Muscular system of the horse Types of muscle There are 3 types of muscle, all found within the equine: Skeletal muscle: Contraction of these muscles leads to the muscle pulling a tendon, which in turn pulls a bone. Moving a bone results in either flexing or extending a joint. 19. Understanding how muscles work is one of the most fundamental concepts that can influence how we ride and train our horses. Movement is created by the skeletal muscles pulling on the bones to operate the joints. Every bone is moved by a muscle. The muscles cross either one joint or several. The longissimus dorsi.

animal muscles Cerca con Google Horse anatomy, Horse behavior, Horses
Understanding the Equine Muscular System November 24, 2021 Posted by Stacey Oke, DVM, MSc The horse's body possesses approximately 700 muscles that control movement. By understanding how. In this article, we will also speak about the horse's skeleton and muscles. You should be able to draw a square on a proportionally built horse - however, as we prove later on while discussing each body part, in reality, horses differ from one another and usually stray from that ideal proportions. Muscles are tissues in your horse's body that allow your horse to walk, gallop, jump, and canter. In essence, horse muscles are the foundation of all movement, so it's key that you learn how to maintain animal muscle health if you want your horse to live his best life. Unfortunately, horses can develop muscle diseases known as myopathies. Skeletal muscles are responsible for posture and movement. They are attached to bones and arranged around the joints. Smooth muscle helps facilitate many involuntary processes in the body, such as the flow of blood (by surrounding arteries) and the movement of food along the digestive tract.
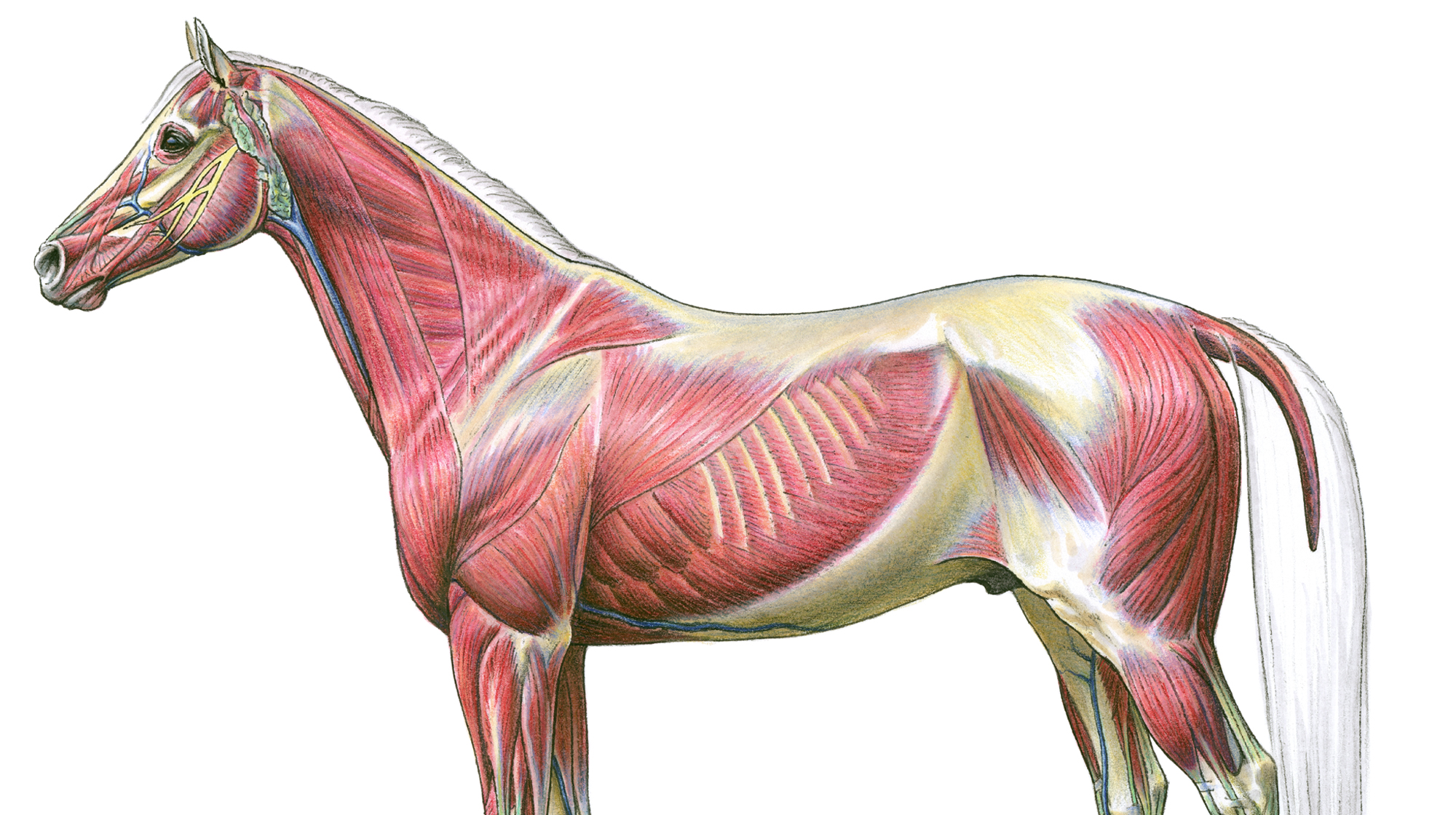
Equine Muscles & Tendons
