Although often called the diamond lattice, this structure is not a lattice in the technical sense of this word used in mathematics. Crystallographic structure Visualisation of a diamond cubic unit cell: 1. Components of a unit cell, 2. One unit cell, 3. A lattice of 3 × 3 × 3 unit cells GCSE OCR Gateway Properties of materials - OCR Gateway Diamond and graphite Carbon atoms can form four covalent bonds. This lets it form many different organic substances, and to exist as.

Isolated 3d Model Of A Crystal Lattice Of Diamond On A White Background Stock Photo 24510613
Optimized for Lattice Devices - Lattice Diamond offers an optimized and tailored design and verification environment for Lattice FPGAs featuring extensive constraints, advanced optimization, accurate analysis, extensive verification, and fast iterations. Features Complete GUI based FPGA design and verification environment. A lattice constant or lattice parameter is one of the physical dimensions and angles that determine the geometry of the unit cells in a crystal lattice, and is proportional to the distance between atoms in the crystal. C (diamond) is the prototype for DC. The Diamond Cubic (DC) unit cell can be imagined as a cube with an atom on each corner, each face, and the (¼, ¼, ¼), (¾, ¾, ¼), (¼, ¼, ¾), and (¼, ¾, ¾) positions. DC has 8 atoms per unit cell, lattice constant a = 8R/√3, Coordination Number CN = 4, and Atomic Packing Factor APF = 34%. Outline Small numbers of defects or impurities (about one per million of lattice atoms) color diamond blue (boron), yellow (nitrogen), brown (defects), green (radiation exposure), purple, pink, orange, or red. Diamond also has a very high refractive index and a relatively high optical dispersion .

Volumetric Crystal lattice of diamond. The position of atoms in a crystal. Vector illustration
Diamond is the allotrope of carbon in which the carbon atoms are arranged in the specific type of cubic lattice called diamond cubic.It is a crystal that is transparent to opaque and which is generally isotropic (no or very weak birefringence).Diamond is the hardest naturally occurring material known. Yet, due to important structural brittleness, bulk diamond's toughness is only fair to good. The crystal structure of a diamond is a face-centered cubic or FCC lattice. Each carbon atom joins four other carbon atoms in regular tetrahedrons (triangular prisms). Based on the cubic form and its highly symmetrical arrangement of atoms, diamond crystals can develop into several different shapes, known as 'crystal habits'. The crystal structure of diamond is equivalent to a face-centred cubic (FCC) lattice, with a basis of two identical carbon atoms: one at (0, 0, 0) and the other at (1/4, 1/4, 1/4), where the coordinates are given as fractions along the cube sides. This is the same as two interpenetrating FCC lattices, offset from one another along a body. Diamond, displaying a completely sp 3 hybridization, is a typical atomic crystal. The lattice constant is 3.57 Å, and the C-C bond is 1.54 Å. The crystal structure is shown in Figure 1. Each unit cell contains eight carbon atoms, and the C-C bond is strong covalence bond.

