The Bohr model explains the stability of the atom and atomic particles. It also talks about the position of various atomic particles inside the atom as well as their charge and other properties. It describes the structure of the atom in detail. 34 4.8K views 1 year ago In this video we'll look at the atomic structure and Bohr model for the Beryllium atom (Be). We'll use a Bohr diagram to visually represent where the electrons are.

Atomic Structure (Bohr Model) for Beryllium (Be) YouTube
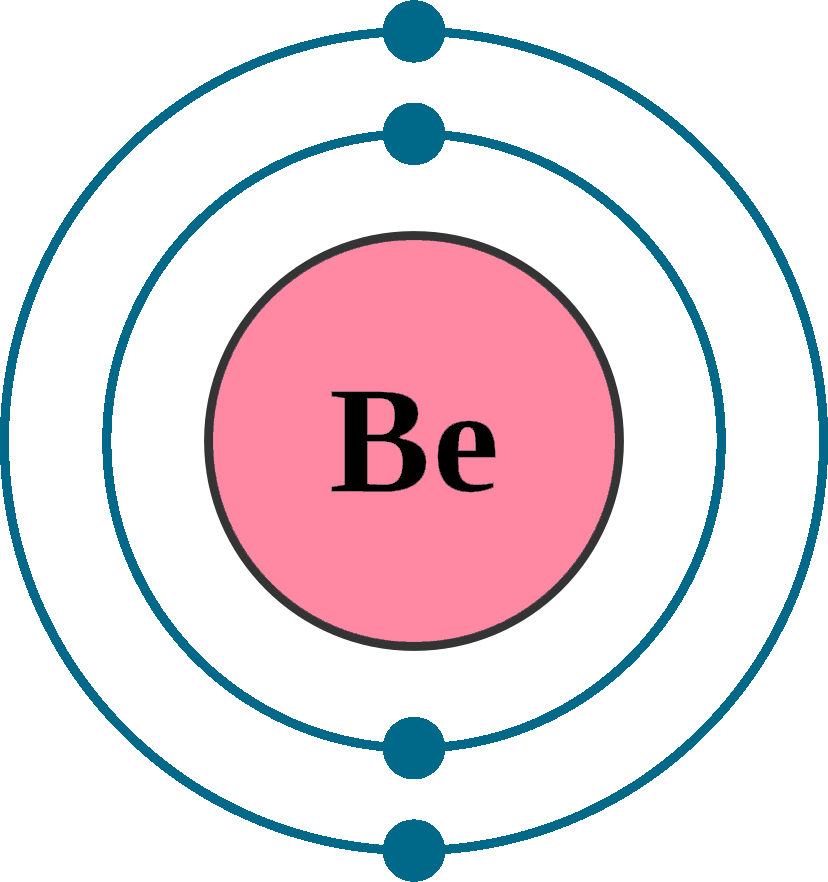
The Bohr Model of Beryllium (Be) has a nucleus that contains 5 neutrons and 4 protons. This nucleus is surrounded by two-electron shells named K-shell and L-shell. The outermost shell in the Bohr diagram of Beryllium contains 2 electrons that also called valence electrons. Page Contents show How to draw Bohr Model of Beryllium (Be)? Bohr diagrams show electrons orbiting the nucleus of an atom somewhat like planets orbit around the sun. In the Bohr model, electrons are pictured as traveling in circles at different shells, depending on which element you have. Figure 2 2 contrast the Bohr diagrams for lithium, fluorine and aluminum atoms. The shell closest to the nucleus is. The model shown in the figure below is for the beryllium atom or any four‐electron ion. Note that the occupancy of the inner orbit is restricted to two electrons (Pauli Principle) and that the orbit radii are constrained by the hydrogen atom result (R 2 = 4R 1 ) leaving only one variational parameter, the