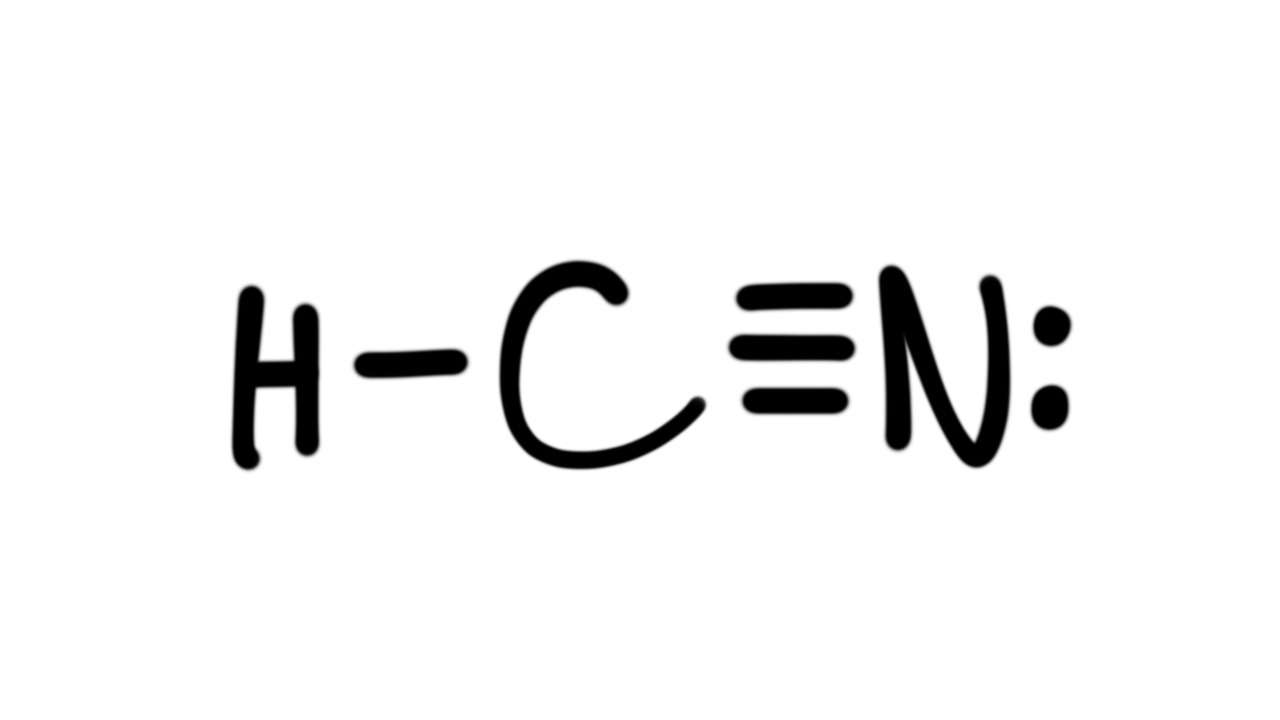Lewis Structure of HCN chemistNATE 260K subscribers Subscribe Subscribed 457K views 10 years ago Lewis Structures The Lewis Structure (Lewis Dot Diagram) for HCN. 1. Count electrons 2.. To start with making the Lewis Structure of HCN, we will first determine the central atom. And then place the remaining atoms in the structure. As Carbon is the least electronegative atom in this molecule, it will take the central position. Place the Hydrogen and Nitrogen atoms on both terminal sides of the Carbon like this:
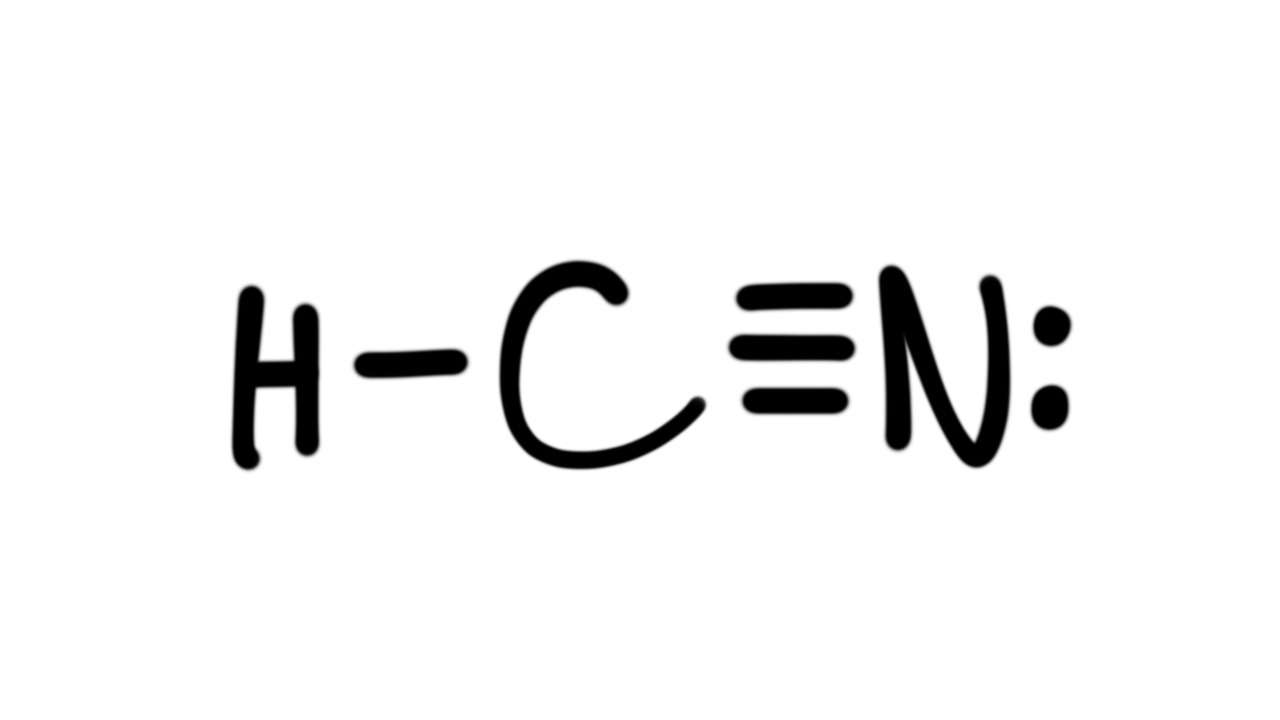
Hydrogen Cyanide YouTube
For the HCN Lewis structure, calculate the total number of valence electrons for the HCN molecule. After determining how many valence electrons there are in HCN, place them around the central. This widget gets the Lewis structure of chemical compounds. Send feedback | Visit Wolfram|Alpha Get the free "Lewis Structure Finder" widget for your website, blog, Wordpress, Blogger, or iGoogle. Find more Chemistry widgets in Wolfram|Alpha. Step 1: The foremost step of creating a Lewis structure is finding the valence electrons. Here we have to find the valence electrons of all three atoms, hydrogen, carbon, and nitrogen. 5.3C: HCN H C N. Page ID. HCN, hydrogen cyanide, is a volatile and poisnous compound with distinguished bitter odor. It is linear molecule with a triple bond between C and N atom and has bond angle of 180 degrees. It can be found in fruits that have pits due to the fact that they contain small amounts of cyanohydrins which slowly releases.

