Linear: (Lengths) Geometric Formulas © Chandler-Gilbert Community College Learning Center Shape Rectangular Solids (Boxes) General Formulas Surface Area (with top and bottom): SA = 2 LW + 2 LH + 2 WH Volume: V = L ⋅ W ⋅ H Picture H L W Cubes Surface Area (with top and bottom): SA = 6s 2 Volume: V = s ⋅ s ⋅ s = List of All Geometry Formulas PDF Geometry formulas are used for finding dimensions, perimeter, area, surface area, volume, etc. of the geometric shapes. Geometry is a part of mathematics that deals with the relationships of points, lines, angles, surfaces, solids measurement, and properties.

Printable Geometry Formulas Cheat Sheet Cheat Dumper
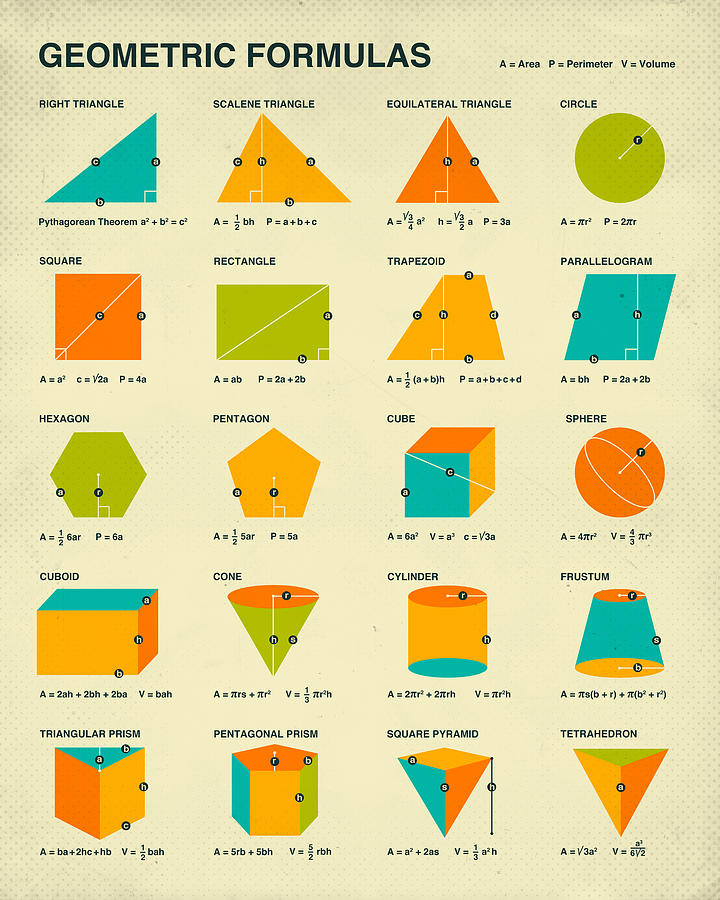
Page Description Chapter 1: Basics 6 Points, Lines & Planes 7 Segments, Rays & Lines 8 Distance Between Points in 1 Dimension 8 Distances Between Collinear Points 9 Distance Between Points in 2 Dimensions 11 Partial Distances and Distance Equations 12 Distance Formula in "n"Dimensions 13 Angles 14 Types of Angles Chapter 2: Proofs 16 Conditional. Name: Polygon Postulates And Theorems Definition Proportional Perimeters and Areas Theorem a If the similarity ratio of two similar figures is , b then the ratio of their perimeter is and the Area Addition Postulate 2 2 a ratio of their areas is 2 or b The area of a region is equal to the sum of the areas of its nonoverlapping parts. Parallelogram Area = b × h Perimeter of a Parallelogram=2(Base+Height) Height of a Parallelogram, Height=Area/Base Diagonal of Parallelogram =p2+q2=2(a2+b2) Geometry Formulas List Shape Formulas Figure Right Triangle Pythagoras Theorem: a 2 + b 2 = c 2 Area = ½ ab Perimeter = a + b + √(a

Area, Surface Area and Volume Reference Sheet Math formula chart, Math formulas, Volume math
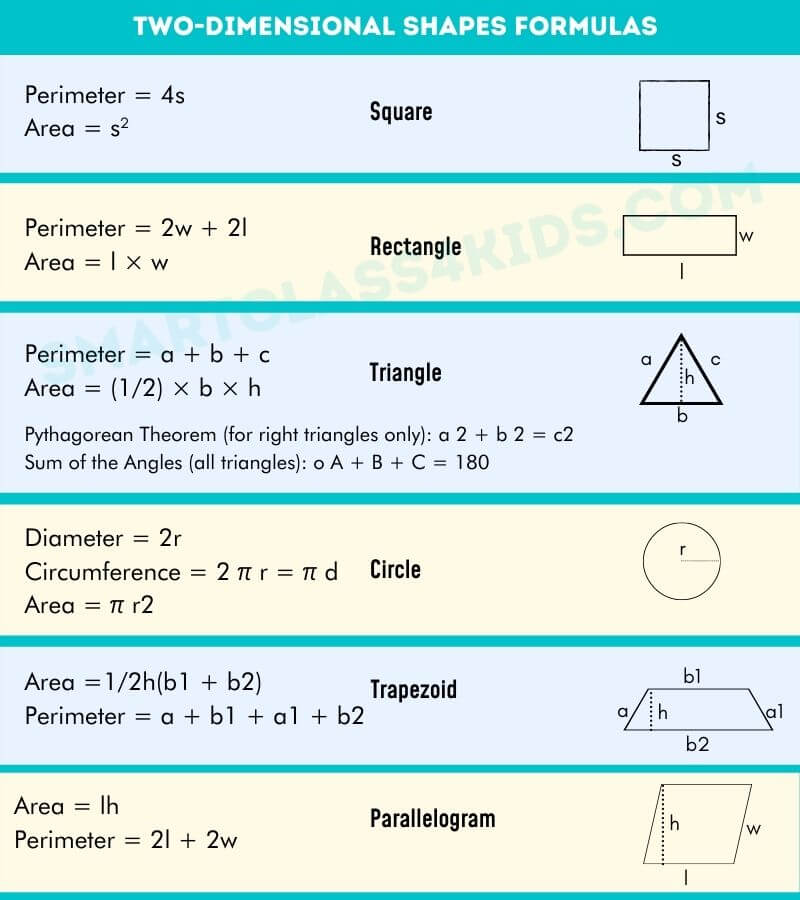
Geometric Formulas Two-Dimensional Objects Rectangle/Square ' ' w w P= 2'+2w A= 'w Triangle h b a c P= a+b+c A= 1 2 bh Circle r C= 2ˇr A= ˇr2 Parallelogram a a b b h P= 2a+2b A= bh Trapezoid a 1 a 2 b 2 b 1 h P= a 1 +a 2 +b 1 +b 2 A= 1 2 h(b 1 +b 2) Regular Polygon a s n= number of sides s=length of sides a=apothem (the radius of. Here is the list of various 2d geometry formulas according to the geometric shape. It also includes a few formulas where the mathematical constant π (pi) is used. Perimeter of a Square = 4 (Side) Perimeter of a Rectangle = 2 (Length + Breadth) Area of a Square = Side 2 Area of a Rectangle = Length × Breadth Area of a Triangle = ½ × base × height This handout is intended as a review of basic geometric formulas and properties. For further or more advanced geometric formulas and properties, consult with a SLAC counselor. Square: Perimeter: P = 4s or 2s + 2s Area: A = s2 Rectangle: Perimeter: P = 2w + 2l Area: A = l × w Triangles: Perimeter: P = a + b + c Area: A = (1/2) × b × h ss s l c h Geometry Formulas and Shape Formula Name Formula Perimeter of a Rectangle Perimeter of a square Perimeter of a triangle Circumference of a circle Area of a rectangle Area of a square Area of a triangle Area of a parallelogram Area of a trapezoid Area of a circle Volume of a rectangular solid.
44+ Math Formulas Geometry List Gif Math Edu
Here you will find our online geometry support page about different Geometry formulas, including properties of angles, 2d and 3d shapes, as well as some common formulas to help you to work out area and volumes. Using these sheets will help your child to: identify 2d shapes and know what special properties they have; Equation of a plane A point r (x, y, z)is on a plane if either (a) r bd= jdj, where d is the normal from the origin to the plane, or (b) x X + y Y + z Z = 1 where X,Y, Z are the intercepts on the axes. Vector product A B = n jAjjBjsin , where is the angle between the vectors and n is a unit vector normal to the plane containing A and B in the direction for which A, B, n form a right-handed set.
Created Date: 3/16/2008 2:13:01 PM 1. Lines in two dimensions Line forms Slope - intercept form: Line segment A line segment y = mx + b Two point form: y − y y − y = 2 1 ( x − x ) 1 x − 1 2 x 1 Point slope form: − y y =
Basic Geometry Formulas Area, Perimeter, Volume
B is the area of the base and P is the perimeter of the base. of the base. The sum of the angles in a triangle is 180°. The sum of the angles in an n-sided polygon is. 180 n 2 . n , where n is the number of sides. Ax By C , where A, B, and C are integers, A and B are not both zero, and A is positive. rate, n is the number of compounds per year. method is commonly used in geometry to express a general circle equation in center-radius form. Example: Express the general equation 62+46+32−63−12=0 in center-radius form. Steps: 1) Determine if the squared. 62+46+32−63−12=0 terms have a coefficient of 1. 2) If there is a constant/number.