Bulk Crystal structure model diamond lattice (diameter 30mm) free shippingin Educational
Diamond is a crystal structure with a face centered cubic Bravais lattice and two atoms in the basis. Carbon, silicon germanium, and α-tin form this crystal structure. Crystal structure: Diamond Bravais lattice: face centered cubic Space group: 227 (F d -3 m), Strukturbericht: A4, Pearson symbol: cF8 Diamond is composed of the single element carbon, and it is the arrangement of the C atoms in the lattice that give diamond its amazing properties. Compare the structure of diamond and graphite, both composed of just carbon.
Lattice constant of isotope diamond have been systematically studied by two research teams. 31 - 34) The lattice constants of diamond crystals consisting of an isotopic mixture of 13 Cx 12 C(1 − x) were measured as a function of the isotopic composition by single-crystal diffractometers using synchrotron X-ray radiation. The isotope ratio of the synthesized diamond samples was determined. The cubic lattice is the most symmetrical of the systems. All the angles are equal to 90°, and all the sides are of the same length (a = b = c).Only the length of one of the sides (a) is required to describe this system completely.In addition to simple cubic, the cubic lattice also includes body-centered cubic and face-centered cubic (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\).
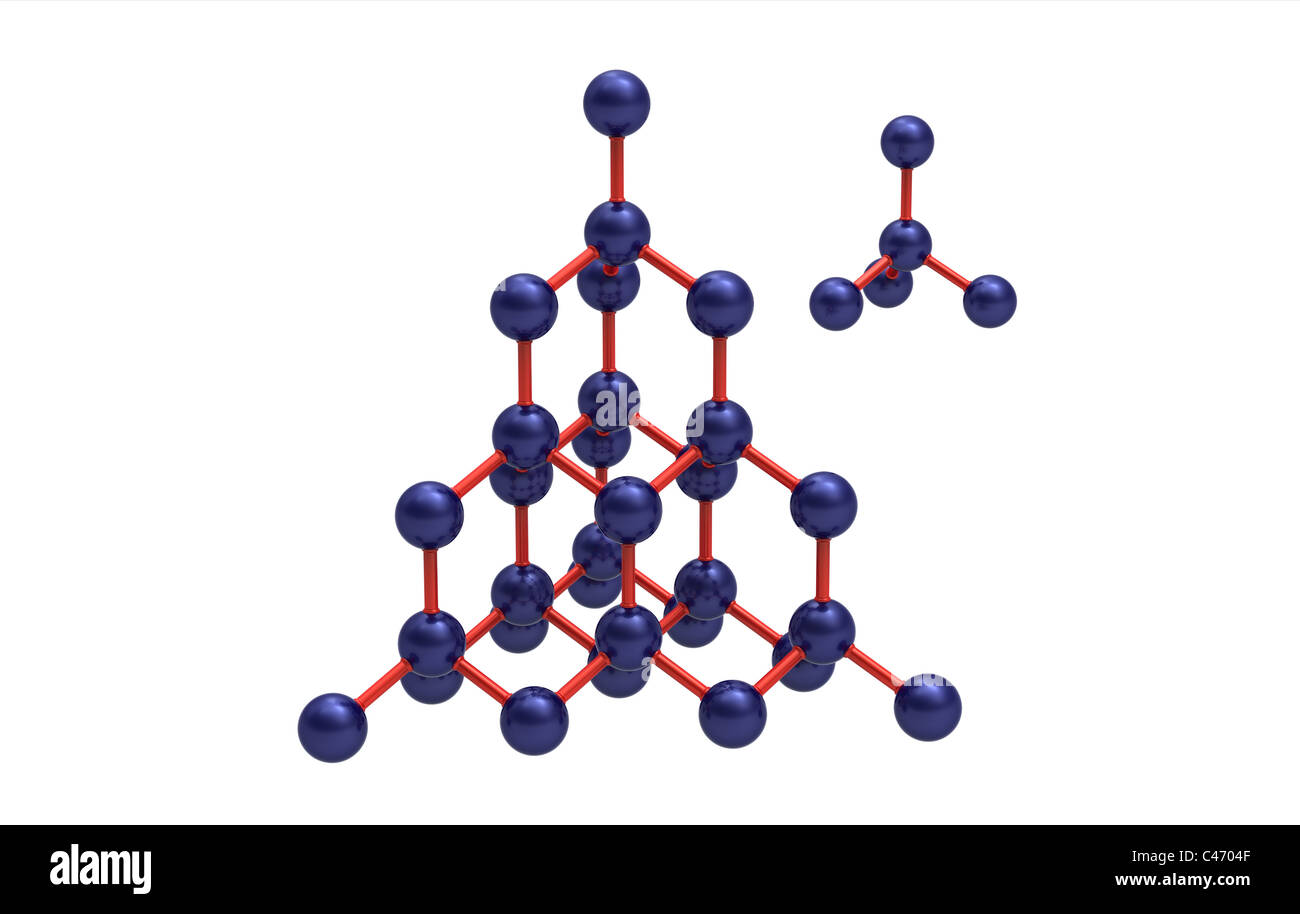
Structure Of Diamond
In Figure 3.5a the first BZ is depicted. It has a volume of [].. Due to the translational invariance of the lattice the wave functions and the energy bands are periodic in the reciprocal space and it is sufficient to consider only the first BZ for band structure calculations [].The diamond structure is invariant not only under translations, but also under several other symmetry operations such. AQA Giant covalent molecules - AQA Diamond and graphite Giant covalent substances have many atoms joined together by covalent bonds. Diamond, graphite and graphene are forms of carbon with.




