Whereas giant breeds can take between 18 months and 2 years for their growth plates to fuse. Speaking of skeletons, a dog has 320 bones in their body (depending on the length of their tail) and around 700 muscles. Muscles attach to bones via tendons. Depending on the breed of dog, they will have different types of muscle fibers. Conclusion. So, the dog organ anatomy consists of different important organs, structures, and parts from the different body systems of a dog. It includes the bones, muscles, digestive apparatus, respiratory apparatus, cardiovascular organs, brains, spinal cord, nerves, urinary organs, and male and female organs.
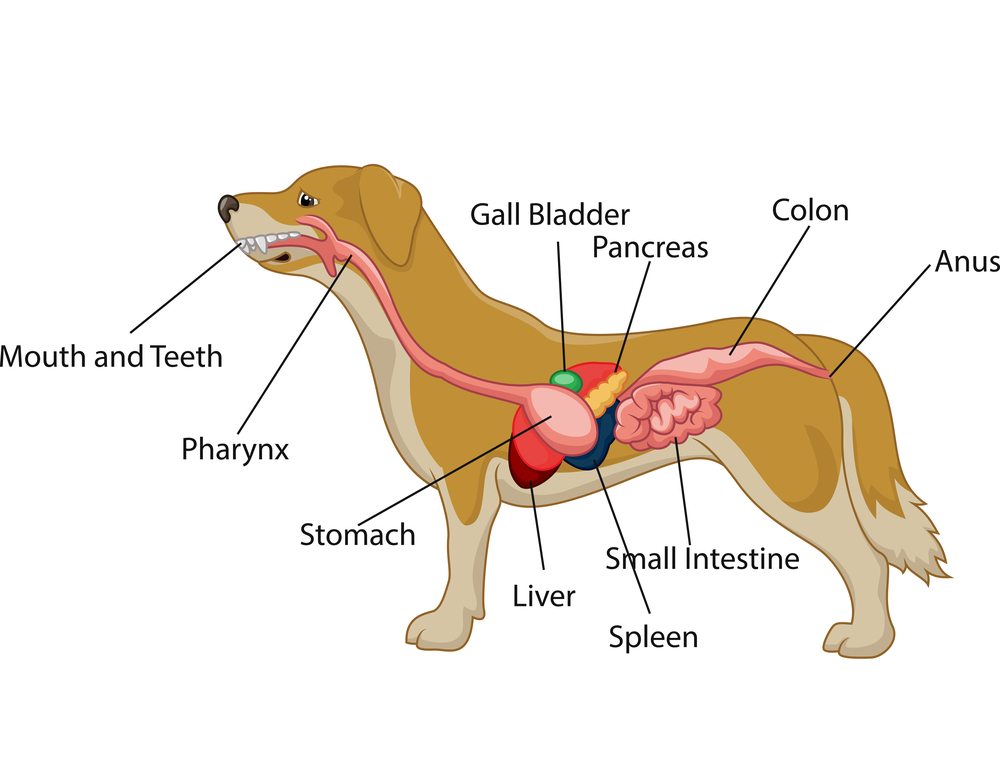
Dog Digestive Process and what the stages are and how it works
Anatomy atlas of the canine general anatomy: fully labeled illustrations and diagrams of the dog (skeleton, bones, muscles, joints, viscera, respiratory system, cardiovascular system). Positional and directional terms, general terminology and anatomical orientation are also illustrated. A female dog's reproductive system has similar organs as a human's. The female dog anatomy external organ is the vulva, which opens to the vagina. A pregnant female dog's anatomy includes two ovaries, which produce eggs, the cervix, fallopian tubes, and the uterus. The uterus becomes the womb for her puppies during their gestation period. Dog anatomy comprises the anatomical studies of the visible parts of the body of a domestic dog.Details of structures vary tremendously from breed to breed, more than in any other animal species, wild or domesticated, as dogs are highly variable in height and weight. The smallest known adult dog was a Yorkshire Terrier that stood only 6.3 cm (2.5 in) at the shoulder, 9.5 cm (3.7 in) in length. The canine axis or C2 has a large spinous process with an expanded arch, a wide body, and large transverse processes (see Figure 5-12). The spinous process is nonbifid. The canine axis is very large relative to the size of other canine cervical vertebrae. The axis has a dens, which projects cranially to allow pivotal motion between the atlas.