radius of the n = 1 orbit. Steps Write protons, neutrons, and electrons of beryllium atom Beryllium has 4 protons, 5 neutrons, and 4 electrons. Learn how to find: Beryllium protons neutrons electrons Draw nucleus of beryllium atom The nucleus of a beryllium atom contains 4 protons and 5 neutrons. So draw the nucleus of beryllium atom as follows: Beryllium nucleus
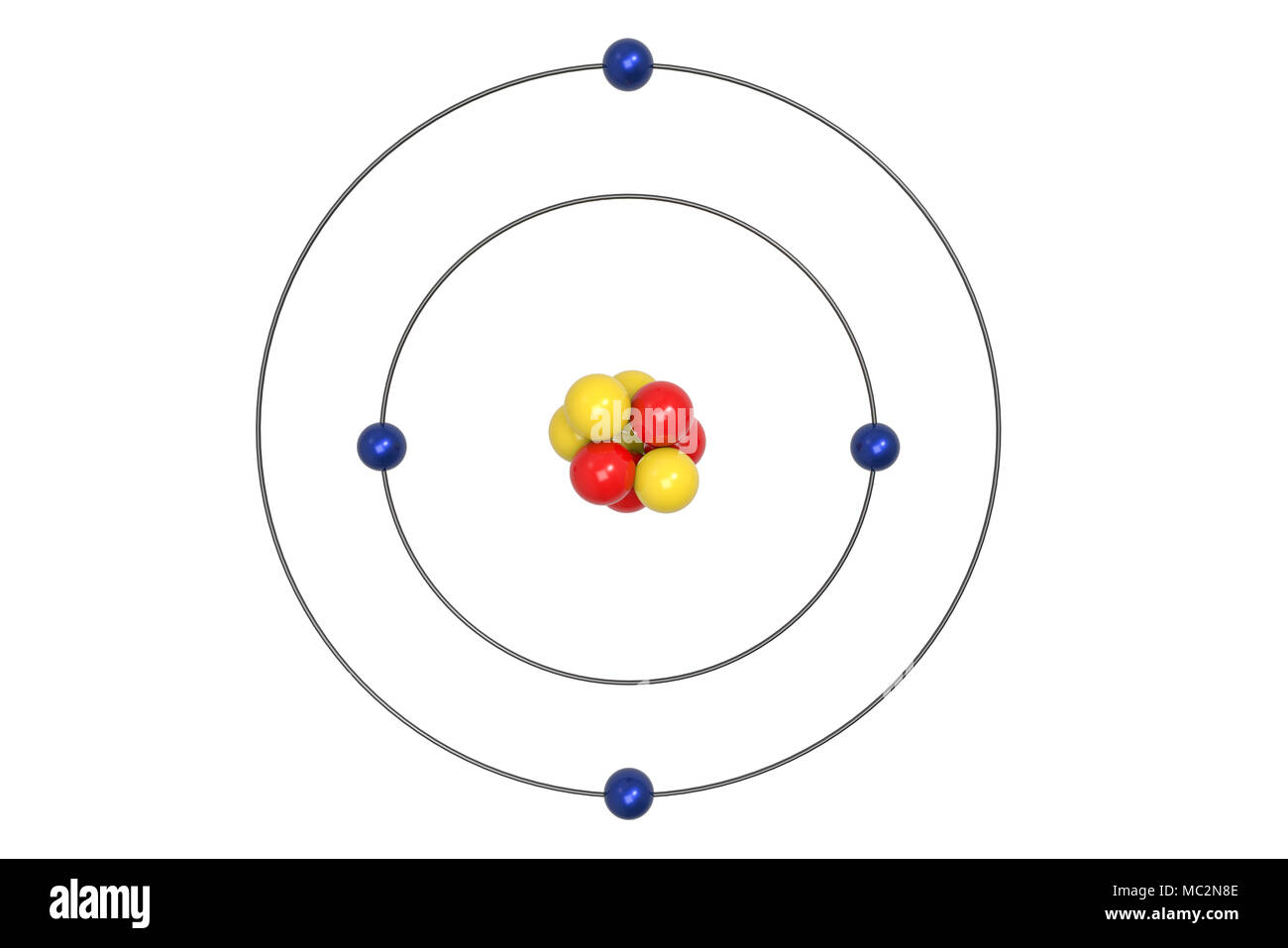
Beryllium Bohr Model Diagram
The Bohr model is a relatively primitive model of the hydrogen atom, compared to the valence shell model. As a theory, it can be derived as a first-order approximation of the hydrogen atom using the broader and much more accurate quantum mechanics and thus may be considered to be an obsolete scientific theory. Welcome to Chem How, in this video atomic structure of Beryllium is shown.This atomic model is according to Bohr's model of atoms.According to Bohr's model o. The calculation for the beryllium atom is carried out as shown below. Required student input is indicated by the highlighted regions. Enter nuclear charge: Z := 4 Kinetic energy: T1 ( R1 ) 1 := 2 ⋅ R12 1 T2 ( R1 ) := 8 ⋅ R12 Electron‐nucleus potential energy: − Z VN1 ( R1 ) := R1 − Z VN2 ( R1 ) := 4 ⋅ R1 In 1913, a Danish physicist, Niels Bohr (1885-1962; Nobel Prize in Physics, 1922), proposed a theoretical model for the hydrogen atom that explained its emission spectrum. Bohr's model required only one assumption: The electron moves around the nucleus in circular orbits that can have only certain allowed radii.
