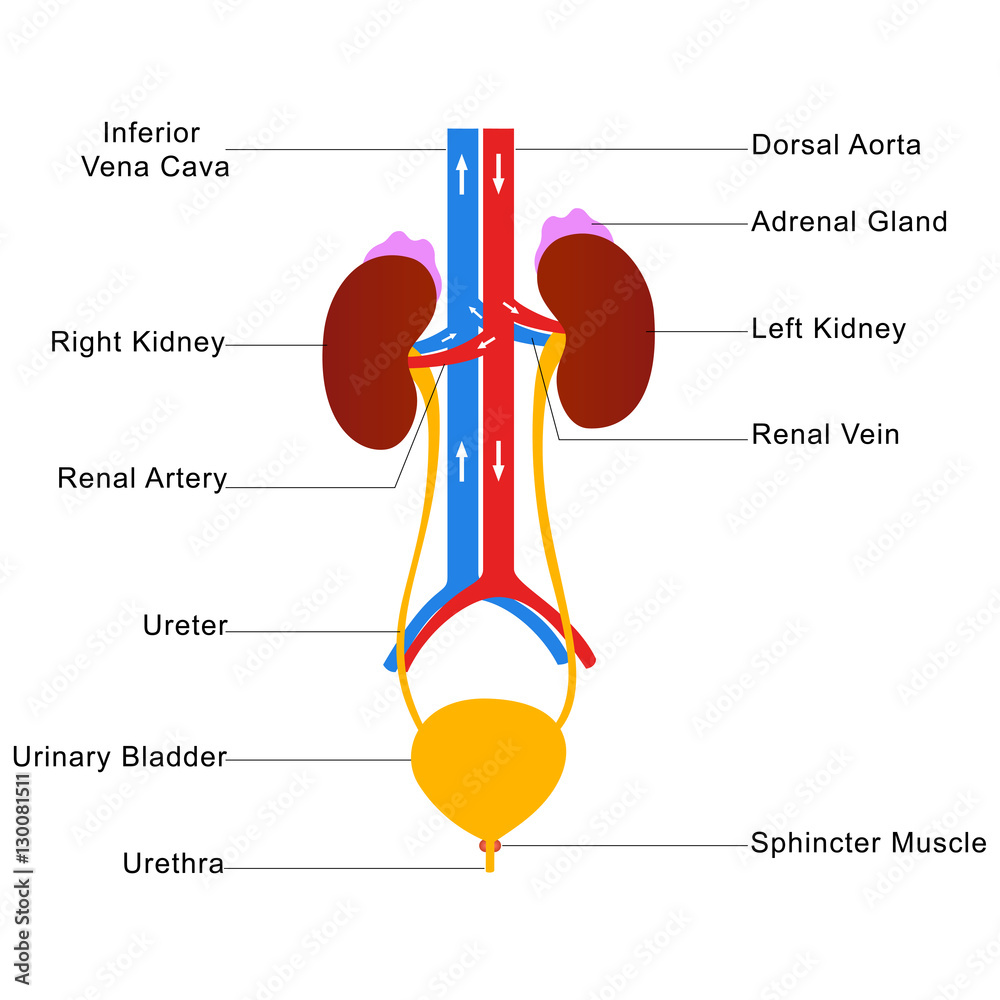
Human urinary system labelled diagram Stock Vector Adobe Stock
The anatomy of the urinary system can be seen here in the urinary system diagram. Kidneys Right kidney Ren dexter 1/9 Synonyms: none The kidneys are paired retroperitoneal organs located anterolateral to the spinal cord, near the posterior body wall. They are roughly 12 cm in length and 6 cm wide, spanning from T12 to L3 vertebral levels. What is the urinary system? The urinary system (or urinary tract) works as your body's filtration system. When your urinary system removes toxins and wastes from your body, it comes out as pee (urine). To be able to pee, your body must pass this waste through a series of organs, ducts and tubes. Anatomy of the Urinary System The urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra. Synonyms: none. The kidneys are bilateral organs placed retroperitoneally in the upper left and right abdominal quadrants and are part of the urinary system. Their shape resembles a bean, where we can describe the superior and inferior poles, as well as the major convexity pointed laterally, and the minor concavity pointed medially.
