ABSTRACT. Immanuel Kant was an enthusiastic geographer. His geographical thought was by his philosophical system as a whole. This influence is particularly strong in the case of Kant argues that geographical space serves as a mental framework for the co-ordination of the world. The fundamental idea of Kant's "critical philosophy" - especially in his three Critiques: the Critique of Pure Reason (1781, 1787), the Critique of Practical Reason (1788), and the Critique of the Power of Judgment (1790) - is human autonomy.
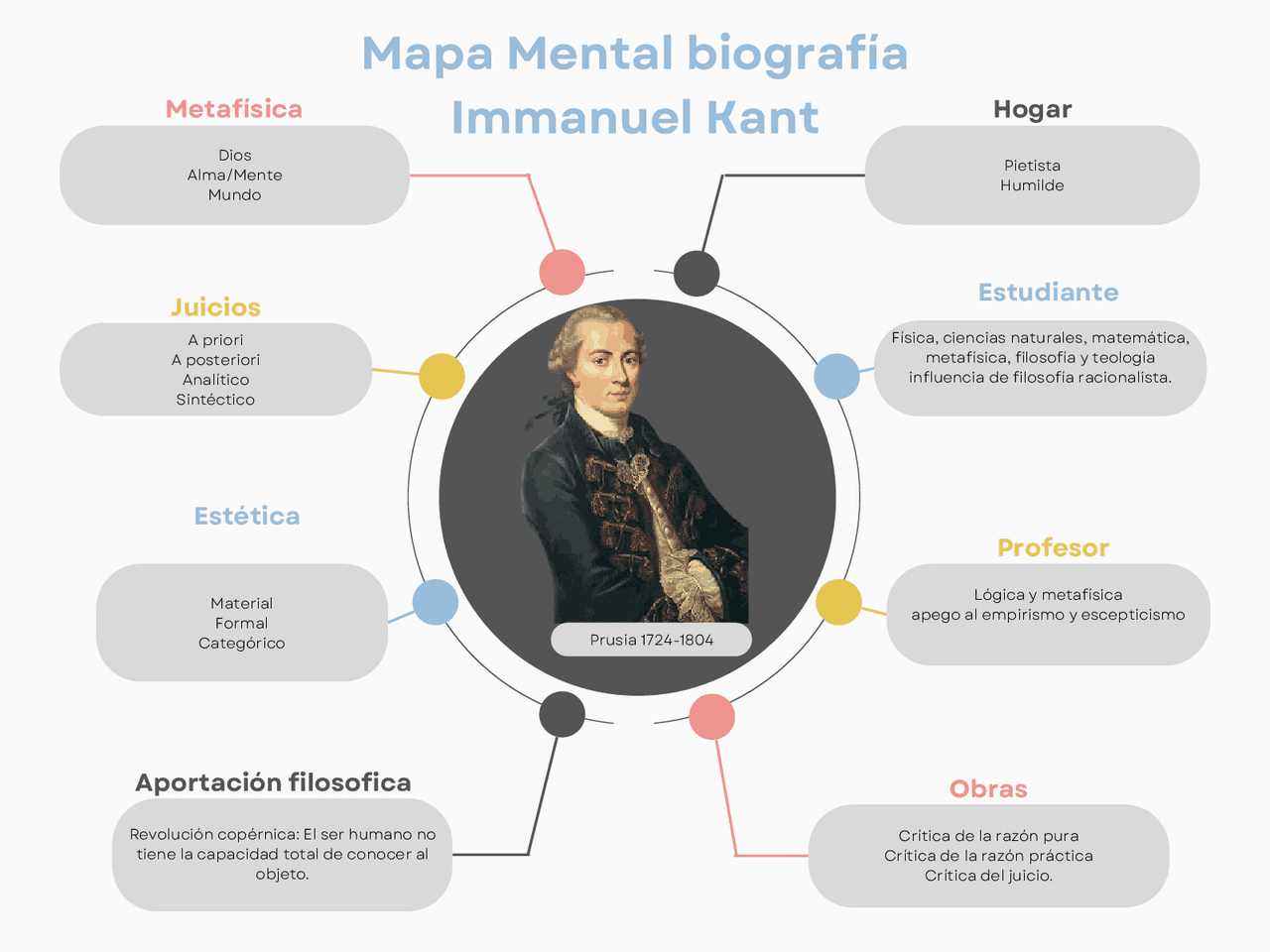
Mapa mental de emanuel Kant Esquemas y mapas conceptuales de Derechos
Kant's View of the mind 3.1 Method 3.2 Synthesis and Faculties 3.2.1 Synthesis of Apprehension in Intuition 3.2.2 Synthesis of Reproduction in Imagination 3.2.3 Synthesis of Recognition in a Concept 3.3 Synthesis: A 90° Turn 3.4 Unity of Consciousness 4. Consciousness of Self and Knowledge of Self 4.1 Thesis 1: Two Kinds of Consciousness of Self Immanuel Kant (1724-1804) was one of the most important philosophers of the Enlightenment Period (c. 1650-1800) in Western European history. This encyclopedia article focuses on Kant's views in the philosophy of mind, which undergird much of his epistemology and metaphysics. In particular, it focuses on metaphysical and epistemological. Immanuel Kant (22 April 1724 - 12 February 1804) was a German philosopher and one of the central Enlightenment thinkers. Born in Königsberg, Kant's comprehensive and systematic works in epistemology, metaphysics, ethics, and aesthetics have made him one of the most influential and controversial figures in modern Western philosophy.. In his doctrine of transcendental idealism, Kant argued. Kant's Moral Philosophy. First published Mon Feb 23, 2004; substantive revision Fri Jan 21, 2022. Immanuel Kant (1724-1804) argued that the supreme principle of morality is a principle of practical rationality that he dubbed the "Categorical Imperative" (CI). Kant characterized the CI as an objective, rationally necessary and.