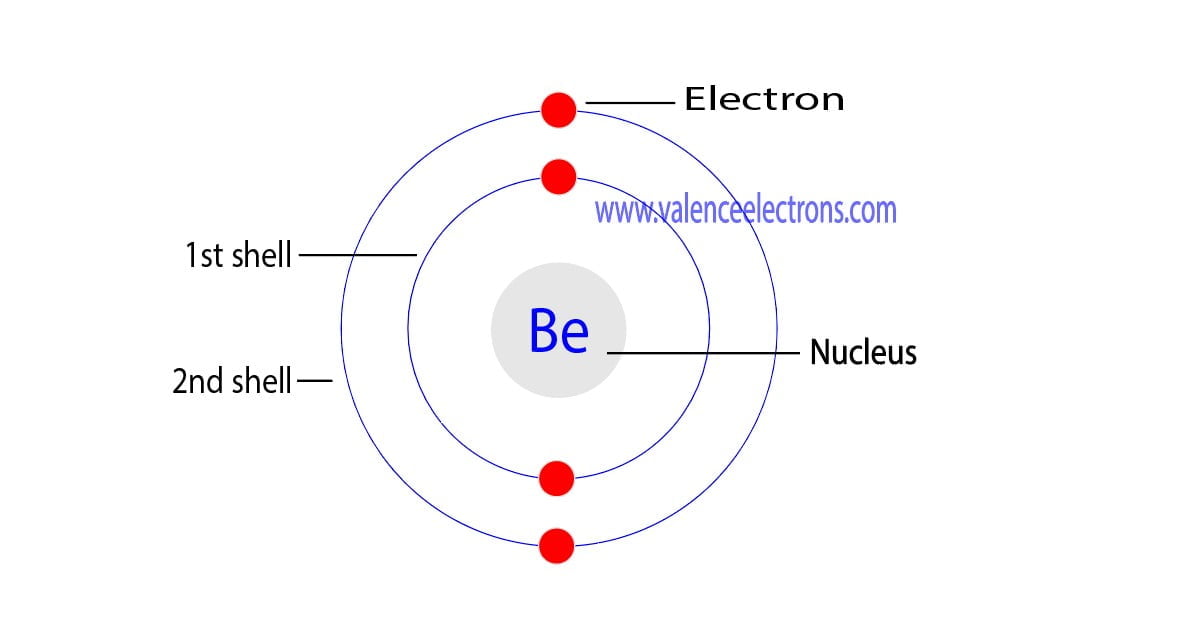
Electron Configuration for Beryllium (Be, Be2+ ion)
Build an Atom - PhET Interactive Simulations Atomic & Molecular Structure How to Make a 3-D Bohr Model ••• Updated April 24, 2017 By Tricia Lobo In your introductory chemistry classes you will have to become familiar with a number of the early models of atoms, which represent scientists' early concepts of the structure of atoms.
6.2 The Bohr Model; 6.3 Development of Quantum Theory; 6.4 Electronic Structure of Atoms (Electron Configurations) 6.5 Periodic Variations in Element Properties;. the beryllium and boron atoms each have only four and six electrons, respectively. It is possible to draw a structure with a double bond between a boron atom and a fluorine atom in. Electrons arrangement or Bohr model: 2, 2: Electronic configuration [He] 2s 2: Atomic radius: 153 picometers (van der Waals radius) Valence electrons: 2: 1st Ionization energy: 9.323 eV:. You have already seen the Bohr model of Beryllium atom in the above table and you have seen that the number of orbits or shells in sodium is 2.
Beryllium Element With Reaction, Properties and Uses Periodic Table
Ai = hν = hc λ A i = h ν = h c λ. Unknown wavelength λ λ can be determined from the Rydberg formula: 1 λ =R∞Z2( 1 n21 − 1 n22) 1 λ = R ∞ Z 2 ( 1 n 1 2 − 1 n 2 2) so that final equation for ionization energy looks like this: Ei = hc e R∞Z2( 1 n21 − 1 n22) E i = h c e R ∞ Z 2 ( 1 n 1 2 − 1 n 2 2) Bohr model of Elements. 1. Hydrogen (H) 1. 2. Helium (He) 2. 3. Lithium (Li)




