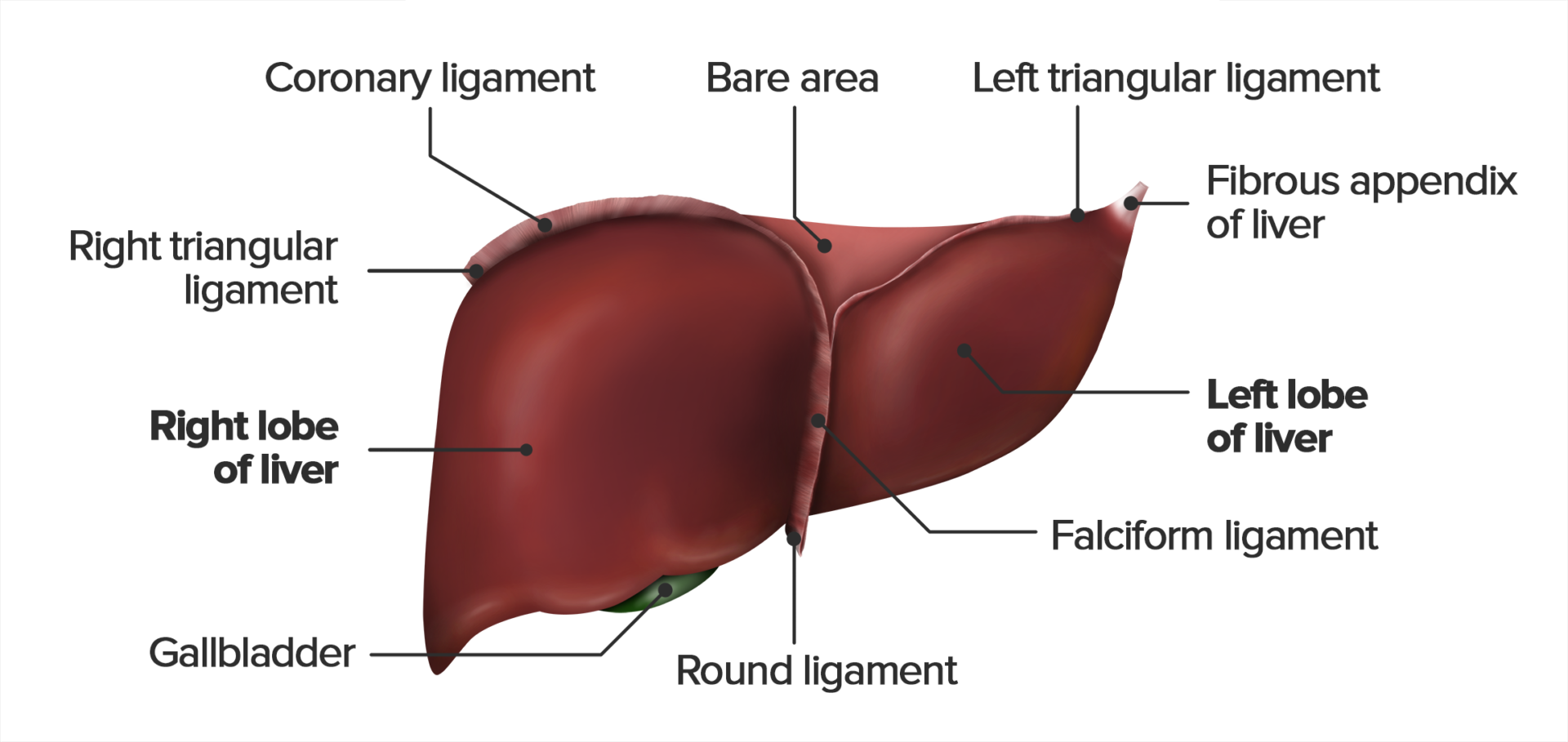
The round ligament of the liver (or ligamentum teres, or ligamentum teres hepatis) is a ligament that forms part of the free edge of the falciform ligament of the liver. It connects the liver to the umbilicus. It is the remnant of the left umbilical vein. The round ligament divides the left part of the liver into medial and lateral sections. Liver ligaments are double-layered folds of peritoneum that attach the liver to surrounding organs, or to the abdominal wall. The majority of ligaments associated with the liver are remnants of embryological blood vessels that regressed as the fetus developed.
