0:00 / 1:57 Atomic Structure (Bohr Model) for Nitrogen (N) 8,229 views 43 In this video we'll look at the atomic structure and Bohr model for the Nitrogen atom (N). We'll use a Bohr. Nitrogen has 2 electrons in its first shell and 5 in its second.Check me out: http://www.chemistnate.com
Bohr atomic model of a nitrogen atom. vector illustration for science
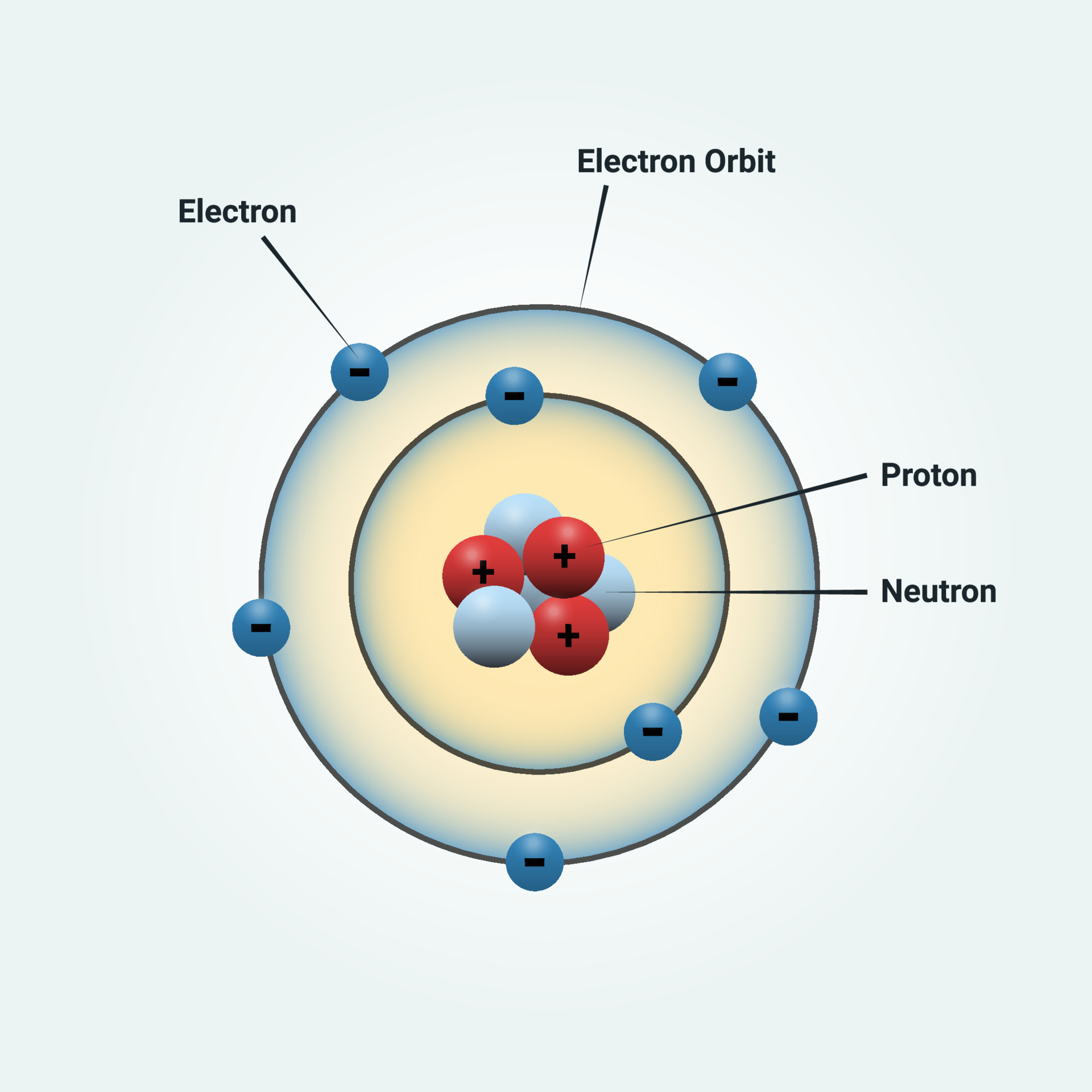
Bohr diagrams show electrons orbiting the nucleus of an atom somewhat like planets orbit around the sun. In the Bohr model, electrons are pictured as traveling in circles at different shells, depending on which element you have. Figure 2 2 contrast the Bohr diagrams for lithium, fluorine and aluminum atoms. The shell closest to the nucleus is. Molecular nitrogen (\(N_2\)) is not reactive at standard temperature and pressure and is a colorless and odorless gas. Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) : A Bohr diagram of the nitrogen atom. Nitrogen is a non-metal element that occurs most abundantly in the atmosphere; nitrogen gas (N 2) comprises 78.1% of the volume of the Earth's air. It only. Figure 8.9.2.1 8.9.2. 1 : A Bohr diagram of the nitrogen atom. Nitrogen is a non-metal element that occurs most abundantly in the atmosphere; nitrogen gas (N2) comprises 78.1% of the volume of the Earth's air. It only appears in 0.002% of the earth's crust by mass. Compounds of nitrogen are found in foods, explosives, poisons, and fertilizers. We use Lewis symbols to describe valence electron configurations of atoms and monatomic ions. A Lewis symbol consists of an elemental symbol surrounded by one dot for each of its valence electrons: Figure 7.9 shows the Lewis symbols for the elements of the third period of the periodic table. Figure 7.9 Lewis symbols illustrating the number of.
