Darwin vs Lamarck - Evolução - Mapas Mentais de Biologia Para o Enem e Vestibulares | Projeto Elisa - Mind Maps neo-Lamarckism. Lamarckism, a theory of evolution based on the principle that physical changes in organisms during their lifetime—such as greater development of an organ or a part through increased use—could be transmitted to their offspring. The doctrine, proposed by the French naturalist Jean-Baptiste Lamarck in 1809, influenced.

Mapa Mental Sobre Lamarck E Darwin ENSINO
1.1 A Brief Historical Review of Lamarck's, Darwin's, and Bald-win's fundamental ideas 1.1.1 Lamarck Jean-Baptiste Lamarck (1744-1829) was a French naturalist and professor of zoology, who. He was partly inspired by observing the natural mental development of his children, and his stepwise theory of cognitive development was a major. 2552 5 0 Resource summary Evolução: Darwin X Lamarck Evolução: Fato ( evidências fósseis, genéticas.) Com o Tempo > Seres Vivos> Se Modificão Adaptações ao Ambiente Lamarck O meio modifica o ser vivo Annotations: O ser vivo se modifica com as modificações do meio.. ENGANO Annotations: Accordingly, Charles Darwin himself may be classified as a Lamarckian. Yet, Darwin's theory underwent its own evolution up to the neo‐Darwinian synthesis, which denied that acquired characteristics could be inherited. Upon the triumph of Neo‐Darwinism in the 20 th century, Lamarck and his ideas were being discredited as absurd or even. The study shows that the main differences between the views of the two founders of evolutionary theory lie in their claims about the speed of evolution and the adoption of an individual or.

Mapa Mental Darwin E Lamarck Ologia
Three scientists whose writings influenced Darwin were Lamarck, Lyell, and Malthus. Jean Baptiste Lamarck (1744-1829) was an important French naturalist. He was one of the first scientists to propose that species change over time. However, Lamarck was wrong about how species change. His idea of the inheritance of acquired characteristics is. Diagram summarizing the evolutionary transformation of species according to Lamarck (A) and Darwin (B). In Lamarck (A1 to A3), this transformation occurs under the effect of external circumstances leading to "needs": here, the giraffe's neck will lengthen (arrows) so that it can feed on the high leaves of the trees. Background The year 2009 is the 200th anniversary of the publication of Jean-Bapteste Lamarck's Philosophie Zoologique and the 150th anniversary of Charles Darwin's On the Origin of Species. Mapas Mentais sobre LAMARCK Última atualização em 10/08/2023 1 2. 6 Todos os mapas mentais da página 1 TEORÍA DE LAMARCK Y CAMBIOS HEREDABLES EN EL ADN

Teorias De Evolucion Lamarck Y Darwin Wallase Mindmeister Mapa Mental
In modern times, Lamarck's view of evolution, based on inheritance of acquired traits has been superseded by neo-Darwinism, based on random DNA mutations. This article begins with a series of observations suggesting that Lamarckian inheritance is in fact operative throughout Nature. I then launch into a discussion of human intelligence that is. We would like to show you a description here but the site won't allow us.
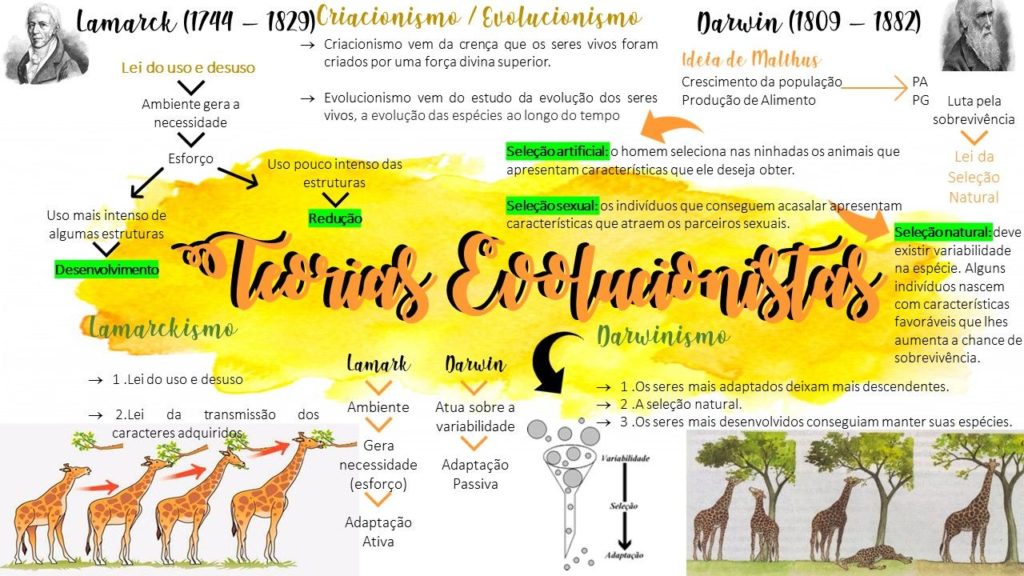
Teorias da evolução das espécies. As teorias da evolução de Darwin e Lamarck, dois cientistas naturalistas, são as mais famosas teorias evolucionistas de todos os tempos. A teoria de Lamarck defendia que os seres vivos modificavam-se ao longo do tempo, ele dizia que de acordo com as pressões exercidas pelo ambiente, estas modificações. Lamarck e Darwin; evolução humana; b)ao nível de aplicação - usar o conhecimento trabalhado em sala para elaborar um mapa mental; e c)ao nível de solução de problemas - criticar e/ou.
Teorias evolutivas [resumos e mapas mentais] Infinittus
Mapas Mentais sobre DARWINISMO Última atualização em 30/08/2023 1 2. 9 Todos os mapas mentais da página 1 EVOLUÇÃO: LAMARQUISMO E DARWINISMO 35 0 0 Resource summary Lamarck / Darwin Jean-Baptiste Lamarck, botânico reconhecido e colaborador no Museu de História Natural de Paris enunciou a lei da gradação, segundo a qual os seres vivos não foram produzidos simultaneamente, num curto período de tempo, mas sim começando pelo mais simples até ao mais complexo.




