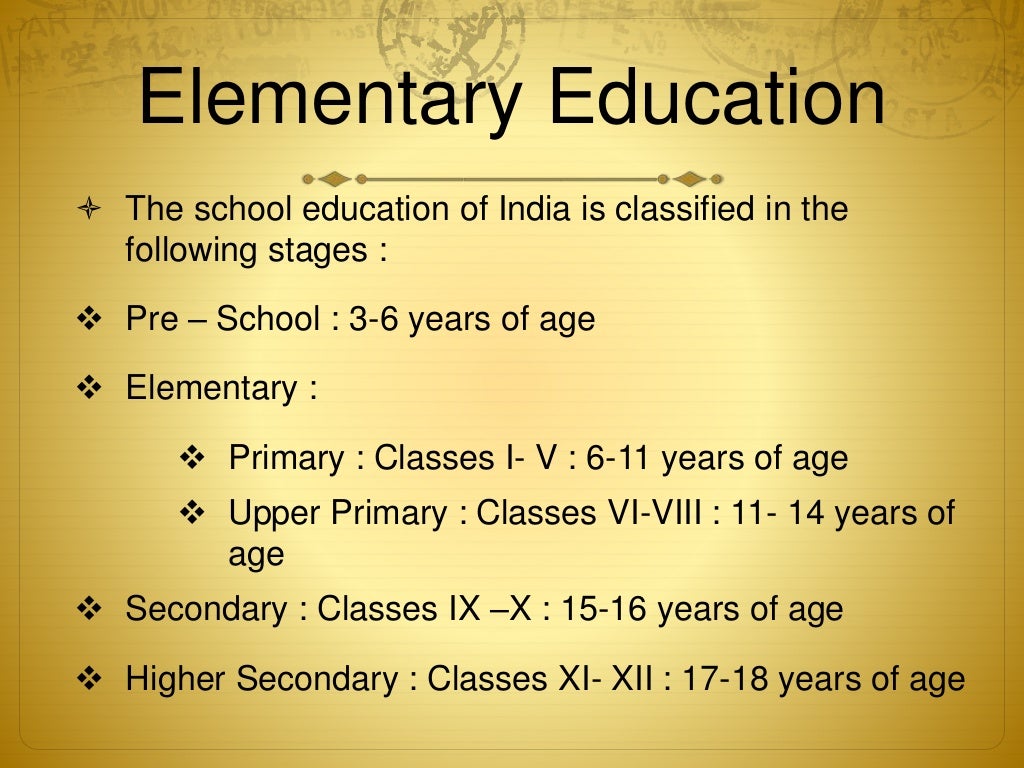
UNIVERSALIZATION OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION IN INDIA The first aspect is the accessibility of elementary education to cent percent children in the age group 6-14 years. It is directed in our constitution to universalize elementary education within a period of 10 years from the commencement of the Constitution (26 Jan., 1950). Universalization of elementary education refers to the enrollment, retention, and universal access to qualitative education for children up to the age of 14. Elementary education is a Fundamental Right. The provisions included in the Constitution of India emphasize offering elementary education to all children.

Universalisation of Elementary Education UEE Lecturer Santosh YouTube
Universalization of Elementary Education: Challenges, Issues and Efforts Parvaiz Ahmad Dar Central University of Kashmir https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6594-3099 DOI: https://doi.org/10.51611/iars.irj.v11i2.2021.165 Keywords: Education, Girls Education, School, Primary Education, Enrolment, Elementary Education Abstract UNIVERSALIZATION OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION: CHALLENGES, ISSUES AND EFFORTS IARS' International Research Journal, vol. 11, núm. 2, 2021 International Association of Research Scholars, Organismo Internacional Disponible en: https://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=663872670004 Far from being smooth, the journey of Universalisation of Elementary Education (UEE) in India has, since Independence, been punctuated by more than a dozen instances of failure to achieve targets set up every time. Universalization of Elementary Education: Challenges, Issues and Efforts CC BY 4.0 Authors: Parvaiz Ahmad Dar Abstract The Indian education system is perhaps the largest system in the world.

Universalisation of Elementary Education Policies and Programmes Neelkamal Publications Pvt. Ltd
The success of the primary education system has a direct bearing on the upper primary, non-formal and adult and continuing education sectors; an efficient primary education system is expected to contribute significantly to total literacy: an appropriate rise in literacy levels improves the functioning of other systems of education. Effective delivery of primary education contributes to. The candidature of primary education is picked up as a policy priority. International agencies too showed interest in giving aid and or soft loans. The bureaucracy in India is too eager to accept such aid. One of the main programmes is stepping up literacy. Universalisation of elementary education in India is earmarked as a policy. The literacy 'Education for all campaign'), or SSA, is an Indian Government programme aimed at the universalisation of Elementary education "in a time bound manner", the 86th Amendment to the Constitution of India making free and compulsory education to children between the ages of 6 and 14 (estimated to be 206 million children in 2001) a fundamental right (. Problems of Uiversal Elementary Education. The universalisation of elementary education not only means universal facilities, universal enrolment and universal retention, but also the availability of a universally high quality of teaching. This review of primary education - the facilities available, enrolment and drop-out rates, and the quality.

Universalization of elementary education...Equity in universalization of elementary education
India's programme for universalisation of elementary education, the Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA), is regarded as the largest such programme in the world. Over the last five years, impressive strides have been made in improving infrastructure, ensuring access, bringing out-of-school children into the mainstream education system and appointing. UPSC Preparation Strategy Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA) Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA) - Definition, Objectives, Significance [UPSC GS-II] What is Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA)? It is a flagship programme of the government of India, that was started in 2001, to achieve the Universalisation of Elementary Education (UEE).
Right to Education (RTE) Act is intended to provide free and compulsory elementary education to all children aged 6-14 years. This article examines key constituents of elementary education in view of the RTE Act such as current attendance rate, types of institutions, medium of instruction, neighbourhood schools, Monthly per capita expenditure on elementary education (MPCEE)and incentives. In this long effort, elementary education was elevated from being part of the Directive Principles to the status of a Fundamental Right in the Indian Constitution making the State responsible.
Universalisation of Elementary Education
Universalisation of Elementary Education (U.E.E.) is an educational term refers to make education available to all children in the age of group of 6-14 or in classes I-VII. It means the education for every child to complete the stage of Elementary or Primary education either formal or non- Universalization of Elementary Education (UEE). Since then, many programmes and mission mode projects have been launched from time to time to accomplish the goal of UEE. But still, wide gender disparities remain across the country with regard to access,.