Liver Anatomy Concise Medical Knowledge
The round ligament, or ligamentum teres, of the liver is a dense ligamentous band of fibrous tissue. It is a remnant of the fetal circulatory system, the umbilical veins. Complete Anatomy The world's most advanced 3D anatomy platform Try it for Free See these models in 3D with Complete Anatomy App Related parts of the anatomy The liver is a large organ found in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen. It is a multifunctional accessory organ of the gastrointestinal tract and performs several essential functions such as detoxification, protein synthesis, bile production and nutrient storage to name only a few. Hepatic portal vein Branches of hepatic portal vein Right branch of hepatic portal vein Left branch of hepatic portal vein Transverse part of left branch of hepatic portal vein Umbilical part of left branch of hepatic portal vein Ligamentum venosum Lateral left branches of hepatic portal vein Umbilical vein Round ligament of liver The free-form edge of the falciform ligament contains the round ligament of the liver which is the remnant of the embryonic umbilical vein. Anatomically the liver has four lobes: right, left, caudate, and quadrate.
Liver Anatomy Concise Medical Knowledge
The liver is a peritoneal organ positioned in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen. It is the largest visceral structure in the abdominal cavity, and the largest gland in the human body. An accessory digestion gland, the liver performs a wide range of functions, such as synthesis of bile, glycogen storage and clotting factor production.. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the. The round ligament of the liver is a ligament that forms part of the free edge of the falciform ligament of the liver. It connects the liver to the umbilicus. It is the remnant of the left umbilical vein. The round ligament divides the left part of the liver into medial and lateral sections. The free edge of the falciform ligament contains the ligamentum teres hepatis (round ligament of the liver): the obliterated umbilical vein, which is attached to the inferior surface of the liver between segment IV on the right and segment III on the left. The ligamentum venosum (the obliterated ductus venosus) is attached to the inferior. . Liver parenchyma consists of hepatocytes and hepatic sinusoids . Hepatic sinusoids drain into the central vein of each lobule. The liver is responsible for energy metabolism, synthesis of various substances (e.g., glucose,