The horse's musculoskeletal system consists of the bones, cartilage, muscles, ligaments, and tendons. Their primary function is to support of the body, provide motion, and protect vital organs. There are 205 bones in the horse's skeleton. Isometric contraction In movement a horse uses all three types of muscle contraction, but it's this isometric muscle activity that plays a huge role in the 'the 'arrow in a bow' concept. Head and Neck - Horse Muscle Anatomy. The muscles of the head and neck allow the horse to flex, extend and tilt its head. Key muscles include: Temporalis - raises the jaw. Masseter - closes the jaw. Sternomandibularis - opens the mouth by lowering the jaw. Brachiocephalicus - flexes the head and neck; turns the head side to side. Muscles of the forehand. Opens and closes the jaw. Allows chewing. movement. Too strong a. forward, raises it in collection, swings the foreleg forward. rein contact stops free forward movement. Moves the head and neck. Over developed in ewe or bull necked horses, difficult to get into a relaxed shape.

A4 Veterinary Poster Muscles of the Horse (Animal Anatomy Picture Pathology) Equine
The four abdominal muscles, the Rectus Abdominus, Transverse Abdominus, and Internal and External Obliques, do much more than support the back. These four muscles compress the abdomen to aid in moving the contents of the various visceral organs through the body efficiently. There are 3 types of muscles: Skeletal muscles. They are the ones connecting the different bone segments to each other. Smooth muscles. These muscles are not voluntarily controlled. Such as: digestive tract muscles, the esophagus and the blood vessels' wall. Cardiac muscles. This is an intermediary between the two previous types of muscles.
Anatomy Pelvic hind limb bears 40-45% of the weight and provides the majority of propulsion for locomotion. Bones Os coxae The Tuber coxae and tuber sacrale both palpable Tuber ischii is located underneath the hamstrings Femur Greater trochanter has a cranial and caudal part for gluteal attachments (deep & middle) There are several types of muscles in the horse: the cardiac muscle (myocardium), the smooth muscles (which manage breathing, digestion, and blood circulation) and the striated muscles which connect the different bone segments together. Throughout its growth, the horse will develop its different muscles. They can be composed of type I fibers.
