In geometry, symmetry is defined as a balanced and proportionate similarity that is found in two halves of an object. It means one-half is the mirror image of the other half. The imaginary line or axis along which you can fold a figure to obtain the symmetrical halves is called the line of symmetry. In Mathematics, symmetry means that one shape is identical to the other shape when it is moved, rotated, or flipped. If an object does not have symmetry, we say that the object is asymmetrical. The concept of symmetry is commonly found in geometry. What is Symmetry in Math?
Fun with Mathematics Symmetry in Art and Nature ( Part 1 of 3) Xplore & Xpress
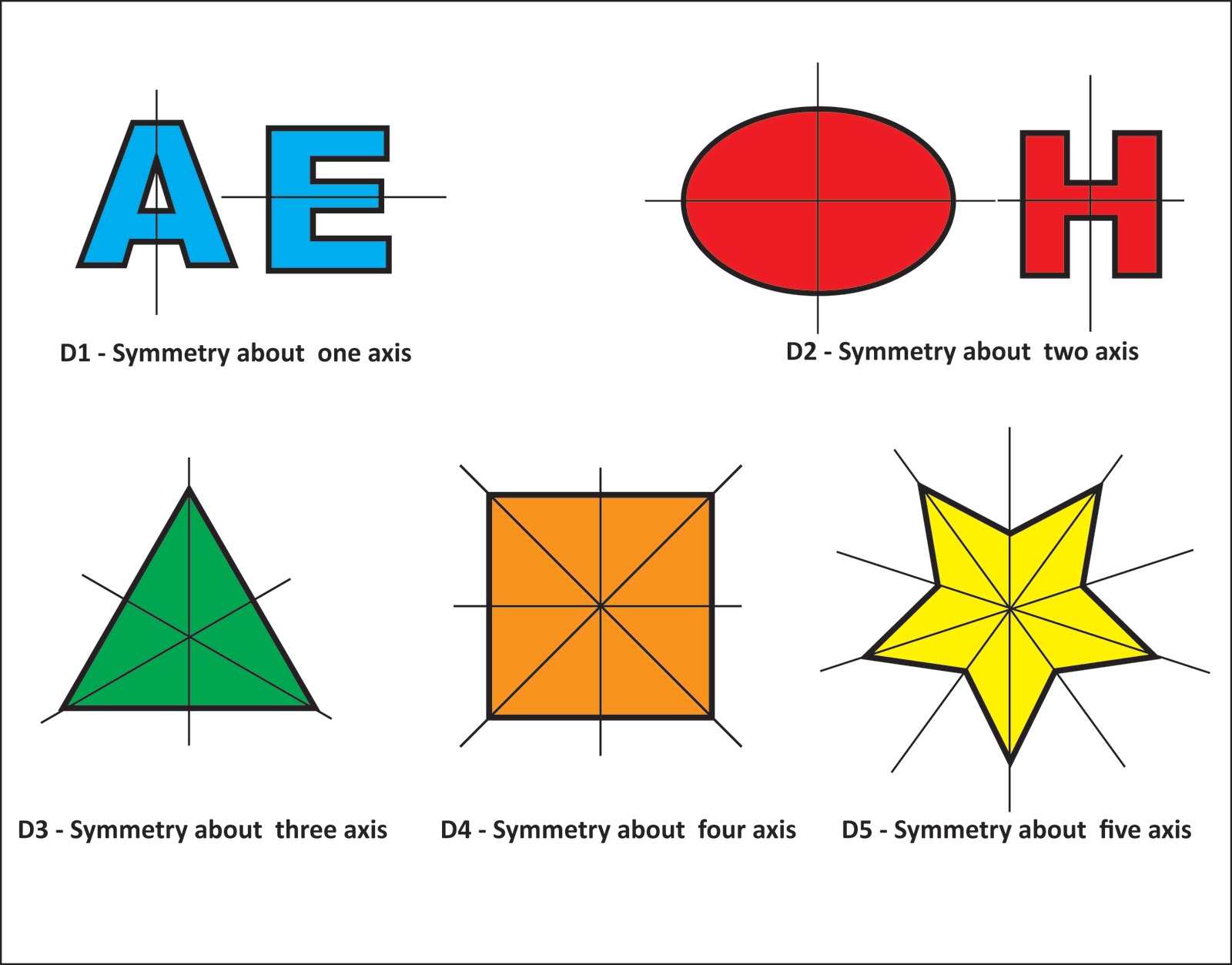
A vertical line that divides an object into two identical halves is called a vertical line of symmetry. That means that the vertical line goes from top to bottom (or vice versa) in an object and divides it into its mirror halves. For example, the star below shows a vertical line of symmetry. The Horizontal Line of Symmetry To identify lines of symmetry in a pattern In this lesson, we will learn to recognise patterns and how they repeat. We will continue to explore what symmetry is and how to recognise lines of symmetry in 2D shapes and patterns containing these shapes. We will continue to develop strong mathematical language about shape, symmetry and pattern. Symmetrical patterns have segments that repeat but instead of repeating in a line, the segments are the same when flipped, folded, or rotated. Butterflies have mirror symmetry—the butterfly wings match when folded along a line through the middle of the butterfly. Snowflakes have mirror symmetry and rotational symmetry. For a geometric object, symmetry is a correspondence between pairs of points that are equally positioned about a point, line or plane. Explorations Begin learning about symmetry with: Symmetric Figures Exploration Symmetry of Stars and Polygons Exploration Symmetry and Celtic Knots Exploration