The round ligament of the liver Download Scientific Diagram
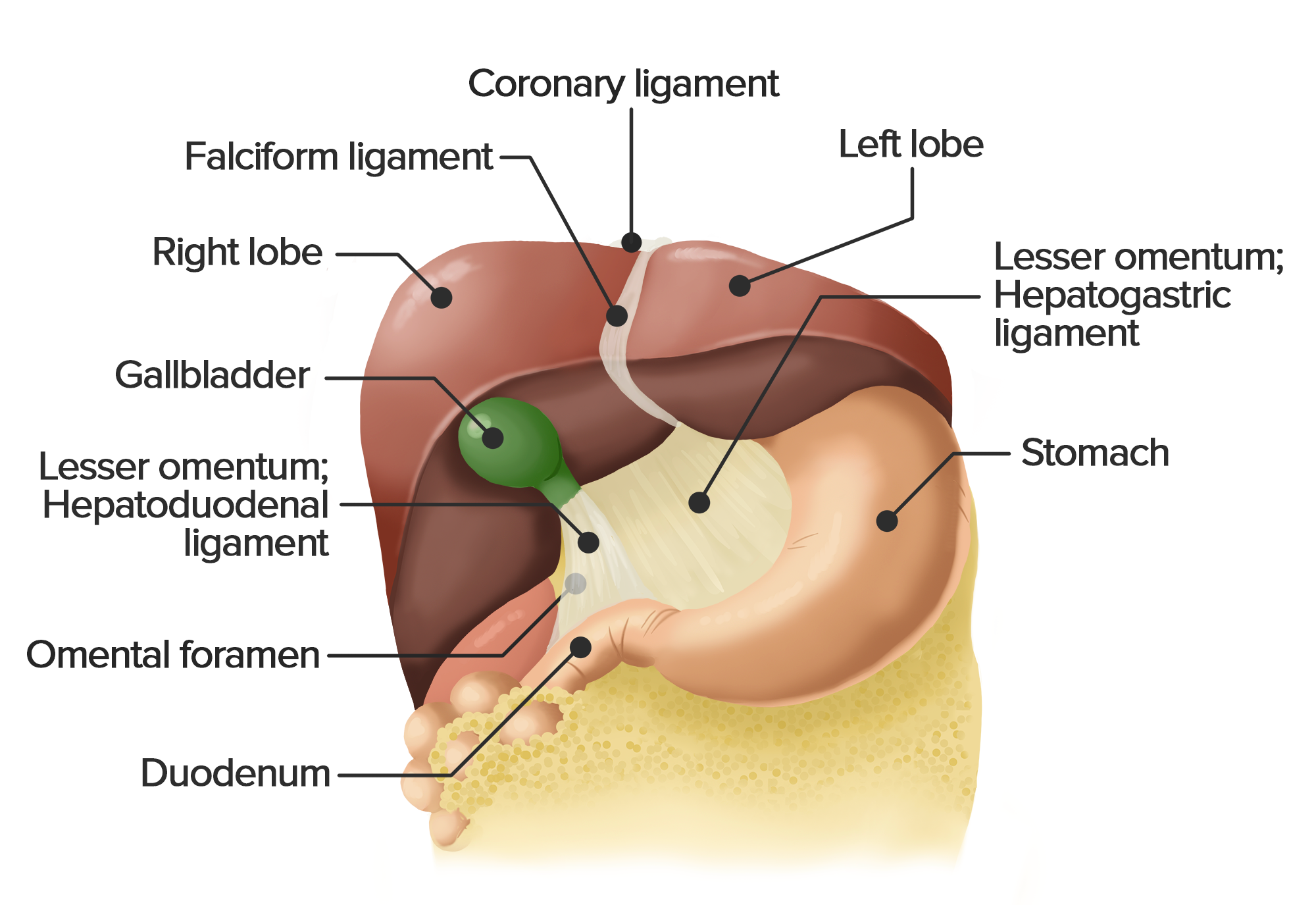
Hepatic ligaments. Several peritoneal ligaments support the position of the liver: round ligament of liver (ligamentum teres), falciform ligament, coronary ligament, triangular ligaments and lesser omentum. The lesser omentum comprises the hepatogastric and hepatoduodenal ligaments which connect the liver to the lesser curvature of the stomach and duodenum. The bridges comprise the ligaments of the liver as follows: the falciform ligament, right and left coronary ligaments, lesser omentum including the hepatogastric ligament and hepatoduodenal ligament.. The obstructed UV is typically exhibited as a small round-shaped structure that arises from the bifurcation (the umbilical portion) of P3 and.
The round ligament of the liver is the fetal remnant of the umbilical vein, which once traveled from the placenta to the fetal liver to deliver oxygenated blood. [1] Go to: Embryology . The round ligament contains the umbilical vein during gestation, which is the main fetal blood source (see table below). Gross Anatomy Location The liver is the largest gland in the body. It extends from the right to the left hypochondriac region (¾ of the liver is in the right superior quadrant).

Liver Encyclopedia Anatomy.app Learn anatomy 3D models, articles, and quizzes
12.1.1 Anatomy The hepatic artery, portal vein, and bile ducts (the portal triad) in the ligamentum hepatoduodenale are encased in a membrane and branch, and they constitute Glisson's system. This system consists of extrahepatic and intrahepatic portions. The two hemilivers are divided on the anterior surface of the liver by the falciform ligament and on the inferior surface by the round ligament as it runs into the umbilical fissure. At the upper margin, the two layers of the falciform ligament divide from each other. On the right side, the falciform ligament attaches the right diaphragmatic.




