Turboprop Turboshaft External thermal engines : Steam power Electric motors : Electric aircraft Clockwork drives: Human-powered Reaction engines Turbines : Turbojet Turbofan Propfan Rocket-powered Air turborocket Air-augmented rocket Motorjet Pulsejet Valveless pulsejet Gluhareff Pressure Jet Aerospike engine Pulse detonation engine turbojet, jet engine in which a turbine-driven compressor draws in and compresses air, forcing it into a combustion chamber into which fuel is injected. Ignition causes the gases to expand and to rush first through the turbine and then through a nozzle at the rear.

How a modern aircraft Jet engine works Nep Stuff
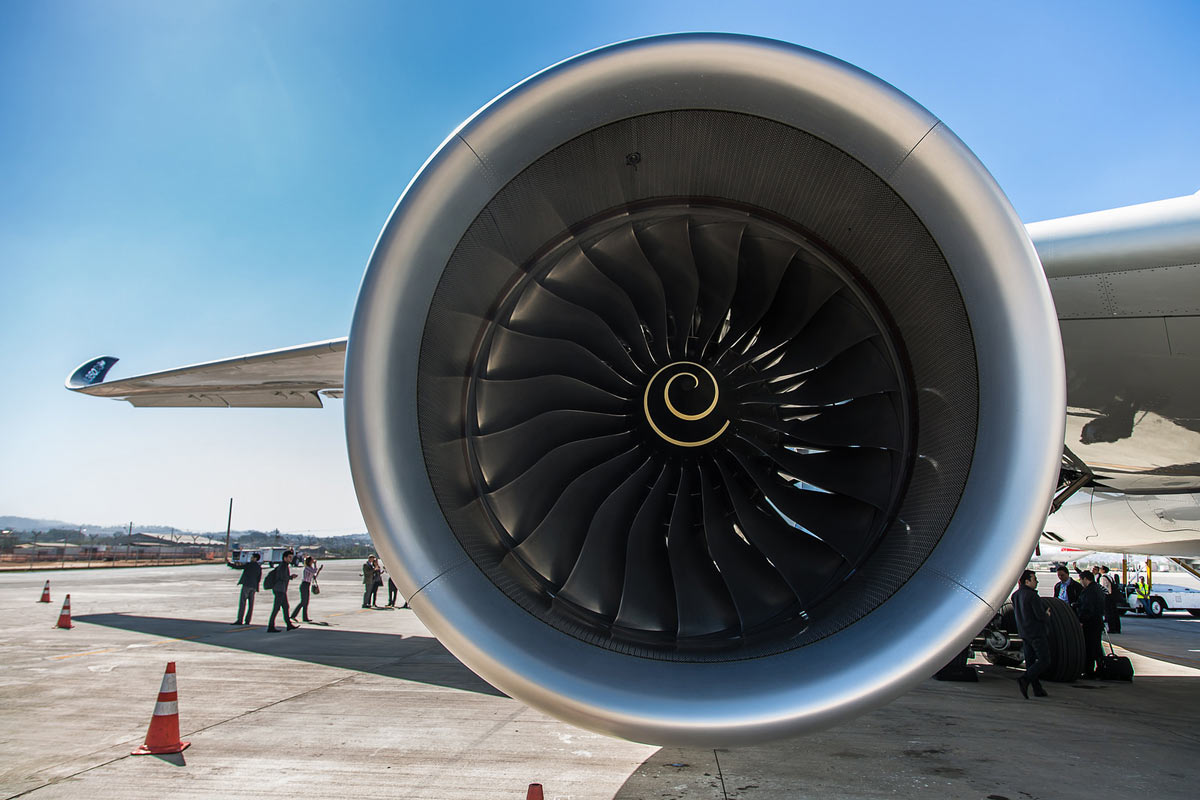
How does a turbojet work? On this slide we show a computer animation of a turbojet engine. The parts of the engine are described on other slides. Here, we are concerned with what happens to the air that passes through the engine. Large amounts of surrounding air are continuously brought into the engine inlet. The turbojet is the name used for a gas turbine engine designed to produce thrust by discharging exhaust gases at high speed out of the rear of the engine (i.e., the "jet"), which is done through a suitably shaped propelling nozzle. An inside look at how jet engines work. Most modern jet propelled airplanes use a turbofan design, where incoming air is divided between a large fan and the. While this broad definition may include rocket, water jet, and hybrid propulsion, the term jet engine typically refers to an internal combustion air-breathing jet engine such as a turbojet, turbofan, ramjet, pulse jet, or scramjet. In general, jet engines are internal combustion engines .