Draw the Lewis dot structure of Hydrogen cyanide (HCN) molecule
Chemistry learning made easy.This tutorial will help you deal with the lewis structure and moleculargeometry for hydrogen cyanide (HCN). Lewis Structure of Hydrogen cyanide - HCN Chemical data of Hydrogen Cyanide-HCN Physical Properties of Hydrogen cyanide-HCN Chemical Properties of Hydrogen cyanide-HCN Hydrocyanic acid reacts with bases like sodium hydroxide forms sodium cyanide and water. The chemical equation is given below. HCN + NaOH → NaCN + H2O The first step is to sketch the Lewis structure of the HCN molecule, to add valence electrons around the cyanide species; the second step is to add valence electrons to the one hydrogen atom, and the final step is to combine the step1 and step2 to get the HCN Lewis Structure. A triple bond forms when three electron pairs are shared by a pair of atoms, as in carbon monoxide (CO) and the cyanide ion (CN -): Writing Lewis Structures with the Octet Rule. For very simple molecules and molecular ions, we can write the Lewis structures by merely pairing up the unpaired electrons on the constituent atoms. See these examples:

HCN Lewis Structure (Hydrogen Cyanide) Molecules, Chemical formula, Lewis
The Lewis Structure of HCN. When creating the Lewis structure of HCN, it is important to start by identifying the central atom, which in this case is carbon. Nitrogen and hydrogen atoms are then placed around the carbon atom, with the hydrogen atoms forming a single bond with the carbon atom and the nitrogen atom forming a triple bond with the. The Lewis structure of XeF 2 shows two bonding pairs and three lone pairs of electrons around the Xe atom: XeF 6: We place three lone pairs of electrons around each F atom, accounting for 36 electrons. Two electrons remain, and this lone pair is placed on the Xe atom: Exercise 4.2. 2: interhalogens.
There is a single covalent bond between the hydrogen and carbon atom, represented by two dots, :, each of which represents a shared electron; a triple covalent bond between the carbon and nitrogen atom, represented by three pairs of dots, :::, representing three pairs of shared electrons, and a lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom, repres. The Lewis structure or dot structure of a hydrogen cyanide (HCN) molecule can easily represent the electron arrangement around the atoms of HCN as it is made by bonding 3 different atoms together. HCN is a linear molecule which is bounded by a hydrogen atom, a carbon atom, and a nitrogen atom.

HCN Lewis StructureHydrogen Cyanide (HCN) Lewis Dot StructureDraw Lewis Structure of HCN
Lewis Structure and Hybridization of HCN (hydrocyanic acid, hydrogen cyanide) HCN has a hydrogen atom single-bonded to a carbon atom, and that carbon atom is triple-bonded to a nitrogen atom. These are all non-metals, so the bonds are covalent and HCN is therefore a covalent (aka Molecular) structure. We can draw Lewis structures for polyatomic ions (ions containing multiple atoms) using the same stepwise procedure as for neutral molecules. In this video, we'll see how to construct the Lewis diagram of the cyanide ion (CN⁻). Created by Sal Khan. Questions Tips & Thanks Want to join the conversation? Sort by: Top Voted Maria Gregory 3 years ago