7 minutos. A covinha sacral pode ser uma simples depressão na pele ou estar relacionada a patologias do desenvolvimento em alguns casos. Explicamos tudo que você precisa saber e quais são as suas implicações. Alguns bebês nascem com uma pequena depressão na parte inferior das costas. Essa área também é chamada de região lombar ou. Inchaço na área. Um caroço gorduroso. Ternura em torno da região. Descoloração ao redor da covinha sacral. Uma marca de nascença ao redor da área. Tamanho da covinha maior ou maior que 5 mm. Um remendo de cabelo pela covinha sacral. Se algum destes sintomas de covinha sacral for observado, o médico recomendará um teste de imagem e, de.

Imaging Coccygeal Trauma and Coccydynia RadioGraphics
Uma covinha sacral pode estar localizada no sulco entre as nádegas. No entanto, alguns atributos podem sinalizar mais defeitos, e eles precisarão ser examinados com um ultrassom. Esses incluem: inchaço na área. marcas na pele. uma marca de nascença na área. um pedaço de cabelo pela covinha. um nódulo gordo. Definição de covinha sacral. A covinha sacral é uma anomalia congênita em que existe uma abertura na região sacral da coluna vertebral. Essa abertura pode variar em tamanho e profundidade, e pode estar presente desde o nascimento ou desenvolver-se ao longo do tempo. A covinha sacral é mais comumente encontrada na região lombar da coluna. Nos recém nascidos, é importante dar uma atenção especial a qualquer deformidade na região sacral, ou seja, na base da coluna vertebral. Algumas vezes, a criança nasce com anormalidades na pele dessa região. Uma das mais comuns é a presença de um "furinho" ou "covinha". Também há casos em que a criança apresenta manchas. Anatomy . The coccyx forms the terminal aspect of the vertebral column. Its name originated from the Greek word for 'cuckoo', as its triangular shape is thought to resemble that of a bird's beak. 2, 3 The dorsal convex aspect of the coccyx has multiple paired coccygeal articular processes, and the most superior of these are termed the coccygeal cornu, which articulate with the sacral cornu.
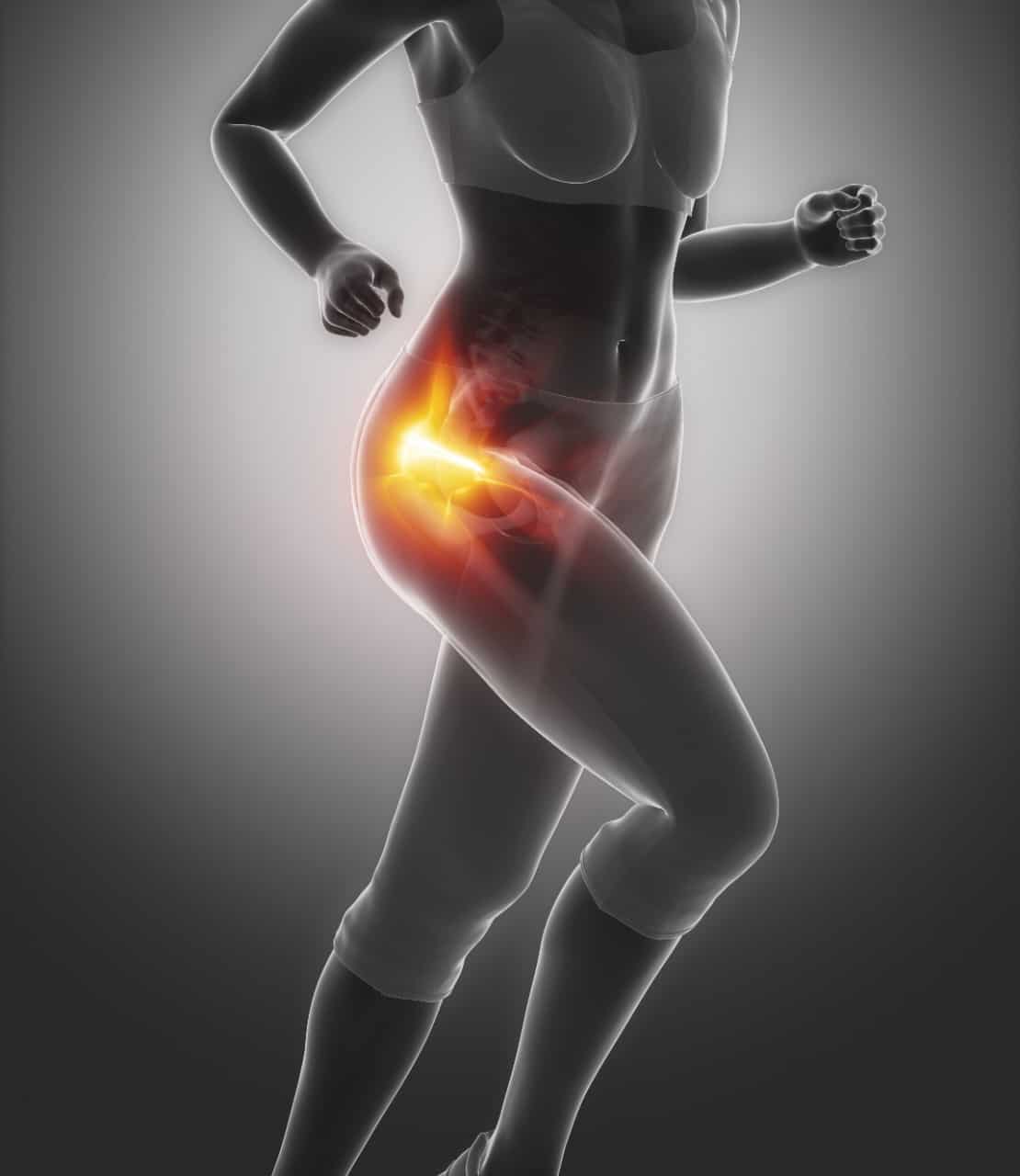
Dor sacroilíaca Conheça a sacroileíte Clínica Dr. Hong Jin Pai