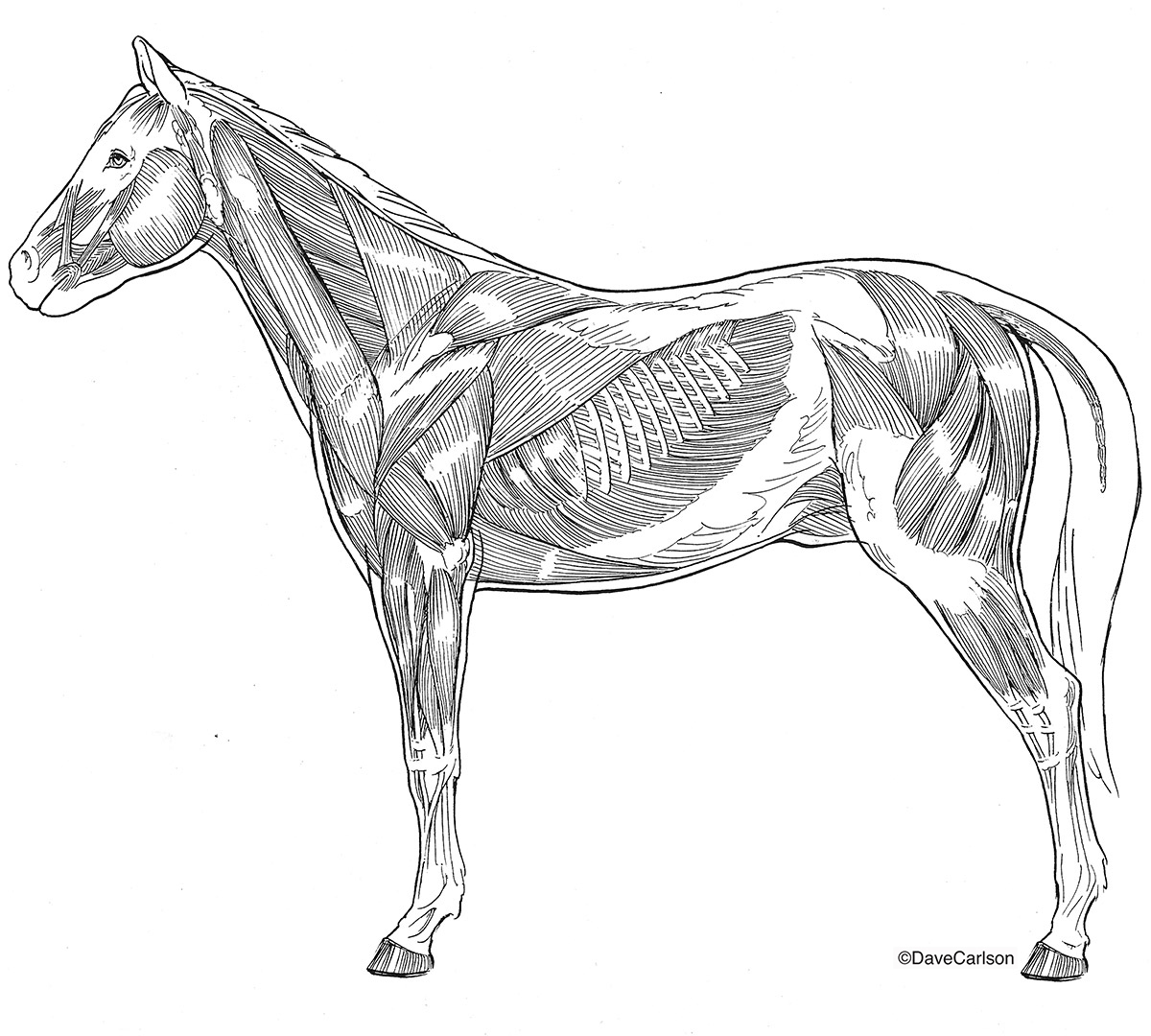
Horse / Equine Superficial Muscles Carlson Stock Art
Propulsive locomotor muscles, such as the gluteus, contain a predominance of fast-twitch type 2 muscle fibers, with the highest density of type 1 fibers located deeper within the muscle. In general, Quarter Horses and Thoroughbreds have the highest percentage of fast-twitch muscle fibers, 80-90%; Standardbreds have an intermediate number, 75%. Equine Spine and Head Anatomy Introduction Equine anatomy refers to the gross and microscopic anatomy of horses and other equids (donkeys, and zebras). This page introduces the Anatomy of Equine Spine and Head. + This is a course page funded by Plus online learning




