The CPU has no power; RAM is refreshed; the system is in a lower power mode than S1. S3 Sleep (Standby) System appears off. The CPU has no power; RAM is in slow refresh; the power supply is in a reduced power mode. This mode is also referred to as 'Save To RAM'. S4 Hibernate System appears off. Essentially the difference between a S1,S2 and S3 safety shoe are the degrees of protection the boots provide to the wearer. Please check out this guide to learn more about which safety boot is right for you. safety shoes manufacturer One professional safety shoes company that produce different type of safety shoes and work boots in China.

Pin on heart sounds
The sacrum is the triangle-shaped bone at the end of the spine between the lumbar spine and the tailbone. The sacral spine consists of five segments, S1 - S5, that together affect nerve communication to the lower portion of the body. It is important to understand that the spinal cord does not extend beyond the lumbar spine. The sacral plexus begins as the anterior fibres of the spinal nerves S1, S2, S3, and S4. They are joined by the 4th and 5th lumbar roots, which combine to form the lumbosacral trunk. This descends into the pelvis to meet the sacral roots as they emerge from the spinal cord. Fig 1 - The spinal cord outflow at each vertebral level. S1 refers to the first sacral bone, S2 to the second sacral bone, and so on. S1 is at the top and S5 is towards the bottom. Each number corresponds with the nerves in that part of the spinal cord. S1 nerves affect the hips and groin. S2 nerves affect the back of the thighs. S3 nerves affect the medial buttock area. What Are The Four Heart Sounds? Medical Editor: William C. Shiel Jr., MD, FACP, FACR Definition Function Lub Dub Sounds What are heart sounds? Using a stethoscope to assess different sounds the heart makes is an important diagnostic tool.

Motor duty and it's types explained.S1,S2,S3,S4 meaning. YouTube
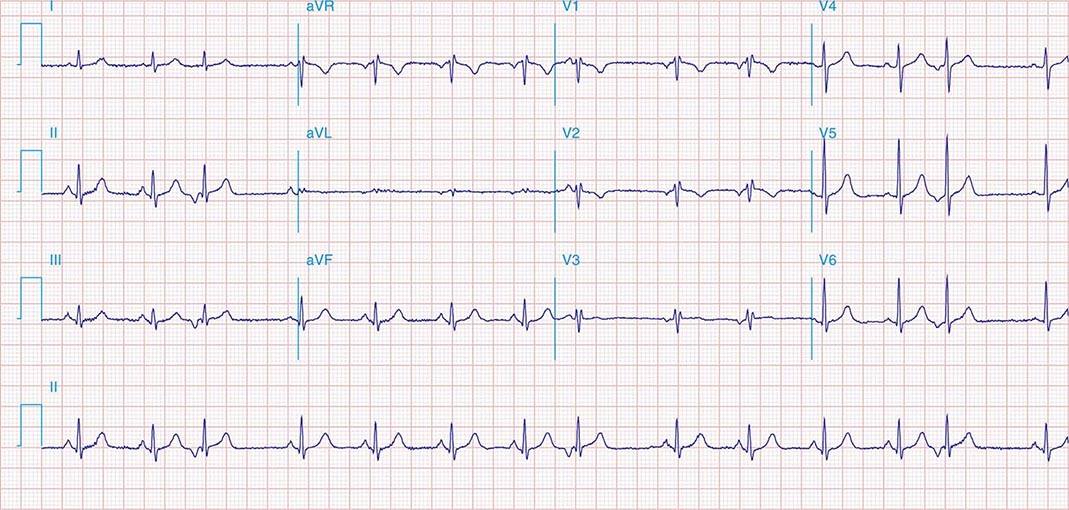
The sacral plexus is a network of nerves formed by the lumbosacral trunk (L4, L5) and sacral spinal nerves (S1 - S4). The sacral plexus is located on the posterior pelvic wall, posterior to the internal iliac vessels and ureter, and anterior to the piriformis muscle. The S1, S2, S3 Syndrome in Chronic Pulmonary Disease E. A. was a 50 -year-old white man with severe far-advanced emphysema. His electrocardiogram is an excellent example of the S 1, S 2, S 3 syndrome. Note that there is a prominent S wave in Leads 1, 2, and 3 and the S waves are equal in duration and magnitude to the preceding R waves. A combination of 5 nerve roots that exit from inside the lower lumbar and upper sacral spine—L4, L5, S1, S2, and S3—forms the sciatic nerve. These 5 nerves group together deep in the buttock, near the front surface of the piriformis muscle, and combine to form the single large, thick sciatic nerve. 1 Davis D, Vasudevan A. Sciatica. Act as a shock absorber for the spine and control the transmission of forces from the lower body into the spine, such as gravitational forces and forces transmitted upward during standing or walking. 2 Wong M, Sinkler MA, Kiel J. Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis, Sacroiliac Joint. [Updated 2020 Aug 10]. In: StatPearls [Internet].

Heart Sounds S1 S2 S3 S4 Pearson+ Channels
Sound is that of S1-S2 at rest ("out") and S1-A2-P2 with inspiration ("in"). S2 splits with inspiration because intrathoracic pressure decreases, drawing more blood into the right ventricle and postponing pulmonic valve closure.. Sound is that of S4-S1-S2-S3 in rapid succession. Recording provided by Jules Constant, MD. Superior gluteal nerve, formed by sections of L4, L5, and S1; Inferior gluteal nerve, formed by sections of L5, S1, and S2; Sciatic nerve, which is the largest nerve of the sacral plexus and among the largest nerves in the body, formed by sections of L4, L5, S1, S2, and S3; The common fibular nerve (formed by L4 through S2) and tibial nerves (formed by L4 through S3) are branches of the.
The sacral spinal nerve 3 (S3) is a spinal nerve of the sacral segment.. It originates from the spinal column from below the 3rd body of the sacrum.. Sacrum, showing bodies in center. Muscles. S3 supplies many muscles, either directly or through nerves originating from S3. They are not innervated with S3 as single origin, but partly by S3 and partly by other spinal nerves. This may be because the three heart sounds — S1, S2, and S3 — in quick succession create a cadence, or rhythm, like a galloping horse. Additionally, the heart sounds follow a similar galloping.
Atlas of Noninvasive Imaging Basicmedical Key
by Ali Al-Hadithi | 26 Jan, 2021 Cardiology Cardiovascular Examination S1 and S2 Heart Sounds, Extra Heart Sounds Login Basics of Heart Sounds - S1 and S2 heart sounds There are 2 main heart sounds that can be heard during auscultation: S 1 and S 2, also affectionately known as 'lub' and 'dub' respectively. S1 is one of the sounds that the heart produces as blood passes through the chambers when the valves open and close. Doctors may refer to the S1 as "lub" and the second heart sound (S2) as.




