Lucidchart's mind map software is quick & easy to use. Use Lucidchart to visualize ideas, make charts, diagrams & more. Amplie seu conhecimento sobre 'John Locke' com os nossos mapas mentais, desenvolvidos para enriquecer sua compreensão.. Os créditos do autor, na maioria das vezes, estarão na própria imagem do mapa mental, em outras situações o autor será considerado desconhecido.Se algum dos mapas mentais for de sua propriedade exclusiva.

MAPA MENTAL SOBRE JOHN LOCKE STUDY MAPS
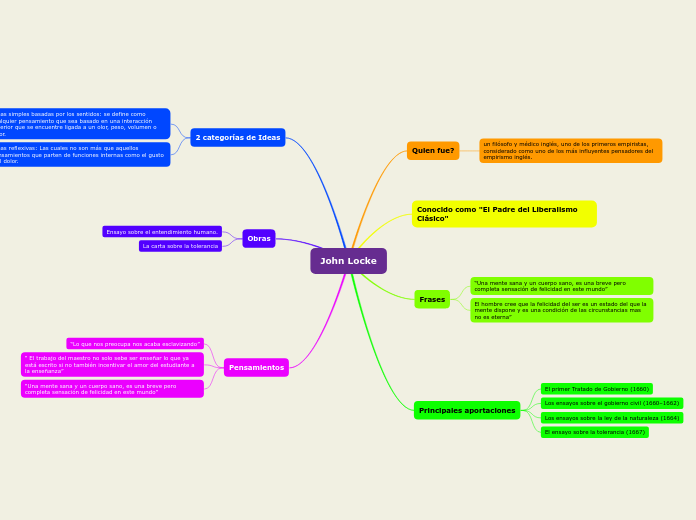
John Locke (b. 1632, d. 1704) was a British philosopher, Oxford academic and medical researcher. Locke's monumental An Essay Concerning Human Understanding (1689) is one of the first great defenses of modern empiricism and concerns itself with determining the limits of human understanding in respect to a wide spectrum of topics. It thus tells us in some detail what one can legitimately claim. John Locke's portrait by Godfrey Kneller, National Portrait Gallery, London. John Locke (/ l ɒ k /; 29 August 1632 - 28 October 1704) was an English philosopher and physician, widely regarded as one of the most influential of Enlightenment thinkers and commonly known as the "father of liberalism". Considered one of the first of the British empiricists, following the tradition of Francis. John Locke (born August 29, 1632, Wrington, Somerset, England—died October 28, 1704, High Laver, Essex) English philosopher whose works lie at the foundation of modern philosophical empiricism and political liberalism, classical liberalism in particular. He was an inspirer of both the European Enlightenment and the Constitution of the United. Take a look at our interactive learning Mind Map about John Locke, or create your own Mind Map using our free cloud based Mind Map maker.
Mapa Mental John Locke EDULEARN
John Locke (1632—1704) John Locke was among the most famous philosophers and political theorists of the 17 th century. He is often regarded as the founder of a school of thought known as British Empiricism, and he made foundational contributions to modern theories of limited, liberal government. He was also influential in the areas of. John Locke's views on the nature of freedom of action and freedom of will have played an influential role in the philosophy of action and in moral psychology.. And there are indications that this mechanistic model of corporeal behavior affects Locke's model of mental phenomena. Throughout the Sections of II.xxi added in E2-5. John Locke (1632-1704) added the chapter in which he treats persons and their persistence conditions (Book 2, Chapter 27) to the second edition of An Essay Concerning Human Understanding in 1694, only after being encouraged to do so by William Molyneux (1692-1693). [] Nevertheless, Locke's treatment of personal identity is one of the most discussed and debated aspects of his corpus. 1. Introduction 1.1 The puzzle of Locke's moral philosophy. There are two main stumbling blocks to the study of Locke's moral philosophy. The first regards the singular lack of attention the subject receives in Locke's most important and influential published works; not only did Locke never publish a work devoted to moral philosophy, but he dedicates little space to its discussion in the.
