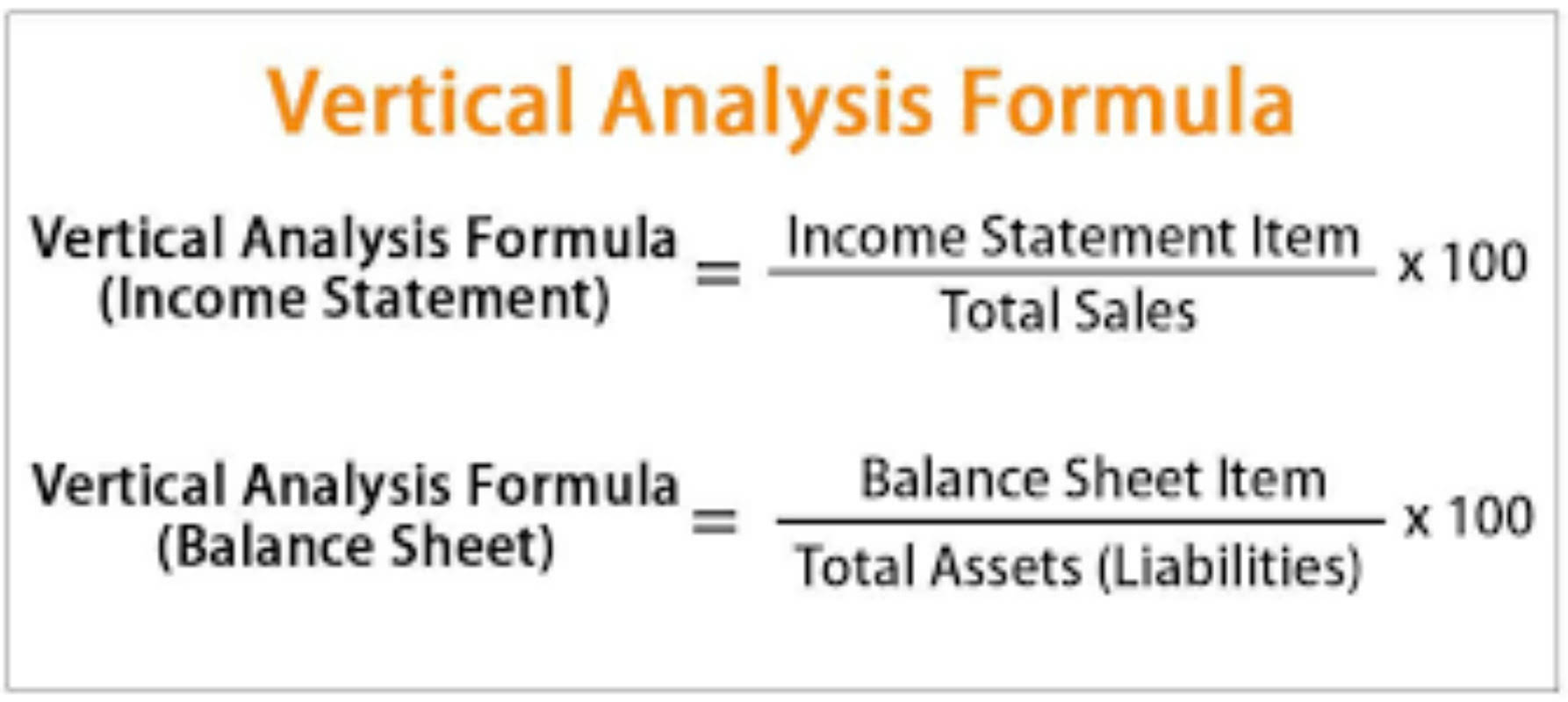
Example of Vertical Analysis Formula. Example of the vertical analysis accounting of the financial statement, which shows the total amount and percentage.. The total sales are $1000000, and the cost of goods sold Cost Of Goods Sold The Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) is the cumulative total of direct costs incurred for the goods or services sold, including direct expenses like raw material, direct. The formula to perform vertical analysis on the income statement, assuming the base figure is revenue, is as follows. Vertical Analysis, Income Statement = Income Statement Line Item ÷ Revenue. In contrast, the process is practically the same for the balance sheet, but there is the added option of using "Total Liabilities" instead of.

Vertical Analysis Double Entry Bookkeeping
The vertical analysis formula can give insight into a company's sales, expenses or revenue streams. While the formula is usually used to understand a company's finances at a glance, it can also be used for more in-depth analysis into what sort of trends a company is facing in its designated market. Here are some examples of how the formula. Vertical analysis is a method of financial statement analysis in which each entry for each of the three major categories of accounts, or assets, liabilities and equities, in a balance sheet is. Advantages of Vertical Analysis. Vertical analysis simplifies the correlation between single items on a balance sheet and the bottom line, as they are expressed in a percentage. A company's management can use the percentages to set goals and threshold limits. For example, management may consider shutting down a particular unit if profit per. Vertical Analysis Formula. The vertical analysis of financial statements is concerned with the proportion of the total amount that each line item represents. This is calculated by dividing the value for each line item by the total and multiplying by 100. % of total = (line item value / total value) * 100.
