Figure: Diagram of parts of a microscope. There are three structural parts of the microscope i.e. head, arm, and base. Head - The head is a cylindrical metallic tube that holds the eyepiece lens at one end and connects to the nose piece at other end. It is also called a body tube or eyepiece tube. ACTIVITY Microscope parts READ MORE MORE Use this interactive to identify and label the main parts of a microscope. Drag and drop the text labels onto the microscope diagram.
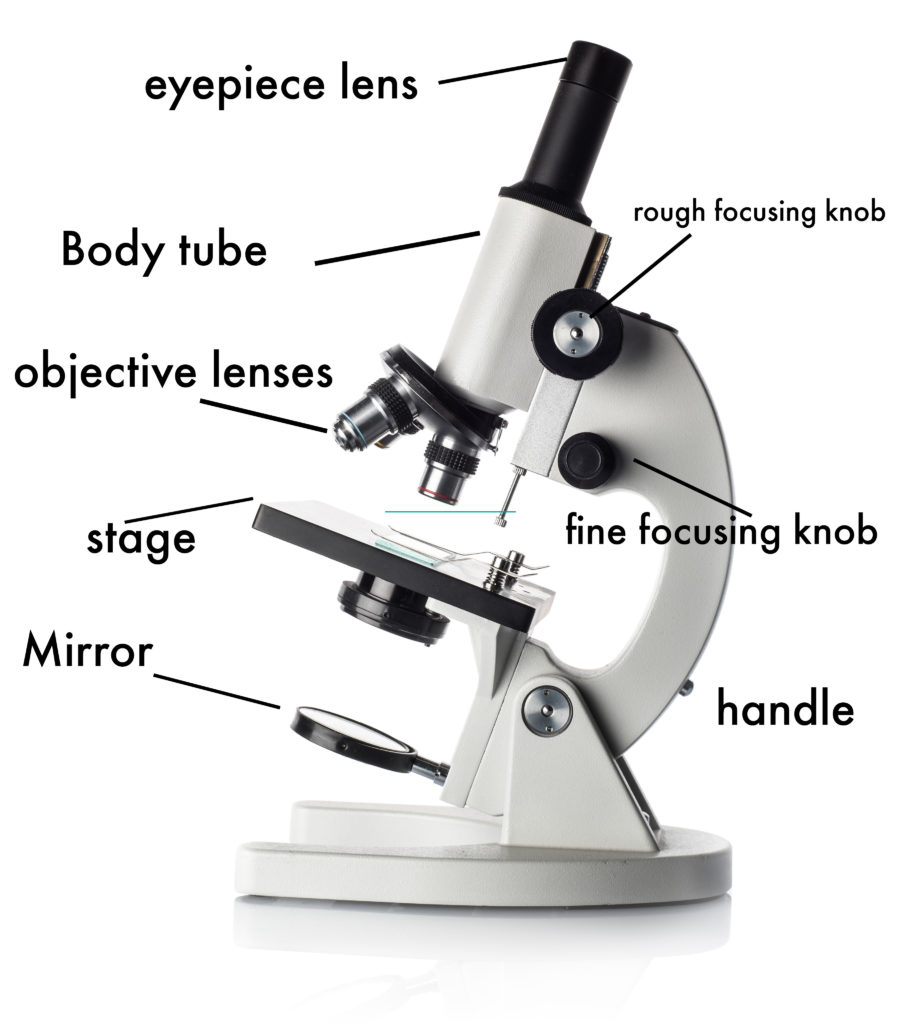
How to Use a Microscope
Iris diaphragm: Adjusts the amount of light that reaches the specimen. Condenser: Gathers and focuses light from the illuminator onto the specimen being viewed. Base: The base supports the microscope and it's where illuminator is located. How Does a Compound Microscope Work? This activity has been designed for use in homes and schools. Each microscope layout (both blank and the version with answers) are available as PDF downloads. You can view a more in-depth review of each part of the microscope here. Download the Label the Parts of the Microscope PDF printable version here. a. Mechanical Parts of a Compound Microscope Foot or Base Pillar Arm Stage Inclination Joint Clips Diaphragm Nose piece/Revolving Nosepiece/Turret Body Tube Adjustment Knobs b. Optical Parts of a Compound Microscope Eyepiece lens or Ocular Mirror Objective Lenses Magnification is a measure of how much larger a microscope (or set of lenses within a microscope) causes an object to appear. For instance, the light microscopes typically used in high schools and colleges magnify up to about 400 times actual size. So, something that was 1 mm wide in real life would be 400 mm wide in the microscope image.