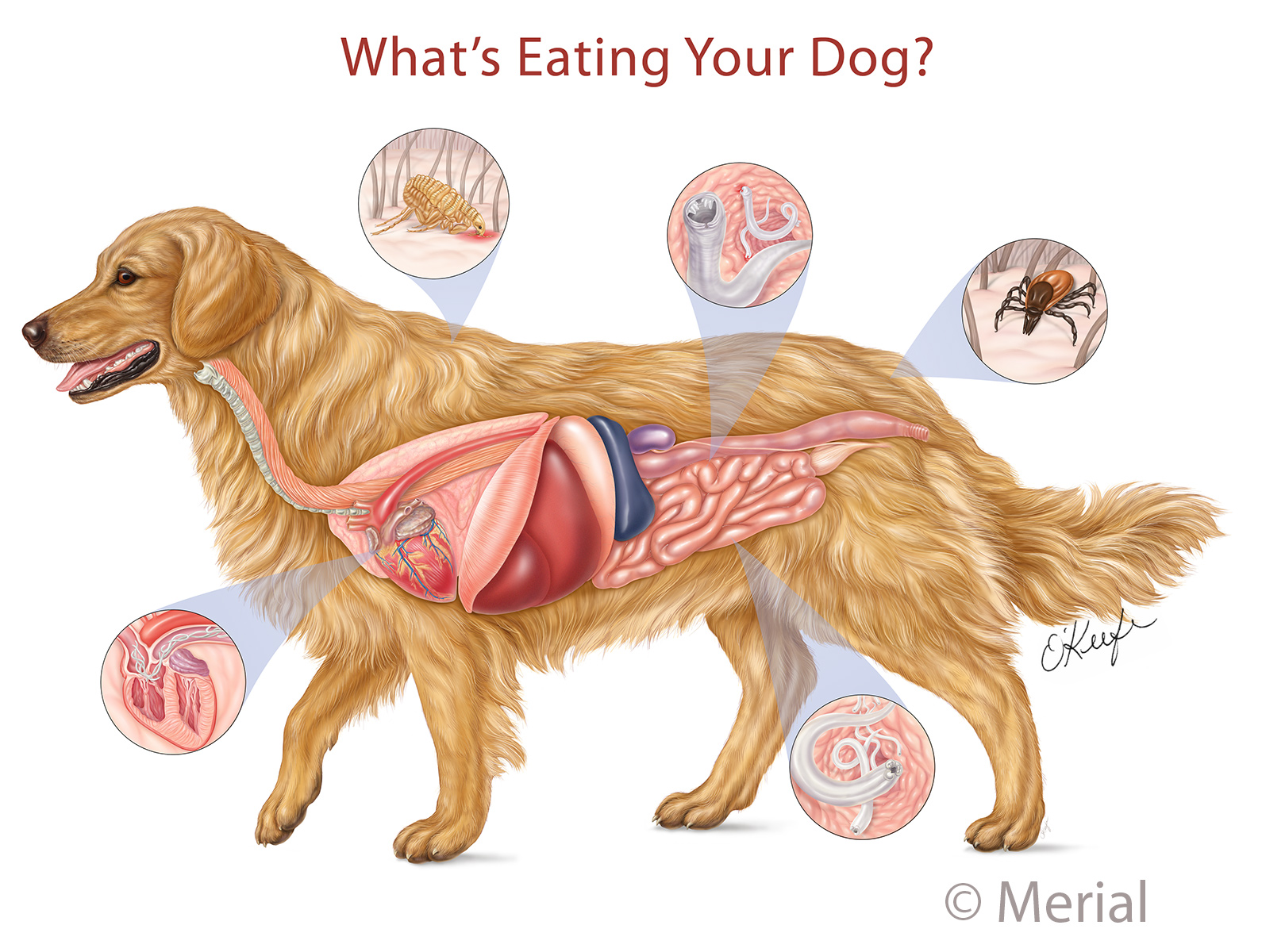
Dog Internal Anatomy Anatomical Charts & Posters
The Atlas is not intended to be an exhaustive review of anatomy, pathology, or medicine. For more information, consult the Bibliography, refer to prescribing information on specific drugs, or call Hill's Veterinary Consultation Service at 1-800-548-VETS (8387) or e-mail
[email protected]. The Atlas contains illustrations of the most. It provides information about a dog's skeletal, reproductive, internal, and external anatomy, along with accompanying labeled diagrams. After mating, dogs experience something called a copulatory tie, wherein they remain in the coital position. The male dog dismounts the female at this time. The dogs can remain in this position from a few. 2021 Ultimate Guide to Dog Anatomy. As the pace of veterinary advancement accelerates, even the most experienced veterinary teams are challenged to keep up with all the changes that impact their practice.. The cardiovascular system refers to the organs and vessels that allow blood to circulate nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, wastes and. The Anatomage Dog is the first highly detailed dog anatomy atlas that comprehensively features internal organs, including vascular systems and muscular-skeletal structures. Originating from real dog data, the Anatomage Dog exhibits the highest level of anatomical accuracy. All of its volumetric 3D and individual structures are segmented, users.
