Blake S 6 years ago Experimental probability is the results of an experiment, let's say for the sake of an example marbles in a bag. Experimental probability would be drawing marbles out of the bag and recording the results. Theoretical probability is calculating the probability of it happening, not actually going out and experimenting. 1. Theoretical probability Theoretical probability is the likelihood that an event will happen based on pure mathematics. The formula to calculate the theoretical probability of event A happening is: P (A) = number of desired outcomes / total number of possible outcomes

PPT Experimental Probability Vs. Theoretical Probability PowerPoint Presentation ID5448081
Part 1: Flipping a coin question a A fair coin has 2 sides (heads and tails) that are equally likely to show when the coin is flipped. What is the theoretical probability that a fair coin lands on heads? P ( heads) = question b Dave flipped a coin 20 times and got heads on 8 of the flips. 1. Use the table below to determine the probability of each number on a number cube. Let's Review: Theoretical probability is what we expect to happen, where experimental probability is what actually happens when we try it out. Theoretical and Experimental Probability What Is Theoretical Probability? Theoretical probability is based on what is expected to happen, or a theory, using reasoning. It is based on. Experimental Probability Theoretical Probability Prediction Solved Examples Frequently Asked Questions What is Probability? The chance of a happening is named as the probability of the event happening. It tells us how likely an occasion is going to happen; it doesn't tell us what's happening.

PPT Experimental Probability Vs. Theoretical Probability PowerPoint Presentation ID9487309
Theoretical probability is calculated using mathematical formulas, while experimental probability is based on results from experiments or surveys. In order words, theoretical probability represents how likely an event is to happen. On the other hand, experimental probability illustrates how frequently an event occurs in an experiment. Theoretical probability is the probability that is calculated using math formulas. This is the probability based on math theory. Experimental Probability Experimental probability is calculated when the actual situation or problem is performed as an experiment. Figure 4-4 shows a graph of experimental probabilities as n gets larger and larger. The dashed yellow line is the theoretical probability of rolling a four of 1/6 \(\neq\) 0.1667. Note the x-axis is in a log scale. Note that the more times you roll the die, the closer the experimental probability gets to the theoretical probability. Figure 4-4 Courses on Khan Academy are always 100% free. Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: https://www.khanacademy.org/math/cc-seventh-grade-math/cc-7th-p.
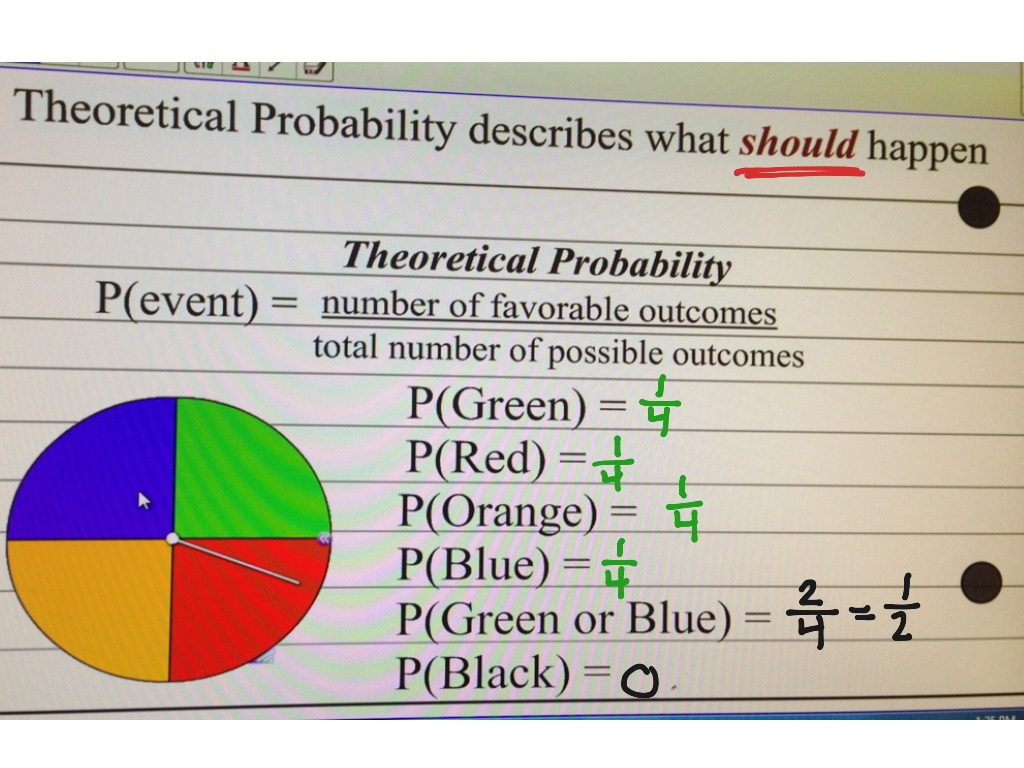
Experimental and Theoretical Probability Math ShowMe
The theoretical probability helps us get close with our prediction, but we can't know for sure until we actually spin the spinner.. I'm using the experimental probability, 4/7 probability, and so, if I'm going to do something 210 times, well, I could expect that it's going to happen 4/7 of the time. I don't know for sure that it's going to. When you are working with the probability that an event could happen, that is called theoretical probability. For example, when rolling a typical six-sided number cube, there is only one "6" on the cube and an equal chance of any number landing face up. There are other types of probability.
Experimental probability describes how frequently an event actually occurred in an experiment. So if you tossed a coin 20 times and got heads 8 times, the experimental probability of getting heads would be 8/20, which is the same as 2/5, or 0.4, or 40%. The theoretical probability of an event will always be the same, but the experimental. To calculate the experimental probability of landing on blue, we have to divide by the total number of spins. P (blue)= 3 / 20 =0.15. Therefore, for this experiment, the experimental probability of landing on blue with 20 spins is 15%. Now let's calculate the theoretical probability. We know that the spinner has 4 equal parts (blue, purple.

PPT 11.2 Theoretical and Experimental Probability PowerPoint Presentation ID2537712
What is the Difference Between Theoretical Probability and Experimental Probability? Theoretical probability is calculated when conducting an experiment is not possible. It gives a fair idea of the likelihood of occurrence of an outcome. In contrast, experimental probability is calculated based on experiments that have been conducted in the past. The experimental probability = 8/50 = 16%. . 2) Theoretical probability is based upon what is expected when rolling two dice, as seen in the "sum" table at the right. This table shows all of the possible sums when two dice are rolled. The theoretical probability of rolling an 8 is 5 times out of 36 rolls.