Vertical Analysis Definition and Formula BooksTime
The vertical analysis formula is known as the common-size ratio (or percentage). It is: Common-Size Ratio = (Comparison Amount/Base Amount) x 100. The comparison amount is a line item in the same. Here is a comparison of each of the formulas for vertical analysis and horizontal analysis: Vertical analysis formula = (Statement line item / Total base figure) X 100. Horizontal analysis formula = {(Comparison year amount - Base year amount) / Base year amount} X 100. However, it is important to remember that you can still use vertical. Vertical analysis is the proportional analysis of a financial statement, where each line item on a financial statement is listed as a percentage of another item. This means that every line item on an income statement is stated as a percentage of gross sales, while every line item on a balance sheet is stated as a percentage of total assets. Vertical Analysis Formula. The vertical analysis formula is a very easy-to-use, straightforward percentage formula. It is as follows: In order to use the vertical analysis equation, you need to figure out your base figure. On a business's balance sheet, you can find the relevant base figure as the company's total assets or liabilities.
Vertical Analysis Definition and Formula BooksTime
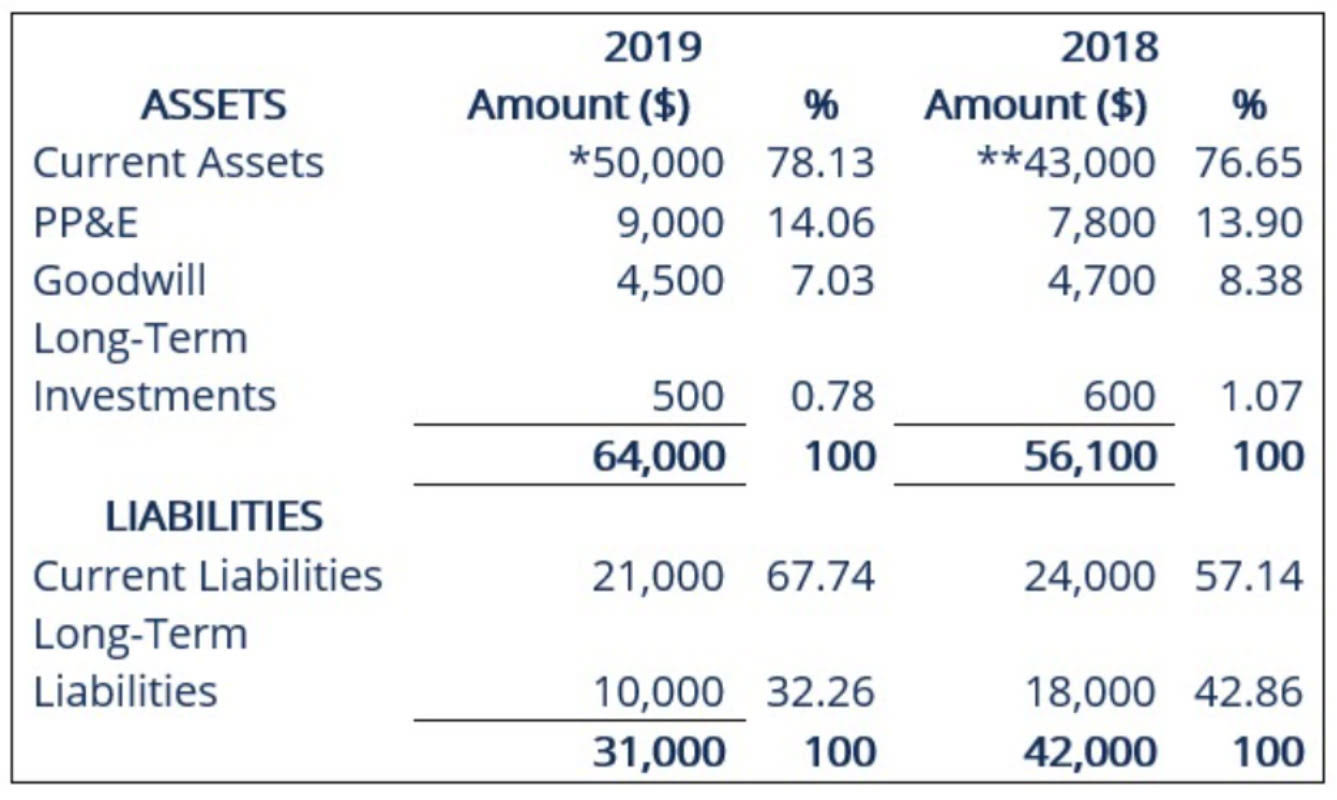
Vertical Analysis - Formula and Advantages. To calculate the percentage for the vertical analysis of financial statements - with reference to the income statement and the balance sheet, the formulas are: Vertical Analysis (Income Statement) = Item in Income Statement/Total Sales * 100. The vertical analysis also shows that in years one and two, the company's product cost 30% and 29% of sales, respectively, to produce. In year three, however, cost of goods sold spikes to 40% of.
The above-mentioned is a general formula for vertical analysis. The specific formula for the common-size balance sheet and income statement is as follows: Common-size Balance Sheet = (Concerned Item of Balance Sheet/Total Assets or Liabilities) * 100. Common-size Income Statement = (Concerned Item of Income Statement/Total Sales) * 100. Vertical Analysis Formula. The formula for vertical analysis is straightforward. You simply divide the figure for a specific line item by the total assets (for a balance sheet) or total sales (for an income statement) and then multiply the result by 100 to get a percentage. This formula can be expressed as:

What is Vertical Analysis? Formula + Calculator
Vertical analysis formula. The vertical analysis formula, also known as the common-size ratio, is a way to express each line item on a financial statement as a percentage of a base amount. Each line item's common-size ratio can then be used to conduct comparative analysis across different fiscal periods or companies, allowing for a. What is the formula for vertical analysis? (Line item/ base amount) x100 . How is vertical analysis used in financial analysis? Vertical analysis is used on a balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement and is used to understand each line item as compared to the base amount. You can use this to compare companies of different sizes.