Symmetry Definition Solved Examples Geometry Cuemath
A line of symmetry is a line that you can draw across a shape and divide it into two mirror-images. That is to say, each half of the shape is the same, but looks like its been flipped from the other. You can also think of a line of symmetry as a line that you can draw, that when you fold the shape over the line both edges would line up exactly. Symmetry is the underlying mathematical principle behind all patterns and is important in art (used in architecture, pottery, quilting and rug making), mathematics (relating to geometry, group. Tessellation. A tessellation is a design using one ore more geometric shapes with no overlaps and no gaps. The idea is that the design could be continued infinitely far to cover the whole plane (though of course we can only draw a small portion of it). See the photos below [1] for examples. This book encompasses a wide range of mathematical concepts relating to regularly repeating surface decoration from basic principles of symmetry to more complex issues of graph theory, group theory and topology. It presents a comprehensive means of classifying and constructing patterns and tilings. The classification of designs is investigated and discussed forming a broad basis upon which.

Tales From a K1 Classroom Symmetry with Pattern Blocks
Symmetry is a type of invariance: the property that a mathematical object remains unchanged under a set of operations or transformations. [1] Given a structured object X of any sort, a symmetry is a mapping of the object onto itself which preserves the structure. This type of symmetry is less common but adds complexity to patterns and designs. Point Symmetry. Point symmetry, often known as central symmetry, occurs when an object looks the same when rotated by 180 degrees around a central point. The figure retains its shape and orientation after this rotation. This type of symmetry is found in various.
The 17 pattern types from Andreas Speiser, arranged in the order of the Artlandia symmetry panel. This unpretentious diagram is unbeatable in its simplicity. You will notice how skillfully Speiser puts straight line segments to play up reflection axes, adds smallish ticks to highlight rotations—or longer ticks to emphasize reflections or. 1. Architecture - Many Islamic buildings such as mosques feature beautiful symmetrical patterns in their decorations. 2. Fabrics - Many rugs, curtains and items of clothing feature symmetrical patterns. 3. Nature (Animals) - Butterflies are an example of symmetrical patterns that occur naturally. Both wings of a butterfly are identical. 4.

21 Unbelievable Photos Of Symmetry In Nature Geometric nature, Geometry in nature, Fractals in
Symmetry means there's harmony in something's dimensions, proportions and arrangement. It provides a sense of harmony and balance. It is portrayed through the distribution of building components and within the spaces between each element. An axis or central line is usually created, then patterns and replicas are created on either side. Rotational symmetry (or radial symmetry) is when an object is rotated in a certain direction around a point. Rotational symmetry in nature is found in everything from the petals of a flower to the topside view of a jellyfish. In art and design, rotational symmetry can be used to portray motion or speed. Even on a static medium, rotational.