John Locke Carte Mentale
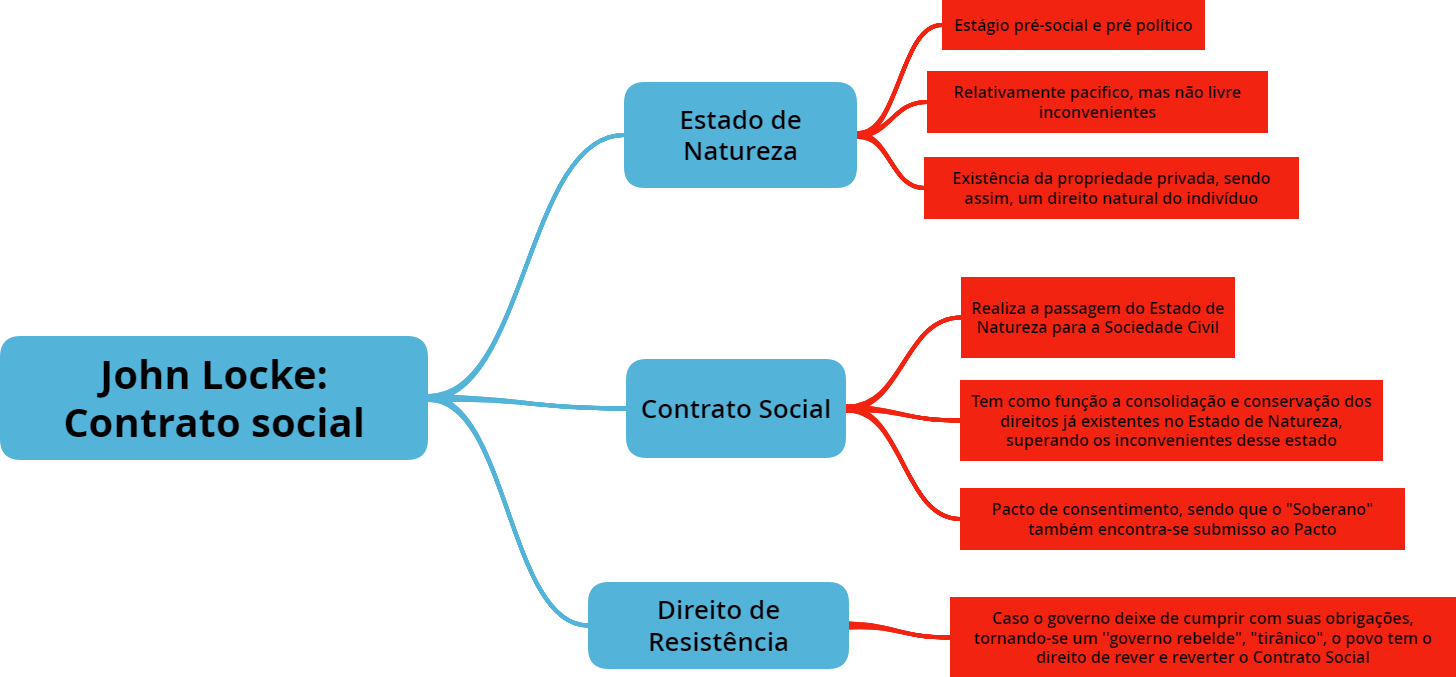
John Locke (1632-1704) is among the most influential political philosophers of the modern period. In the Two Treatises of Government, he defended the claim that men are by nature free and equal against claims that God had made all people naturally subject to a monarch.He argued that people have rights, such as the right to life, liberty, and property, that have a foundation independent of. Quick Reference. (1632-1704) English philosopher. Locke was born in Wrington, Somerset and educated at Oxford, where he seemed destined for a career in medicine. In 1666 he met Anthony Ashley-Cooper, later the 1st Earl of Shaftesbury, who became his friend and patron. Locke supervised a major operation to remove a hydatid cyst of the liver.
John Locke was born in 1632 in Wrighton, Somerset. His father was a lawyer and small landowner who had fought on the Parliamentarian side during the English Civil Wars of the 1640s. 1. Introduction. Two features of Locke's intellectual landscape are most salient for understanding his philosophy of science, one of which concerns the new science's methodology, and the other its content. First, then, is the new methodological approach to understanding the natural world. This approach is accompanied by profound shifts in.

mapa mental john locke Iluminismo história, John locke, Ciência política
John Locke, as perceived by your senses. In his brilliant 1689 work An Essay Concerning Human Understanding, Locke argues that, at birth, the mind is a tabula rasa (a blank slate) that we fill with 'ideas' as we experience the world through the five senses. By 'idea', Locke means "whatsoever is the Object of the Understanding, when a. In the case of Locke, I examine three of his arguments in order to illustrate the indispensable role of transparency in his polemic against central Cartesian doctrines such as innatism and the thesis that the soul always thinks. Keywords: Consciousness, John Locke, memory, René Descartes, transparency 1. Introduction1