Mapa Conceptual de Kant Realizado por Tania Jackson Galván Francisco
Immanuel Kant (born April 22, 1724, Königsberg, Prussia [now Kaliningrad, Russia]—died February 12, 1804, Königsberg) German philosopher whose comprehensive and systematic work in epistemology (the theory of knowledge), ethics, and aesthetics greatly influenced all subsequent philosophy, especially the various schools of Kantianism and. First Online: 31 October 2020 349 Accesses 2 Citations Abstract Kant's conception of mental illness is unlikely to satisfy contemporary readers. His classifications of mental illness are often fluid and ambiguous, and he seems to attribute to human beings at least some responsibility for preventing mental illness. This chapter maps the system of powers, many of their respective types of accidents, the interrelations of these powers and accidents, and many of the perspectives and groups of powers, which Kant identifies in the human soul. It first discusses the confusion regarding Kant's account of the mind's powers. In a 1964 lecture on Shakespeare, Jorge Luis Borges offers us 'one possible definition of the work of genius: a book of genius is a book that can be read in a slightly or very different way by each generation' (Borges 1999: 473).Immanuel Kant's Critique of Pure Reason fits this bill. Since its publication, it has been read in a wide variety of often conflicting ways.

Mapa Mental Immanuel Kant brebadimapa
Kant, in his book Anthropology from a Pragmatic Point of View (Kant 1974), claims that in the case of good fortune (wealth, power, and aristocracy), people have an innate propensity to think that they have the merit to deserve all these fortunes, and this egotistical delusion provokes them to act certain moral evils to others in society. Goodwill would produce good spontaneously and naturally. 40 0 Resource summary KANT Epistemología El conocimiento se basa en la formulación de juicios Juicios a posteriori Tienen su origen en la experiencia Juicios a priori Razonamientos Juicios analíticos Obvio Juicios sintéticos Aporta nueva información Giro copernicano
Mapa mental sobre Immanuel Kant. Entenda o coração de 'Immanuel Kant' com nossos mapas mentais, projetados para desmistificar conceitos complexos.

Tiempo Y Espacio Kant
mapa mental de kant filosoffia filos sofia tercero Mind Map by cecilia Saldivar Rodriguez , updated more than 1 year ago 189 0 0 Resource summary Immanuel Kant. Caracteristicas generales La estética trascendental Fundamentos de la moralidad Los tres postulados de la razón practica imperativo categorico Planteo del problema Dialectiva trascendental Immanuel Kant was a German philosopher during the Enlightenment era of the late 18th century. His best-known work is the 'Critique of Pure Reason.'