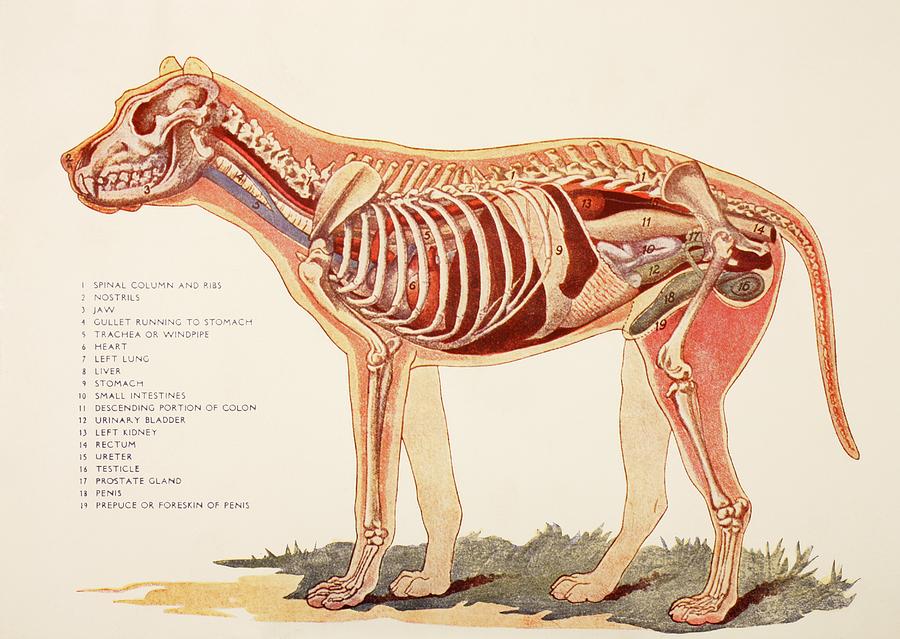
Internal Organs Of A Male Dog. From Photograph by Ken Welsh Pixels
Dog skeleton. As with any vertebrate animal, the skeleton of a dog has the function of supporting the body for movement and protecting its internal organs. We can divide the canine skeleton into three main sections: Axial skeleton: skull, spine, ribs and sternum bones. Appendicular skeleton: bones of the extremities. ISSN 2534-5087. This vet-Anatomy module presents an anatomy atlas of the abdomen and pelvis of the dog in CT. CT images are from a healthy 6-year-old castrated male dog. This module displays cross-sectional labeled anatomy images of the canine abdominal cavity and the pelvis on a Computed Tomography (CT) and 3D images of the abdomen of the dog.
Xiphoid region (Cranial abdominal region) Zygomatic bone. Zygomatic gland. Zygomatic region. Radiographic anatomy: labeled images in the transverse plane of a healthy dog's whole body, using tomodensitometry. Introduction to the anatomy of the skull, thorax, abdomen, pelvic cavity, muscles and blood vessels: main anatomical structures identified. Dog Anatomy Flash Cards by Bryan Edwards Publishing The Dog Anatomy is a comprehensive reference tool covering the skeletal system, muscular system, joints & ligaments, and the 10 major organ systems of the dog. This set consists of 47 flash cards.
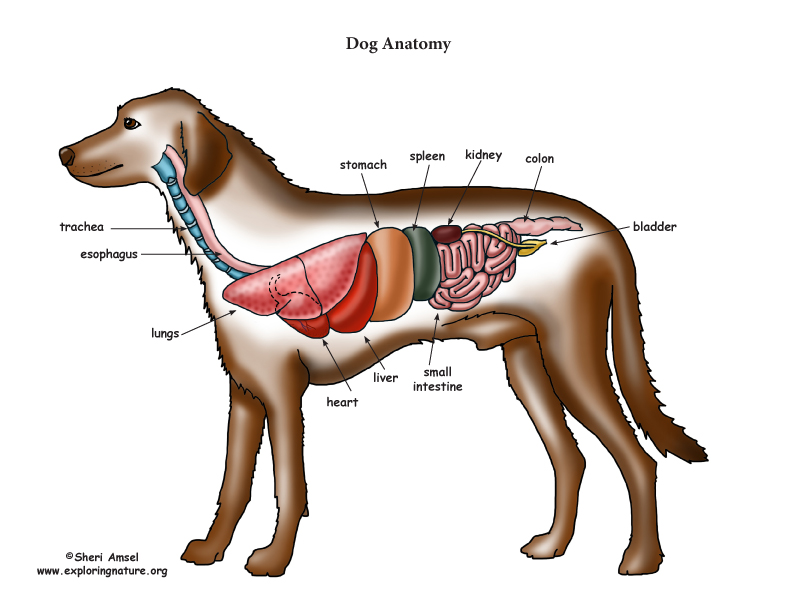
Dog Anatomy (Thoracic and Abdominal Organs)
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. This canine internal anatomy poster illustrates the internal anatomy of a dog in beautifully rendered detail. This dog organ anatomy poster has been designed exclusively for AnatomyStuff and is medically accurate, making it the perfect choice for display in a veterinary classroom or practice, or in a vet clinic for owner education.. This canine organs chart offers the following features:




