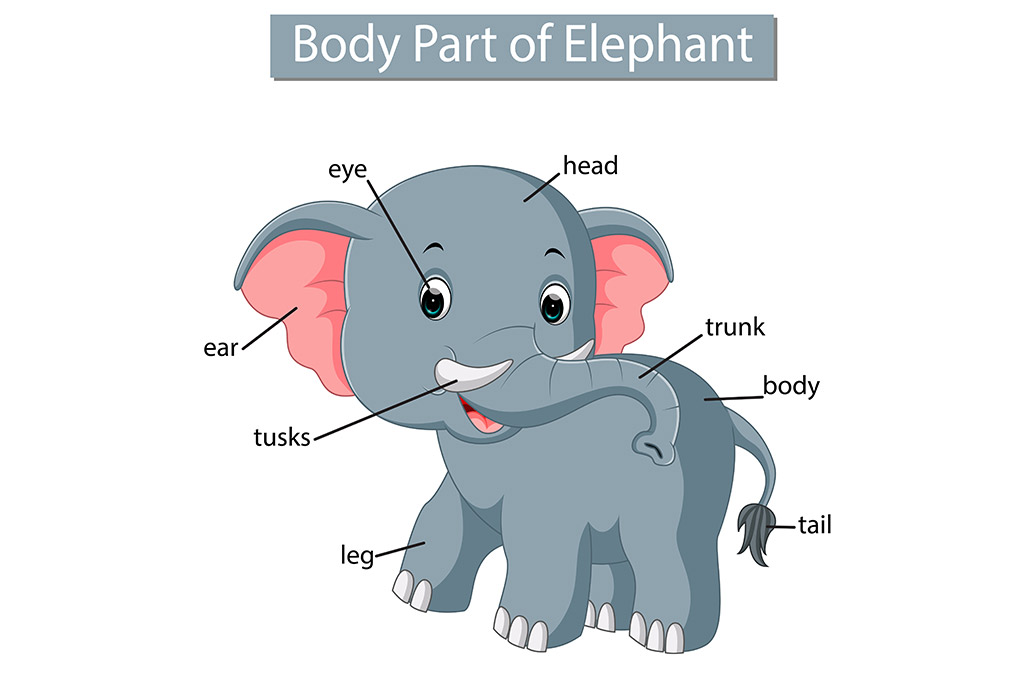
Elephant Body Parts List Eyes Ears Trunk Legs Tusks Toes Tail Elephant Parts Image Parts of an Elephant with Examples Learn these parts of an elephant to enhance your English words about animal parts in English. Eyes The elephant's eye is positioned on the side of its head, giving it excellent peripheral vision. Ears The elephants body is well adapted for the survival of rugged conditions of their habitats in Africa and Asia. Elephants have strong, long trunks that perform multiple tasks, sharp tusks used for carrying heavy objects and for fighting with, large ears which they flap to keep themselves cool as well as having other functions.

Elephant Parts Elephant Body Parts with Pictures • 7ESL
Tusks Elephants have two long, curved tusks made of ivory that protrude from their upper jaw. Tusks are used for root digging, brush clearing, fighting over females, and self-defense. They also protect their trunks, which are an important part of an elephant's body. Ears The elephant's large ears are one of its most distinguishing characteristics. Discover the intricate details of elephant anatomy, revealing nature's fascinating blend of strength, adaptability, and grace. Explore now! Discover the Elephant's Anatomy: It's nothing like any other animal Consider this your hub for all information related to the awe-inspiring anatomy of elephants. We'll explore their remarkable trunks, towering limbs, intricate bone structure. Learn Animal Body Parts - Elephant Body Parts - Wild Animals Rainbow Super Kids 1.25M subscribers Subscribe 61K views 3 years ago English vocubulary Learn different parts of elephant and. The body parts of an elephant include the trunk, tusks, teeth, ears, legs, skin and a tail. In common with all vertebrates, they also have skeletons and internal organs. Elephants also have a brain that is four times the size of a human brain, making it the largest brain of any known land animal.
Teach Your Kids About Elephant Body Parts (With Picture)
The elephant ear is very large and peculiar in shape. Ears are used for auditory purposes, balancing the body, thermoregulation and for signalling. Elephants have difficulty in losing excess body heat through the skin surface. An elephant's ear will shed almost 100% of the total heat when maximally vasodilated and flapped gently. The elephant's trunk is an extension of the upper lip and nose. It functions for grasping, breathing, feeding, dusting, smelling, drinking, lifting, sound production/communication, defense/protection, and sensing. The trunk contains an estimated 100,000 muscles and tendons in the trunk, giving it extreme flexibility and strength. 4.5K views How Am I Different from an Elephant? Of course, elephants are much bigger than even the largest humans. They can weigh up to six tons and grow to be ten feet tall - almost the size of. Important Body Parts: Elephant Lungs Important Body Parts - Elephant Trunk Important Body Parts - Elephant Tusks Important Body Parts - Elephant Teeth Important Body Parts - Elephant Mouth Important Body Parts - Elephant Feet Important Body Parts - Elephant Limbs Important Body Parts - Elephant Tail Jacobson's Organ Communication Elephant Hearing

body parts of an elephant Stock Photo Alamy
Elephants have a unique body design that makes it hard to confuse them with any other animal in the world. They are very large animals with an anatomy that is developed so that they have a very good chance of survival in their natural habitat. All of us are familiar with the trunk of an elephant. Parts of an elephant For KidsElephant Body Parts with animation for explain each part of elephant ,Animal Body Parts for Kids,RhymsoTVKidsSubscribe to our C.
1/500th of the body weight; Human brain weighs about 1.6 kg (3 lbs 8oz) or 1/50th of the body weight; Eyesight. Eyesight poor. Best in dim light; Tear ducts are vestigial. Harderian glands (accessory lachrymal glands associated with the nictitating membrane or third eyelid) lubricate the eyes; Distinguishing features of savannah and forest. The leader of a female group, usually the oldest cow, is known as the matriarch . Males (bulls) leave their family groups when they reach puberty and may live alone or with other males. Adult bulls mostly interact with family groups when looking for a mate.

Different parts of wild elephant Royalty Free Vector Image
Elephant trunks may be one of the most sensitive body parts in the animal kingdom. Michael Brecht at the Bernstein Center for Computational Neuroscience in Berlin and his colleagues dissected the. Scroll over the different elephant body parts to read their descriptions. Trunk This is an elephant's most useful body part! A trunk is an elongation of the nose and upper lip. Elephants use their trunks to: - smell - bring water to their mouths to drink - store water to drink later - dig holes - spray water over their bodies to bathe