7 Remarkable Facts About Jet Engines
The turbofan or fanjet is a type of airbreathing jet engine that is widely used in aircraft propulsion.The word "turbofan" is a combination of the preceding generation engine technology of the turbojet, and a reference to the additional fan stage added.It consists of a gas turbine engine which achieves mechanical energy from combustion, and a ducted fan that uses the mechanical energy from the. Description A turbojet engine is a jet engine which produces all of its thrust by ejecting a high energy gas stream from the engine exhaust nozzle. In contrast to a turbofan or bypass engine, 100% of the air entering the intake of a turbojet engine goes through the engine core. Turboshaft External thermal engines : Steam power Electric motors : Electric aircraft Clockwork drives: Human-powered Reaction engines Turbines : Turbojet Turbofan Propfan Rocket-powered Air turborocket Air-augmented rocket Motorjet Pulsejet Valveless pulsejet Gluhareff Pressure Jet Aerospike engine Pulse detonation engine The turbojet engine is a closed cycle gas turbine engine that is used in aircraft and other industries by the burning of fuel and the use of several components like the compressor, Turbine, propeller, and more. Open cycle Gas Turbine: Here the working fluid is air or gas. It is an internal combustion engine. It involves four processes:

How Does A Turbofan Engine Work? Boldmethod
Jet engine manufacturers often put in huge amounts of resources into innovation to ensure that these complex machines not just meet but also exceed weight, efficiency, safety, and durability standards. The more modern turbofan engines with higher thrust ratings are always the most expensive airplane engines. For example, a single unit of the. The General Electric J85 is a small single-shaft turbojet engine. Military versions produce up to 2,950 lb f (13.1 kN) of thrust dry; afterburning variants can reach up to 5,000 lb f (22 kN). The engine, depending upon additional equipment and specific model, weighs from 300 to 500 pounds (140 to 230 kg).
The Pratt & Whitney J58 (company designation JT11D-20) is an American jet engine that powered the Lockheed A-12, and subsequently the YF-12 and the SR-71 aircraft. It was an afterburning turbojet engine with a unique compressor bleed to the afterburner that gave increased thrust at high speeds. I explain how to build a simple, inexpensive turbojet engine. We cover the selection of the turbocharger, the terminology and design principles for the entir.
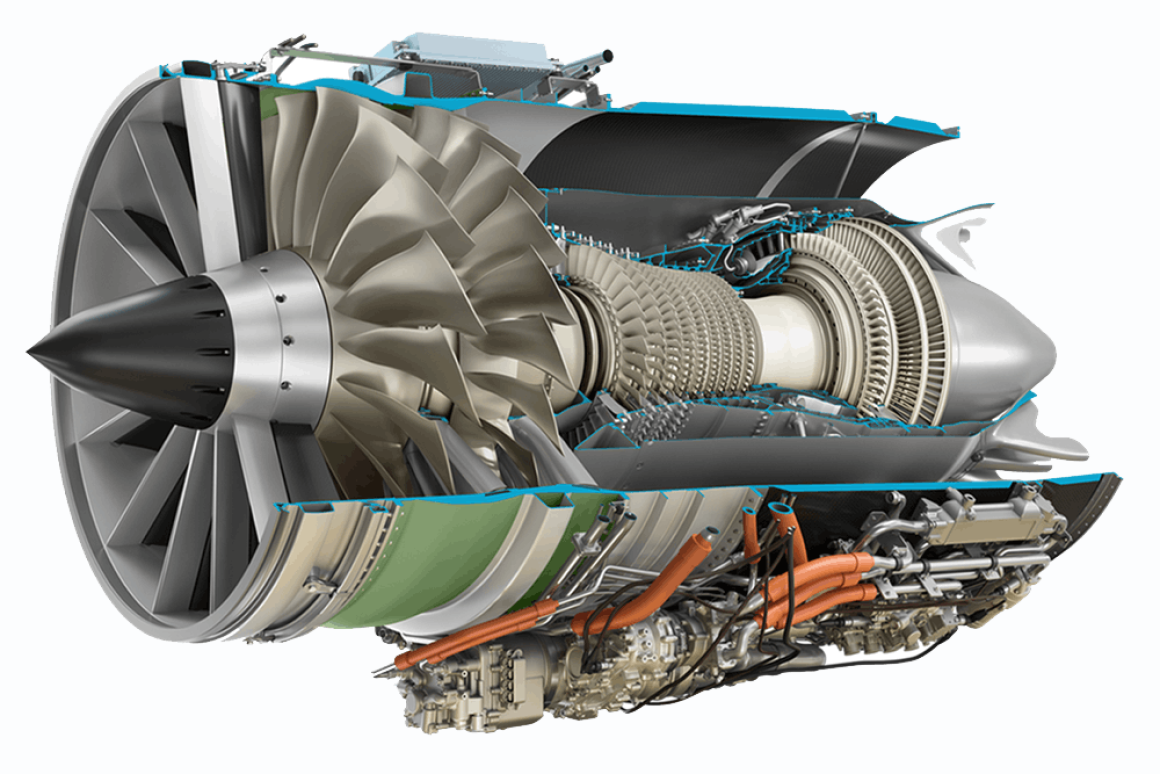
GE unveils new supersonic commercial jet engine
Storm Shadow / SCALP EG. RBS-15. Variants. Microturbo TRI-40. The Microturbo TRI 60 is a small, expendable turbojet engine developed for use in cruise missiles, target drones, and other small unmanned air vehicles. Variants of this engine produce from 3.5 to 5.3 kN (790 to 1,190 lbf) of thrust. The engine first ran in 1974. Atlanta company Hermeus has its sights set on Mach 4 next year, to beat the Mach 3.3 benchmark set by the SR-71 Blackbird way back in 1976. Watch its Chimera hybrid engine nailing the switch.