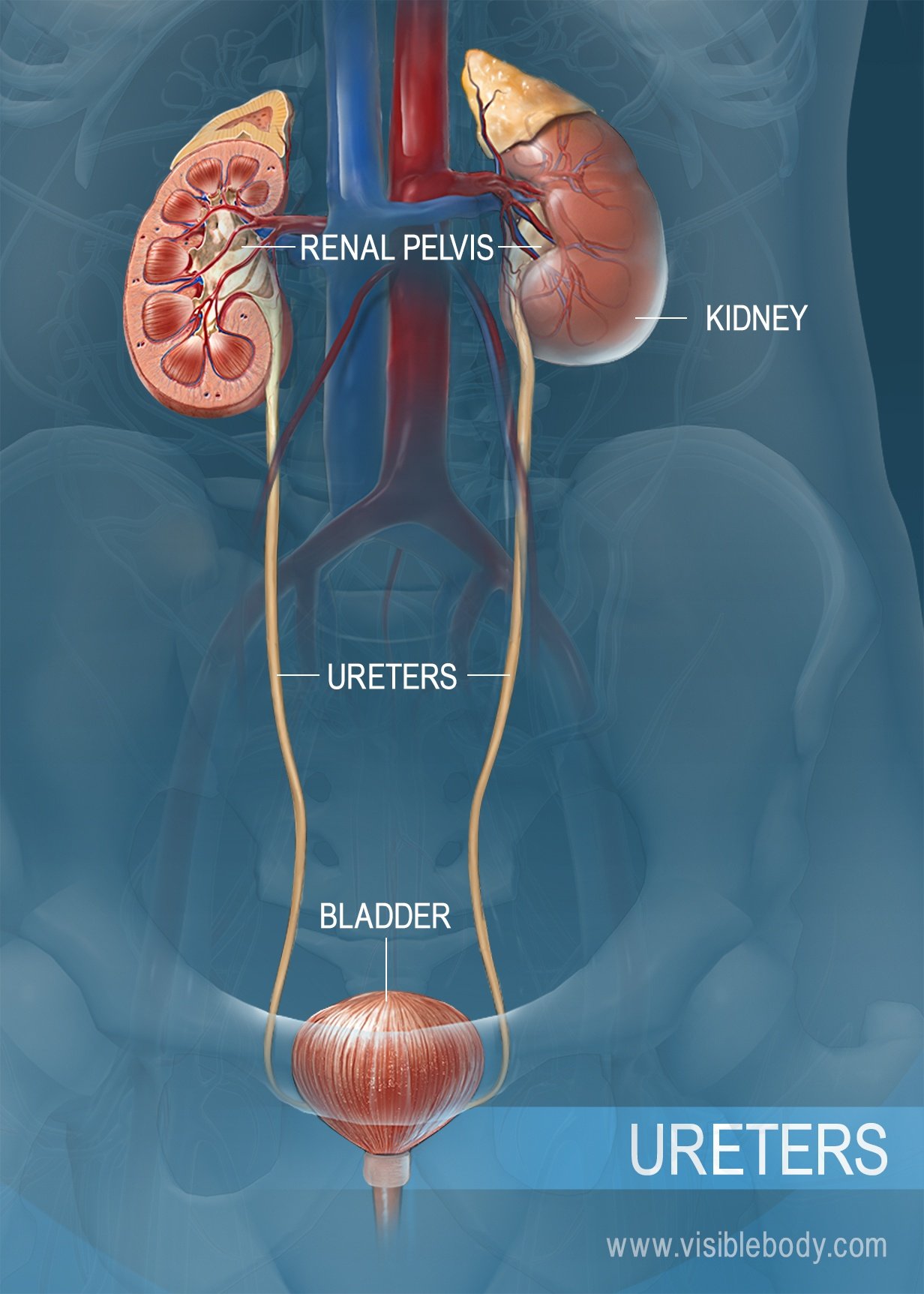
Urinary System Structures
The urinary bladder and urethra are pelvic urinary organs whose respective functions are to store and expel urine outside of the body in the act of micturition (urination). As is the case with most of the pelvic viscera, there are differences between male and female anatomy of the urinary bladder and urethra. In our entire urinary system series, the urinary bladder and urethra represent the. The urinary system is a remarkably efficient machine, responsible for the production, transport, storage and excretion of urine - not to mention its role in filtering the blood, maintaining blood volume, blood pressure, blood pH and electrolyte balance. Phew. The Urinary System Explore the anatomy and physiology of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra, learning all about how our bodies filter out and remove waste through urine. By: Tim Taylor Last Updated: May 10, 2021 2D Interactive NEW 3D Rotate and Zoom + − Click To View Large Image 11.1: Introduction to the Urinary System; 11.2: Physical Characteristics of Urine; 11.3: Gross Anatomy of Urine Transport; 11.4: Gross Anatomy of the Kidney; 11.5: Microscopic Anatomy of the Kidney; 11.6: Physiology of Urine Formation; 11.7: Tubular Reabsorption; 11.8: Regulation of Renal Blood Flow; 11.9: Endocrine Regulation of Kidney Function
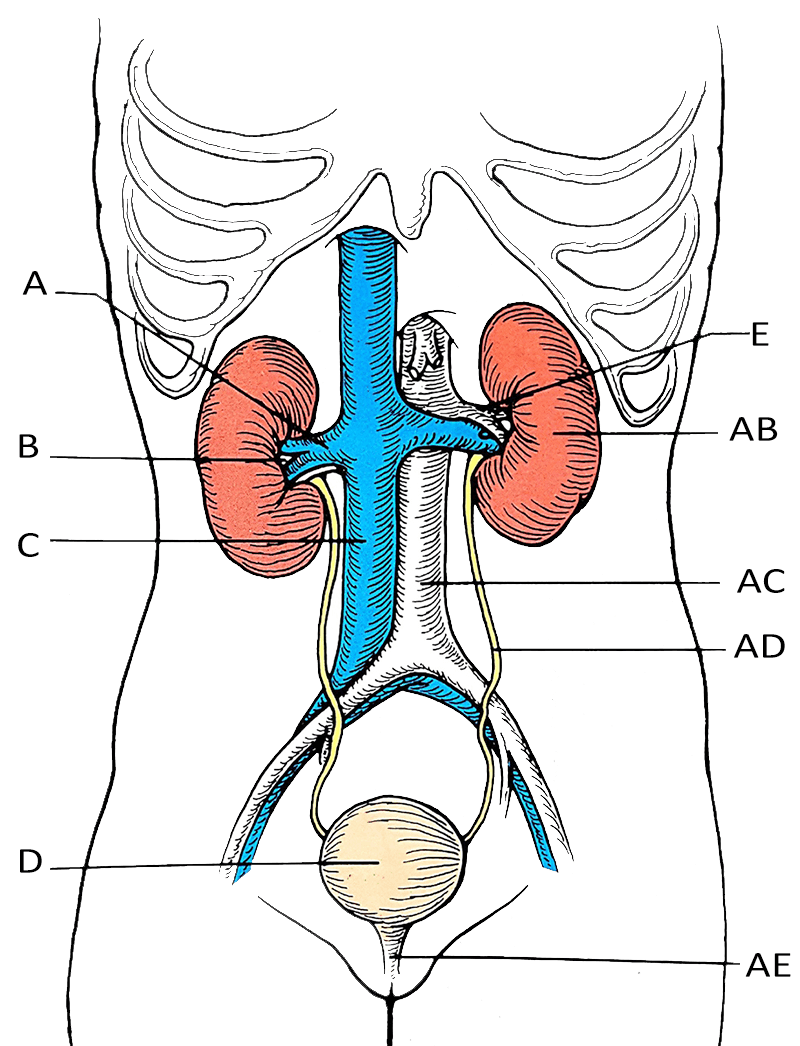
Label the Urinary System