301 Moved Permanently
1. Eyepiece 2. Body tube/Head 3. Turret/Nose piece 4. Objective lenses 5. Knobs (fine and coarse) 6. Stage and stage clips 7. Aperture 9. Condenser 10. Condenser focus knob 11. Iris diaphragm 12. Diopter adjustment 13. Arm 14. Specimen/slide 15. Stage control/stage height adjustment 16. On and off switch 17. Base Simple microscope is a magnification apparatus that uses a combination of double convex lens to form an enlarged, erect image of a specimen. The working principle of a simple microscope is that when a lens is held close to the eye, a virtual, magnified and erect image of a specimen is formed at the least possible distance from which a human eye. Microscope - Types, Diagrams and Functions By Editorial Board October 13, 2022 Microscope - Let's split the name into two parts to understand what it actually means. " Micro " means very small (typically not visible to the naked eye) and " scope " means to assess or investigate carefully. Tube: Connects the eyepiece to the objective lenses. Arm: Supports the tube and connects it to the base. Base: The bottom of the microscope, used for support. Illuminator: A steady light source (110 volts) used in place of a mirror. If your microscope has a mirror, it is used to reflect light from an external light source up through the bottom.
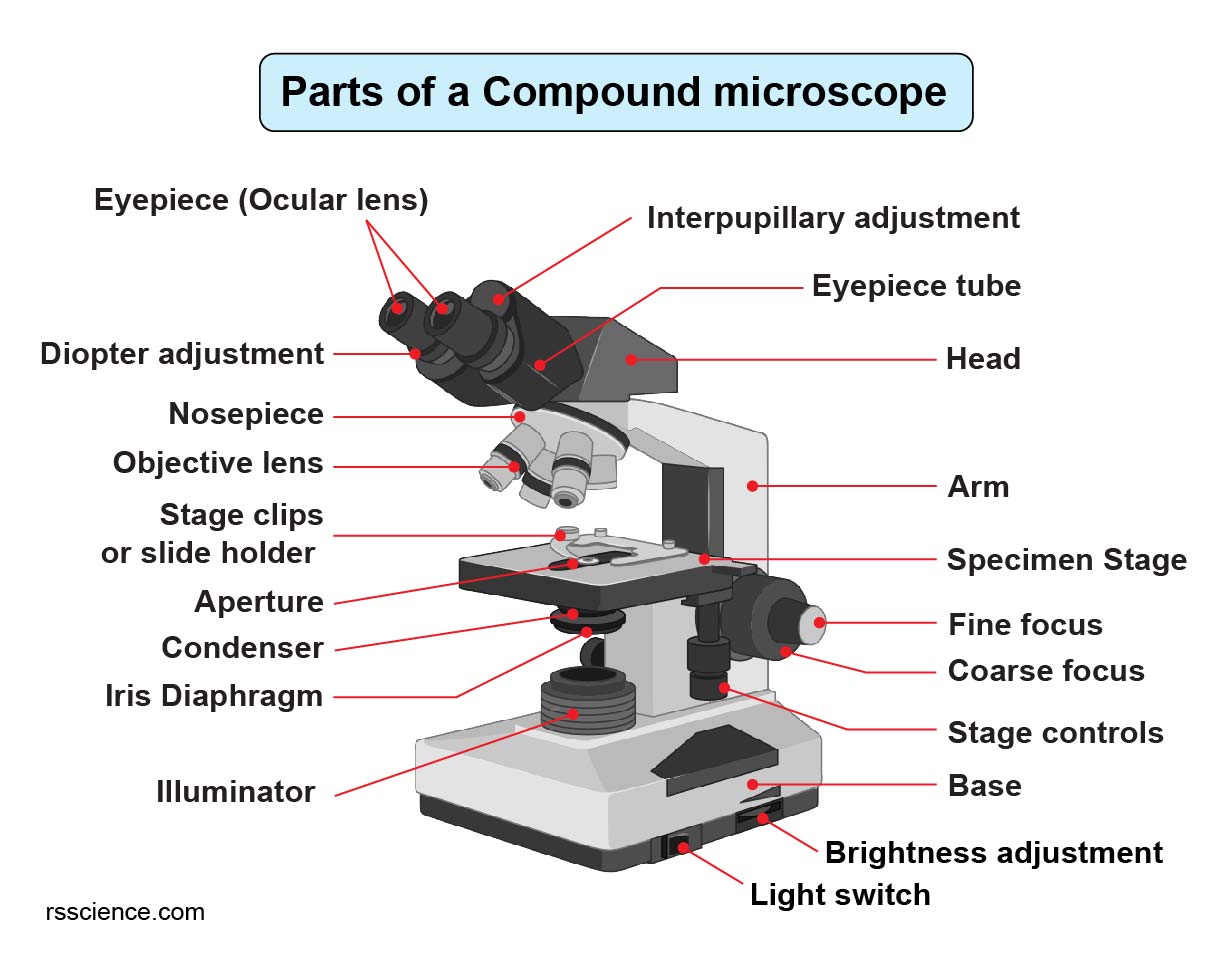
Compound Microscope Parts Labeled Diagram and their Functions Rs' Science
Compound Microscope Parts, Functions, and Labeled Diagram Compound Microscope Parts, Functions, and Labeled Diagram Parts of a Compound Microscope Each part of the compound microscope serves its own unique function, with each being important to the function of the scope as a whole. Compound Microscope Parts - Labeled Diagram and their Functions Microscopes / By Rachael Sharing is caring! This article will review the structure of a compound microscope and explain to you how each part works to give us the magnification images. This article covers An overview of microscopes What is a "compound microscope"?
