Structure and surrounding structures of a tooth seen in cross section. The tooth is one of the most individual and complex anatomical as well as histological structures in the body. The tissue composition of a tooth is only found within the oral cavity and is limited to the dental structures. 1. Introduction In order to understand tooth morphology, it is necessary to understand the anatomy of the structures within the tooth. In order to understand these, it is helpful to understand tooth development. Therefore, this chapter will cover tooth development and explain the tissues and structures involved in tooth growth.
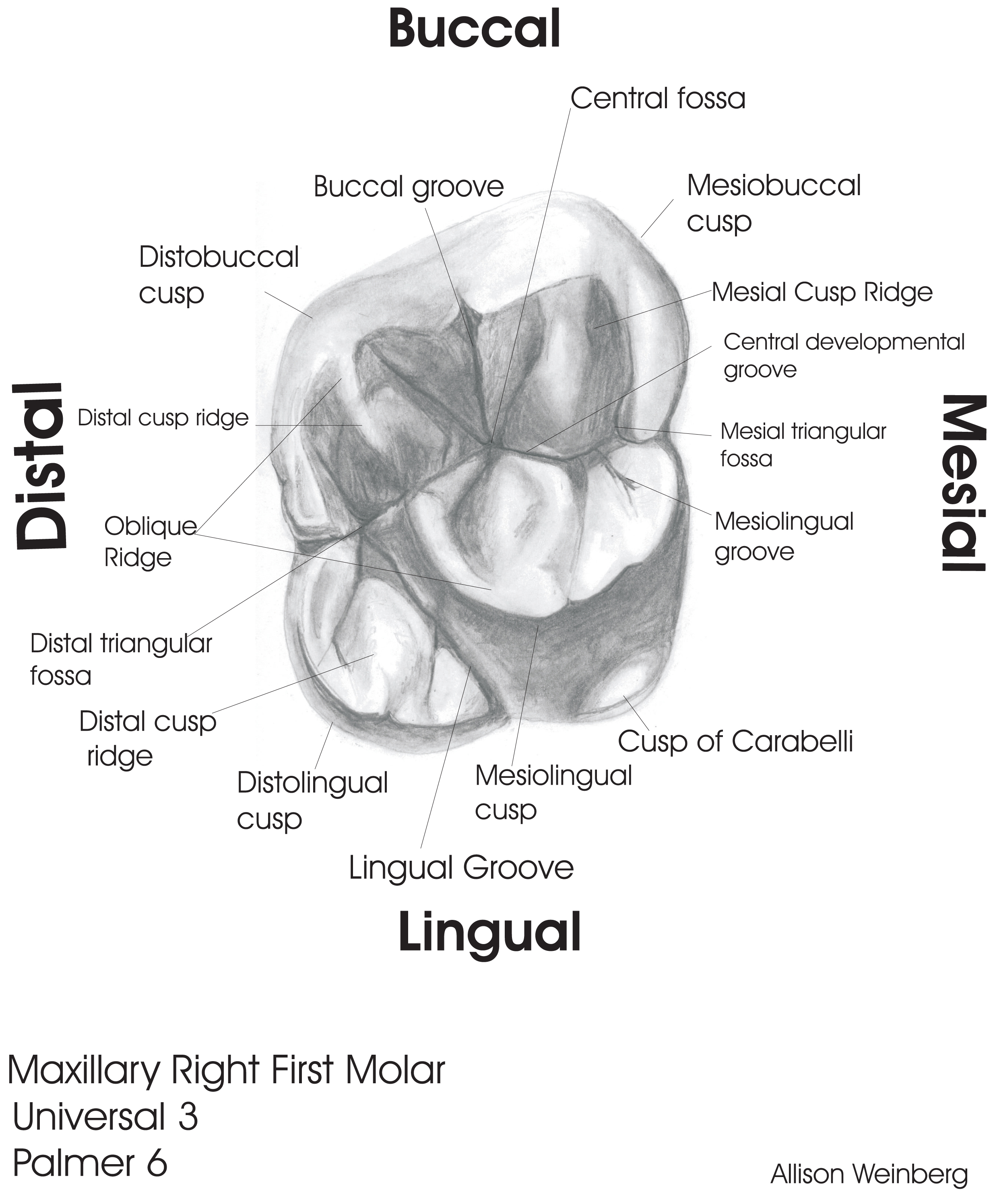
Sample Drawings Tooth Morphology
The present chapter is proposing a detailed and illustrated description of dental morphology of permanent dentition. The main topics are related to nomenclature, age of emergence, a description of teeth's tissues (pulp, dentin, enamel, and cement), and morphology of all permanent teeth. The teeth are multifunctional appendages that essential in basic human functions, like eating and speech. Teeth are composed of multiple unique tissues with varying density and hardness that allows them to tolerate the significant forces and wear of mastication. They are attached to the maxilla (upper jaw) and the mandible (lower jaw) of the mouth. Dental anatomy Dental anatomy is a field of anatomy dedicated to the study of human tooth structures. The development, appearance, and