Title: Urinary System, Male, Anatomy. Description: Anatomy of the male urinary system; shows the right and left kidneys, the ureters, the bladder filled with urine, and the urethra passing through the penis. The inside of the left kidney shows the renal pelvis. An inset shows the renal tubules and urine. Also shown is the prostate. The urinary system - also known as the renal system - produces, stores and elimiates urine, the fluid waste excreted by the kidneys. The system works with the lungs, skin and intestines to.
Female urinary system. Your urinary system includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. The urinary system removes waste from the body through urine. The kidneys are located toward the back of the upper abdomen. They filter waste and fluid from the blood and produce urine. Urine moves from the kidneys through narrow tubes to the bladder. renal system, in humans, organ system that includes the kidneys, where urine is produced, and the ureters, bladder, and urethra for the passage, storage, and voiding of urine. In many respects the human excretory, or urinary, system resembles those of other mammalian species, but it has its own unique structural and functional characteristics.

8 Facts About The Urinary System Every Nursing Student Should Know.
Kidneys and ureters are organs of the urinary system. They take part in urine production and its transport to the urinary bladder, respectively. Fun fact is that the kidneys filter around 180 liters of blood each day, meaning that your entire blood volume passes through them around 60 times every day. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY Kidney The paired kidneys lie in a retroperitoneal position (between the dorsal body wall and the parietal peritoneum) in the superior lumbar region. Extending approximately from T12 to L3, the kidneys receive some protection from the lower part of the rib cage.