These joints sit where the lower spine and pelvis meet. Sacroiliitis can cause pain and stiffness in the buttocks or lower back, and the pain might go down one or both legs. Standing or sitting for a long time or climbing stairs can make the pain worse. Sacroiliitis can be hard to diagnose. It can be mistaken for other causes of low back pain. Home treatments for sacroiliitis pain include: Pain relievers you can get without a prescription. Medicines such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) may help relieve the pain of sacroiliitis. Some of these medicines can cause stomach upset, or kidney or liver problems. Rest. This is called the sacral canal and the gap inferior to it the sacral hiatus2. The sacral hiatus is normally closed by fibrous tissue that forms the superficial sacrococcygeal ligament. On either side, it has the sacral cornua, which are an extension of inferior processes of the fifth sacral vertebra. These cornua are used to mark the area of. The sacrum is a large trilateral bone located at the base of the vertebral column serving to transfer the body weight from the trunk to the pelvis and lower extremities. Over the years, an abundance of sacral anatomical divergences has been reported, including numerical and/or morphological variations of sacral entities. The majority of these anatomical alternations has been incidentally.

Sacrum and Coccyx Anatomy
The sacral vertebrae—also called the sacral spine—consists of five sacral vertebrae bones. These bones fuse together to form the sacrum, the shield-shaped bony structure located at the base of the lumbar vertebrae (the five cylindrical bones forming the spine of the lower bank) and connected to the pelvis. The sacral vertebrae are represented by segments S1 through S5 and located between. Gross anatomy. The sacrum is an irregularly-shaped bone, shaped roughly like an inverted triangle, with its base superior and apex inferior. It is curved with an anterior concavity and posterior convexity. The sacrum consists of five fused sacral vertebral and costal segments (numbered one-to-five) that form a central sacral body and paired.