Nitrogen (N) AMERICAN ELEMENTS
The electron configuration and the orbital diagram are: Following hydrogen is the noble gas helium, which has an atomic number of 2. The helium atom contains two protons and two electrons. The first electron has the same four quantum numbers as the hydrogen atom electron ( n = 1, l = 0, ml = 0, ms = +12 m s = + 1 2 ). How to draw an electron configuration diagram. Find the element on the periodic table. The atomic number tells you how many electrons to draw in total. For example, potassium has 19 electrons. Draw a small circle and write the symbol in the centre. This represents the nucleus. In order to make a Bohr diagram, you need to know the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons the element has. In this section, we'll show a sample Bohr diagram for hydrogen. H —Hydrogen 1 proton 1 electron 0 neutrons You can see the principles outlined in the section above at work in the Bohr model for the hydrogen atom. Chemistry Bohr Model of the Atom Bohr Model of the atom 1 Answer Belle Jun 20, 2018 Use the periodic table to find the number of protons, neutrons and electrons of a particular atom. Explanation: 1: The number of protons is the atomic number Nitrogens atomic number = 7, so there is 7 protons 2: Electrons are the same as protons
Nitrogen Structure
Bohr model, description of the structure of atoms, especially that of hydrogen, proposed (1913) by the Danish physicist Niels Bohr.The Bohr model of the atom, a radical departure from earlier, classical descriptions, was the first that incorporated quantum theory and was the predecessor of wholly quantum-mechanical models. The Bohr model and all of its successors describe the properties of. Here, we will draw the Bohr diagram of the Nitrogen atom with some simple steps. Steps to draw the Bohr Model of Nitrogen atom 1. Find the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons in the Nitrogen atom Protons are the positively charged particles and neutrons are the uncharged particles, both these are constituents of the atom nuclei.
In drawing Bohr diagrams, different amounts of shells are required to store a specific atom's electrons. Looking at a Bohr diagram for the carbon atom, one can see that two energy levels/shells are required for its six electrons.. Bohr model of nitrogen: (CC BY-SA 2.0 uk; Greg Robson); Answer b. Bohr model of calcium: (CC BY-SA 2.0 uk;Greg. The Bohr model of the hydrogen atom ( Z = 1) or a hydrogen-like ion ( Z > 1 ), where the negatively charged electron confined to an atomic shell encircles a small, positively charged atomic nucleus and where an electron jumps between orbits, is accompanied by an emitted or absorbed amount of electromagnetic energy ( hν ). [1]

Nitrogen atom heavykesil
The Bohr model of nitrogen contains a nucleus having 7 protons and 7 neutrons in the center, and around this nucleus, there are two electron shells containing 7 electrons. Atomic Structure (Bohr Model) for Nitrogen (N) Watch on Contents Steps #1 Write protons, neutrons, and electrons of nitrogen atom #2 Draw nucleus of nitrogen atom Key points Bohr's model of hydrogen is based on the nonclassical assumption that electrons travel in specific shells, or orbits, around the nucleus. Bohr's model calculated the following energies for an electron in the shell, n : E ( n) = − 1 n 2 ⋅ 13.6 eV