A Study of the Microscope and its Functions With a Labeled Diagram - Science Struck A Study of the Microscope and its Functions With a Labeled Diagram To better understand the structure and function of a microscope, we need to take a look at the labeled microscope diagrams of the compound and electron microscope. The hand magnifying glass can magnify about 3 to 20×. Single-lensed simple microscopes can magnify up to 300×—and are capable of revealing bacteria —while compound microscopes can magnify up to 2,000×. A simple microscope can resolve below 1 micrometre (μm; one millionth of a metre); a compound microscope can resolve down to about 0.2 μm.
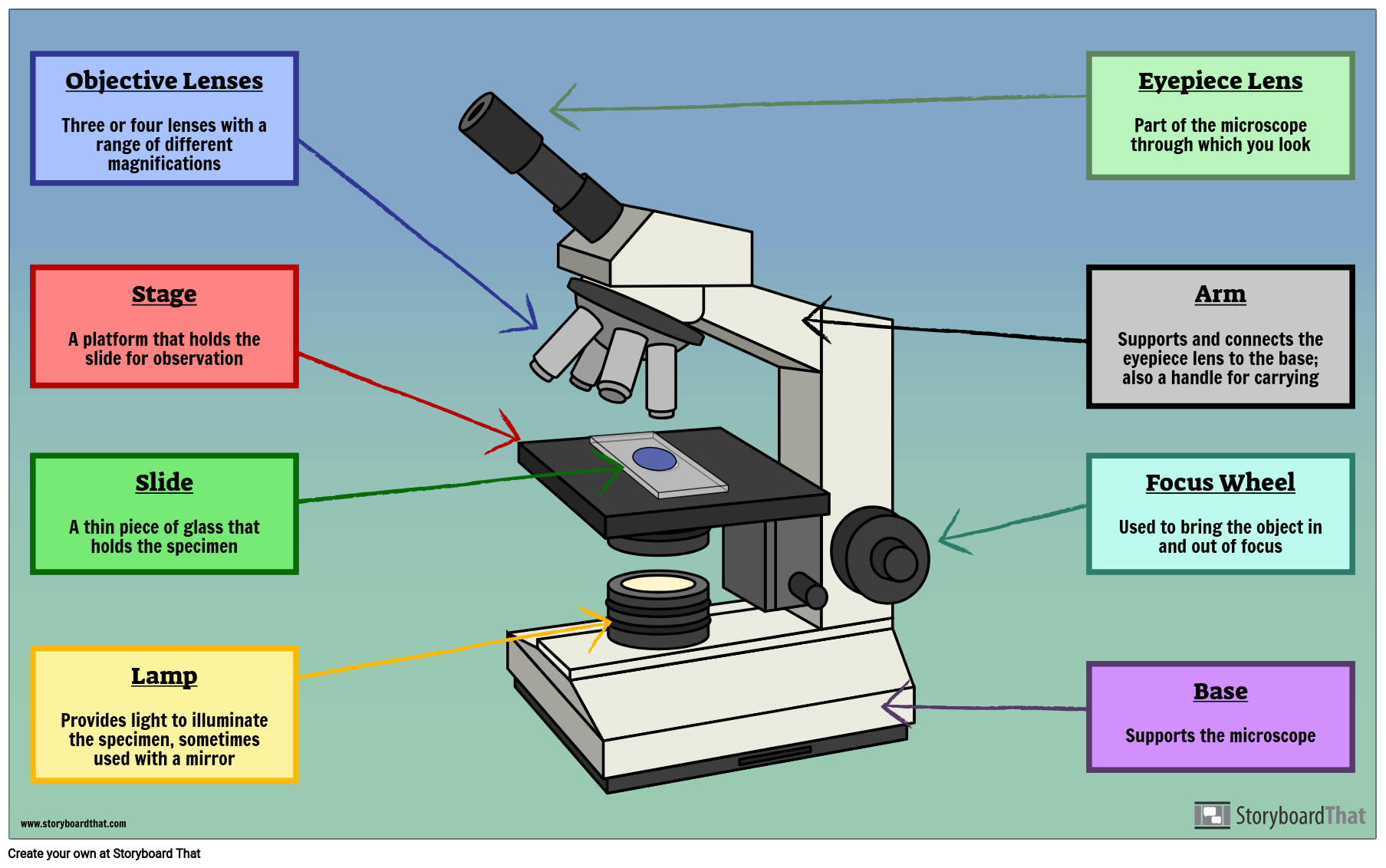
Labelled Microscope with Functions Storyboard by oliversmith
The web page titled "Parts of a Microscope with Labeled Diagram and Functions" has the following key takeaways: 🔍 The microscope is an essential tool for scientists, researchers, and medical professionals. 🧬 The main function of a microscope is to provide a magnified view of small objects or organisms, such as bacteria, cells, or tissues. Parts Of a microscope. The main parts of a microscope that are easy to identify include: Head : The upper part of the microscope that houses the optical elements of the unit. Base: The base is attached to a frame (arm) that is connected to the head of the device. The base of the microscope provides stability to the device and allows the user.