"ladder" appearance (15,16). The median sacral vein runs along the midline of the sacrum and is duplicated in up to 80% of patients (12,15,17). In cadaveric studies, the average median sacral vein size has been reported to be 2 mm. The median sacral vein drains into the CIV, almost always on the left, while the LSVs drain into the IIVs. A covinha ou fosseta sacral é uma pequena depressão na pele logo acima do bumbum do bebê, uma pequena deformidade que ocorre durante o desenvolvimento do bebê no útero. Elas podem ou não indicar uma anomalia na coluna vertebral e acarretar em anormalidades neurológicas e mau funcionamento da bexiga que é controlada pelos nervos dessa região.
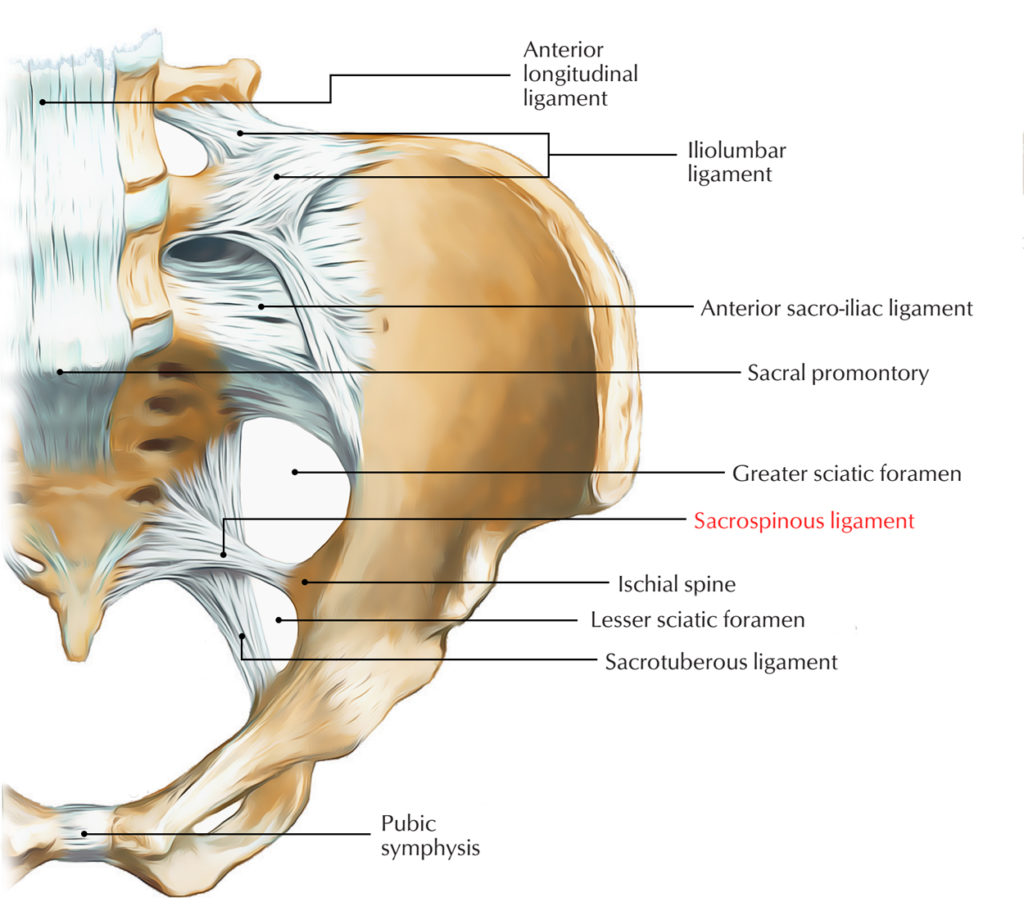
Sacrospinous Ligament Earth's Lab
The sacral plexus is a network of nerves emerging from the lower part of the spine. These nerves provide motor control to and receive sensory information from most of the pelvis and leg. A plexus is a web of nerves that share roots, branches, and functions. There are several plexi (plural of plexus) throughout the body, and the sacral plexus. Function. Associated Conditions. The sacrum is a single bone comprised of five separate vertebrae. It is shaped like an upside-down triangle and sits at the bottom of the spinal column, connecting it to the pelvis. This robust bone can endure a lot of pressure and motion.




