Animal cells are the fundamental units of life in protozoa and multicellular animals. Each cell is a wonder in its own right, plus they work together as building blocks for tissues, organs, and organ systems. Animal cells are mostly microscopic, ranging in size from 1 to 100 micrometers. An animal cell is a eukaryotic cell that lacks a cell wall, and it is enclosed by the plasma membrane. The cell organelles are enclosed by the plasma membrane including the cell nucleus. Unlike the animal cell lacking the cell wall, plant cells have a cell wall.

Pictures Of The Animal Cells ANIMALSD
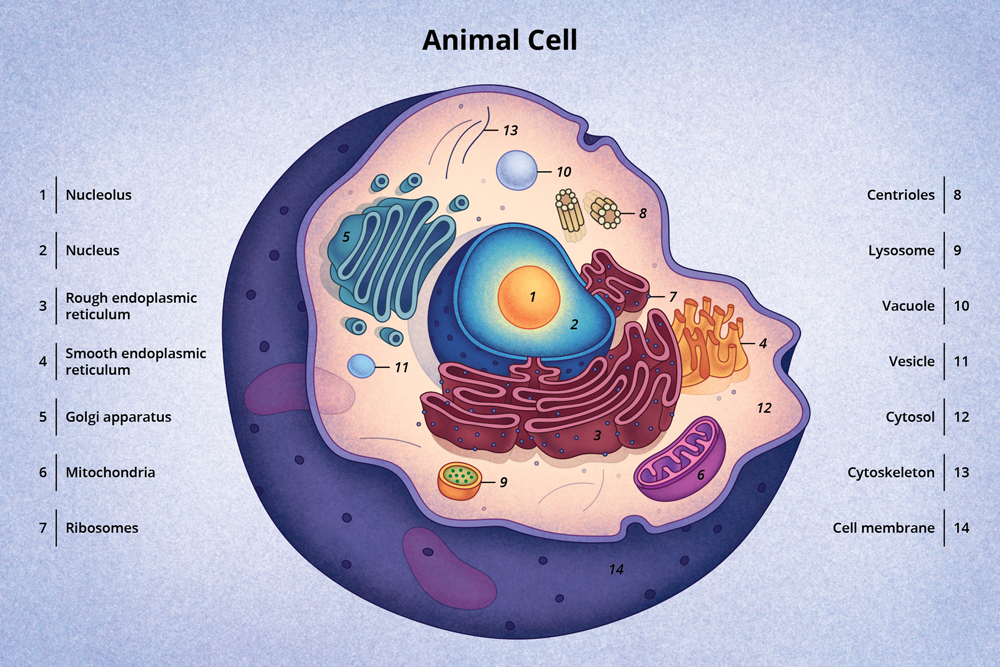
Animal cell diagram detailing the various organelles Though this animal cell diagram is not representative of any one particular type of cell, it provides insight into the primary organelles and the intricate internal structure of most animal cells. Definition Animal cells are the basic unit of life in organisms of the kingdom Animalia. They are eukaryotic cells, meaning that they have a true nucleus and specialized structures called organelles that carry out different functions. Key points: All cells have a cell membrane that separates the inside and the outside of the cell, and controls what goes in and comes out. The cell membrane surrounds a cell's cytoplasm, which is a jelly-like substance containing the cell's parts. Cells contain parts called organelles. Each organelle carries out a specific function in the cell. Cell Membrane The thin layer of protein and fat that surrounds the cell. The cell membrane is semipermeable, allowing some substances to pass into the cell and blocking others. Centrosome (Microtubule Organizing Center) A small body located near the nucleus - it has a dense center and radiating tubules.
Discovery and Structure of Cells Biology Visionlearning
Structure of a cell: Unit test; About this unit. This unit is part of the Biology library. Browse videos, articles, and exercises by topic.. Overview of animal and plant cells (Opens a modal) Practice. Extracellular structures and intercellular junctions Get 3 of 4 questions to level up! Animal cells are typical of the eukaryotic cell, enclosed by a plasma membrane and containing a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles. Unlike the eukaryotic cells of plants and fungi, animal cells do not have a cell wall. This feature was lost in the distant past by the single-celled organisms that gave rise to the kingdom Animalia. The animal body has several types of cells. Examples of common animal cell types include skin cells, muscle cells, blood cells, fat cells, nerve cells, sex cells, and stem cells. Skin cells are cells that make up the skin or epithelial tissue. Muscle cells (also called myocytes) are cells that make up muscular tissue. Animal and plant cells share common elements like plasma membranes, cytoskeletons, and mitochondria. However, they differ in certain aspects. For example, plant cells have a cell wall and a central vacuole, while animal cells contain centrosomes.. The lipid bilayer is a more general term that refers to the structure of the membrane itself.

The animal cell diagram. Vector illustration on white Etsy in 2021
Animal Cell Diagram. 1) Centrioles. They are paired tube-like organelle composed of a protein called tubulin. Centrioles are about 500nm long and 200nm in width that are found close to the nucleus and helps in cell division.They are also found in cilia and flagella.. Functions A Labeled Diagram of the Animal Cell and its Organelles There are two types of cells - Prokaryotic and Eucaryotic. Eukaryotic cells are larger, more complex, and have evolved more recently than prokaryotes. Where, prokaryotes are just bacteria and archaea, eukaryotes are literally everything else.
Animal cell diagram Centrioles Cilia and Flagella Endoplasmic Reticulum Endosomes and Endocytosis Golgi Apparatus Intermediate Filaments Lysosomes Microtubules Mitochondria Nucleus Peroxisomes Fat Cells Animal Cells vs. Plant Cells Reference Animal cell Definition Animal cells perform multiple functions essential for the survival and adaptation of organisms. Animal cell is eukaryotic in nature and exhibit DNA within the nucleus. It also contains various cellular structure and organelles like the cytoplasm, Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, mitochondria, etc. Animal cells function together to carry out various.

The Structure and Functions of an Animal Cell
Image 1: Structure of Animal cell (diagram) Image created with the help of biorender Difference between Prokaryotic Cell and Eukaryotic Cell Prokaryotic cells are unicellular that do not contain membrane-bounded organelles. Their nucleic material is dispersed in the cytoplasm. All animal cells are surrounded by a protective membrane which is called as cell-membrane or plasma membrane. It is also called as cytoplasmic membrane. Plasma membrane is a thin, elastic and semi-permeable membrane. It is mainly composed of 32% lipids, 12% protein, 6% carbohydrates and 20% water. The pores of the membrane allow the passage of.




