Introduction Stability in the Lumbo-Pelvic Region 3Anterior Oblique Sling (AOS) 4Posterior Oblique Sling (POS) 5Deep Longitudinal Sling (DLS) 5.1Complications and Treatment 6Lateral Sling (LS) 7How Do These Link to Low Back Pain? Effects on the Passive System Pain, Muscles and Motor Control 8Conclusion 9References Introduction[ edit | edit source] Oblique Sling Exercise Progressions and Assessment - [P]rehab This article will cover a brief overview of the oblique sling systems as well as sling exercise progressions and assessment!
Posterior Oblique Sling Enhancing Swimming Performance
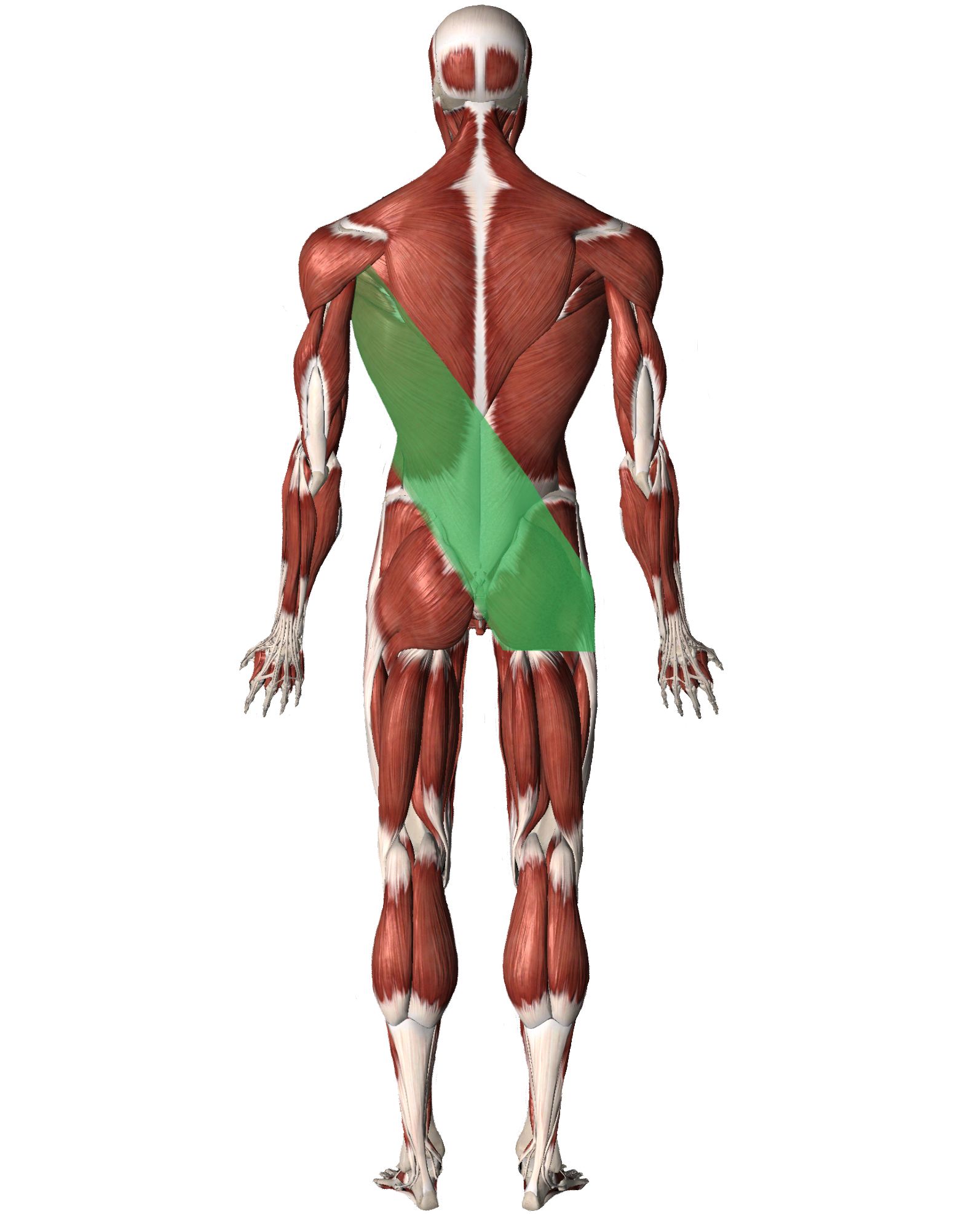
Ligaments that play an important role in SIJ stability are the iliolumbar ligament (ventral side), the posterior sacroiliac ligaments, interosseus ligaments, sacrotuberous and sacrospinous ligaments. The pubic ligaments, the anterior sacroiliac ligaments and the dorsal side of the iliolumbar ligaments have the least effect on pelvic stability. Although there are many muscles groups involved from head to toe, and it can vary depending on whether we're relying more on the posterior or the anterior oblique sling, these slings rely directly and indirectly on the upper body (shoulders, pectoral, and lats), on one side of the body, working with the contralateral or opposite hip. The posterior oblique sling consists of the latissimus dorsi that extends diagonally through the thoracolumbar fascia and blends with fibres of the opposite gluteus maximus. The superficial fibres of the gluteus maximus then blend with the superficial fibres of the TFL and ITB on the side. The posterior oblique sling consists of the latissimus dorsi muscle, the opposite side gluteus maximus muscle, and the interconnecting thoracolumbar fascia. This sling crosses at the level of.