classification of teeth fall within its purview. (The function of teeth as they contact one another falls elsewhere, under dental occlusion .) Use tooth morphology to predict dietary preference and ecological function. Overview In this lab, we will study the evolution of the tetrapod feeding apparatus with a focus on tooth morphology. Teeth vary in structure and attachment to the skeleton depending on the animal's diet and feeding mechanism.

The Different Types of Teeth Mortenson Family Dental
Incisors. These are the chisel-shaped teeth that help you cut up food. Canines. These pointy teeth allow you to tear and grasp food. Premolars. The two points on each premolar help you crush. Tooth anatomy (anterior view) The tooth anatomy is an interesting but challenging topic that demands the respect of any health science student or professional. The human teeth are quite special because they grow twice during a lifespan, are essential structures for the mechanical digestion of food, and support certain facial features. The macromorphology of human teeth is of great importance to the scientific disciplines of anatomy, dentistry, physical anthropology, and forensic medicine. Morphological studies concerning the interrelation between the form and the function of teeth are essential to the understanding of ontogenetic and phylogenetic processes. The tooth can be divided into two main parts: the crown and the root. An indentation (cervical line) encircles the tooth marking a distinction between the crown and the root. The crown is the part that emerges from the maxillary or jaw bone, has a hard and translucent surface (enamel); the root anchors the tooth to the alveolar bone and provides blood and nerve supply through the apical foramen.
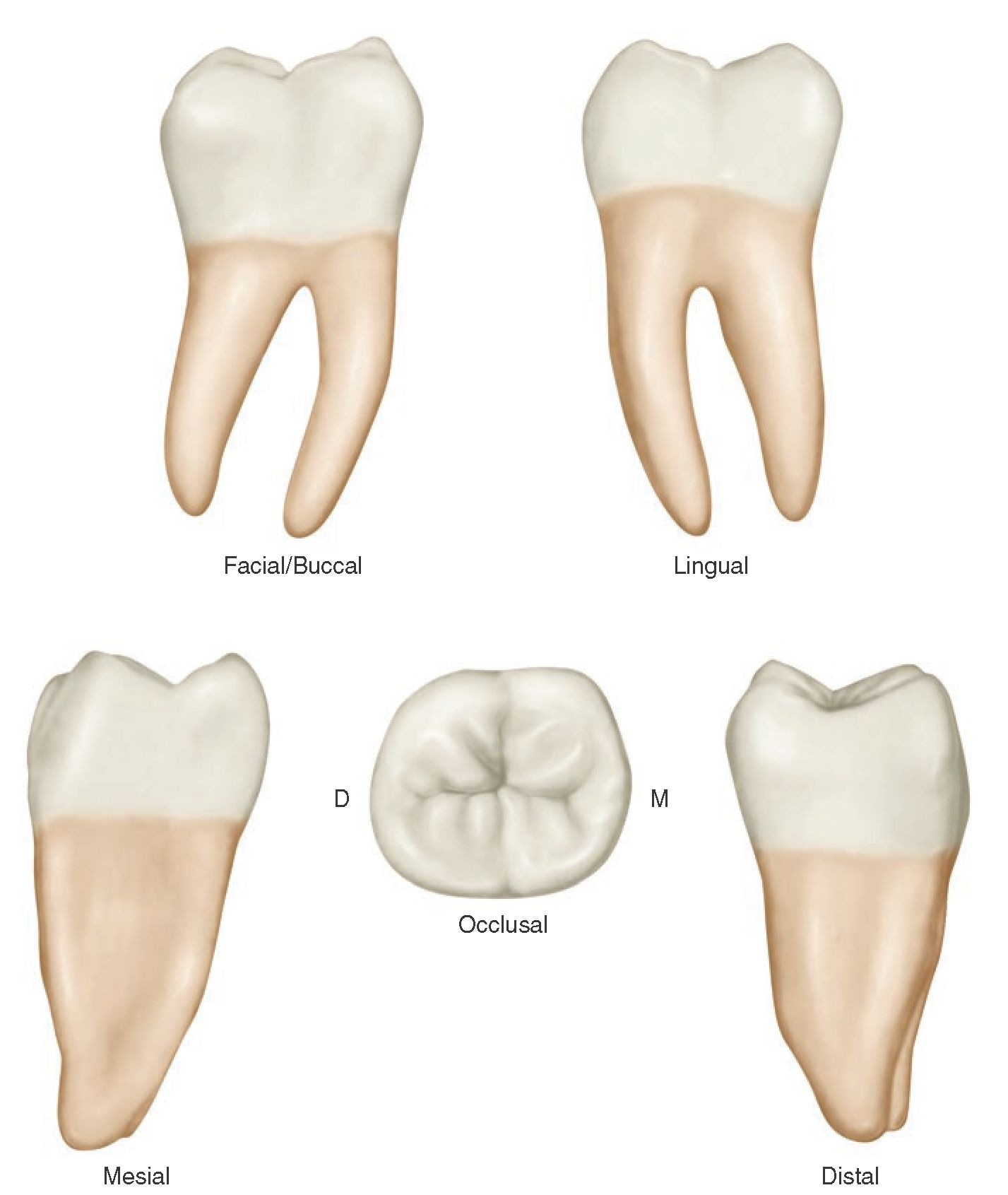
Anatomy Of A Molar Tooth Anatomical Charts & Posters
The size of teeth crowns, number of roots, and morphology of occlusal surfaces, including cusps, interconnecting depressions, grooves, or pits, may differ among populations and genders [ 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 ]. There are two sets of teeth during lifetime, the deciduous teeth and the permanent teeth. Synopsis. This article provides a brief review of recent investigations concerning the structure and properties of the tooth. The last decade has brought a greater emphasis on the "durability" of the tooth, an improved understanding of the fatigue and fracture behavior of the principal tissues and their importance to tooth failures.
Types of teeth Number of teeth Summary Teeth names include incisors, canines, premolars, and molars. Each type of tooth has a specific function, including biting, chewing, and grinding up. Humans have two sets of teeth during their lifetime: the initial deciduous (primary) teeth and the successive permanent (secondary) teeth. [1] There are typically 20 deciduous teeth divided evenly across the maxilla and mandible.