Posterior Oblique Sling Exercise Progression YouTube
The Posterior Oblique Sling (POS) couples the glute max with the opposite lat dorsi. Through the thoracolumbar fascia, this sling stabilises the sacroiliac joint (SIJ) and creates stability at the back of the pelvis, especially during single-leg propulsion. The Posterior Oblique Sling is made up of: The latissimus doors, The contralateral gluteus maximus, and The inter-connecting thoracolumbar fascia It provides stability and force transference for the body allowing kinetic energy to be released for efficient locomotion. The posterior oblique sling consists of the latissimus dorsi muscle, the opposite side gluteus maximus muscle, and the interconnecting thoracolumbar fascia. This sling crosses at the level of the lumbosacral junction and provides what is known as force closure to the sacroiliac (SI) joint. [Conclusions] According to the results of this study, increase in muscular activation from the direction of muscular fiber and posterior oblique sling seems to be an important factor that influencontralateral crector spinae on muscular activation of POS. Key words: Posterior oblique sling, Electromyography, Prone hip extension Go to: INTRODUCTION

Posterior Oblique Sling & Hamstring Stretch Stick Mobility Exercise YouTube
1) Anterior oblique sling (AOS) Muscles: external oblique, internal oblique, contralateral hip adductor, abdominal fascia. Function in Sport: - Increased firing in the transition between walking. and running. - Important for increasing speed and acceleration. - Prominent in tennis, hockey, soccer, basketball: Agility. There are four primary fascial slings- including the anterior (oblique) sling, posterior (oblique) sling, deep longitudinal sling, and lateral sling (as shown left to right in the graphic above).
TIMESTAMPS ⏱0:00 Intro1:18 Posterior/Anterior Oblique Sling Assessment 3:34 Bird Dog Row 4:15 Reverse Lunge Shoulder Pulldown-Band 5:42 Standing Chop Band 6:. The posterior oblique subsystem contributes to propulsion when we walk, run or sprint. It is also a key contributor to rotational forces such as swinging a golf club or baseball bat, or.

Posterior Oblique Sling Prog 1 YouTube
Posterior Oblique Sling Includes the latissimus dorsi,the contralateral/ opposite gluteus maximus and biceps femoris. This sling provides stability by simultaneous contraction of the latissimus dorsi and contralateral gluteus maximus. They also act on the sacrotuberous ligaments thereby compressing the SI joint. Longitudinal Sling Learn to understand the oblique sling subsystem. Best way to train the neural-pathways is on the ground so spine and nervous system can feel supported. Work.