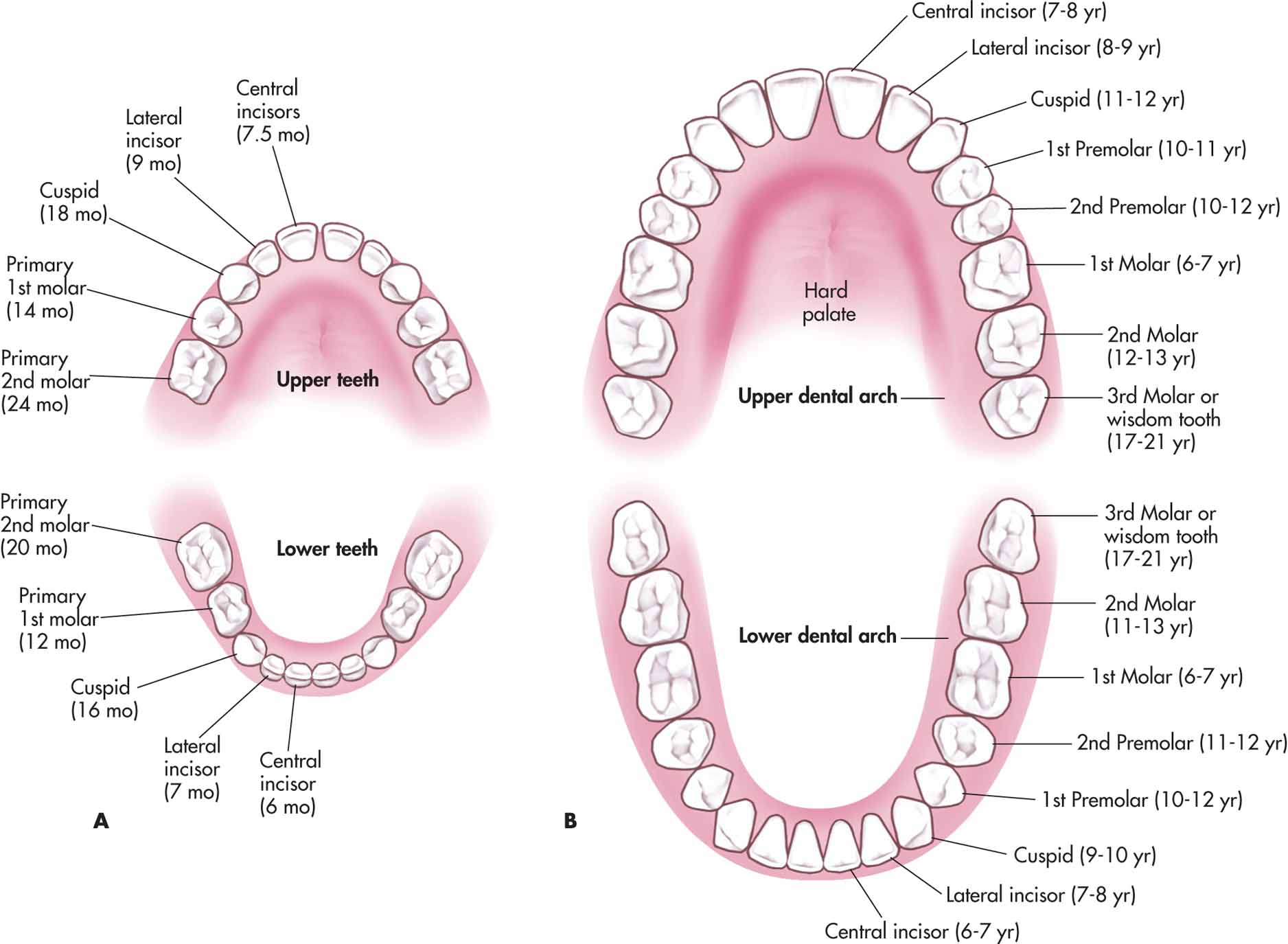
Deciduous And Permanent Teeth and Structure of a Tooth Earth's Lab
). Innovative teaching methods are currently being incorporated into the teaching of tooth morphology (Nagasawa et al. ) in order to provide visualization and 3D comprehension of the dental morphological anatomy (Mitov et al. ). However, extracted teeth are still preferred for learning tooth morphology and also for examinations (Suh et al. Tooth types The 4 main tooth types are incisors, canines, premolars, and molars. Premolars are only present in the permanent dentition. Incisors There are 8 incisors in both the permanent and primary dentition, with four in each dental arch. The two types are the central incisors and lateral incisors.




