In order to calculate the formal charges for H2SO4 we'll use the equation:Formal charge = [# of valence electrons] - [nonbonding val electrons] - [bonding el. It has a molecular weight of 98.079 g/mol. H2SO4 works as an oxidizing and dehydrating agent. Furthermore, it's diprotic in nature which holds the capacity of releasing two protons together. It is colorless, odorless, and extremely corrosive in nature.
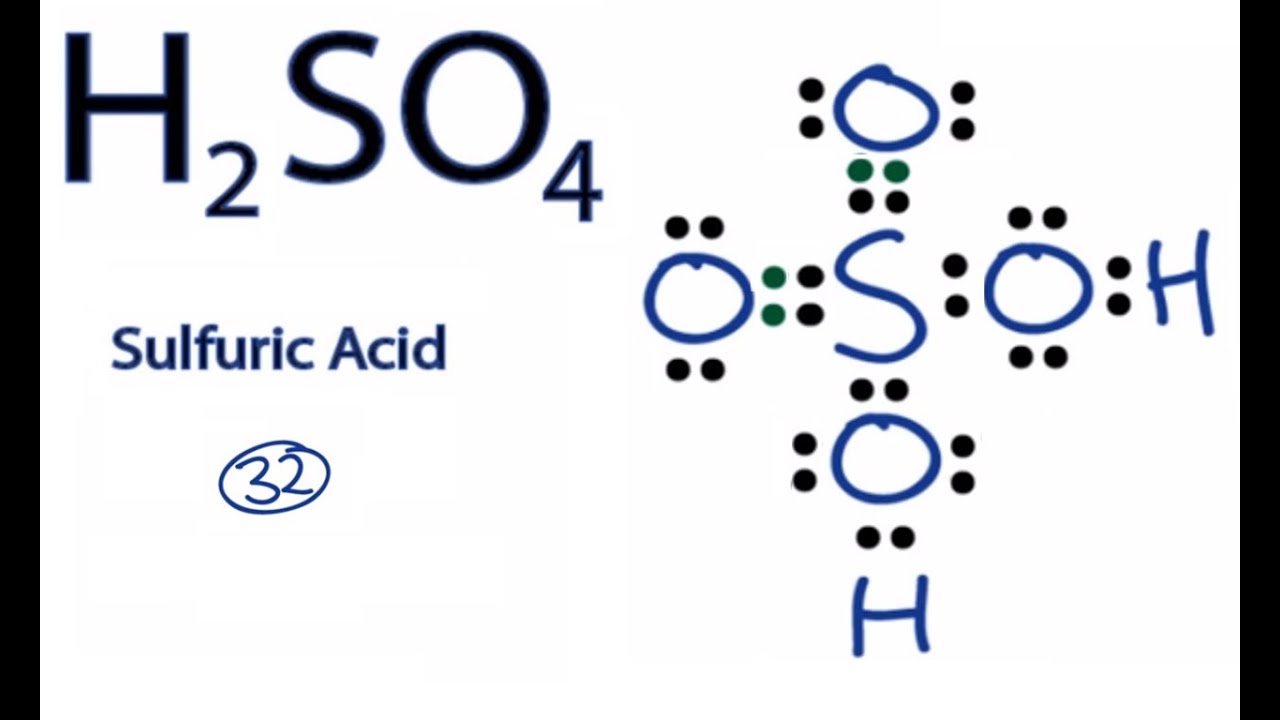
lewis dot structure for h2so4
Sulfuric acid is a dibasic strong acid. It means, it can release two hydrogen atoms to show acidic characteristics. Therefore, we can assume, there should be two -OH bonds in sulfuric acid molecule. Lewis structure of H 2 SO 4 Most stable lewis structure of H 2 SO 4 is shown below. Steps of drawing lewis structure of H 2 SO 4 Sulfuric acid ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling ), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen, and hydrogen, with the molecular formula H2SO4. It is a colorless, odorless, and viscous liquid that is miscible with water. [6] And Why? May 26, 2023 by Jay Rana The Charge of H2SO4 (Sulfuric acid) is 0. But the question is how can you say that the charge on H2SO4 (Sulfuric acid) is 0? Well you can say this by calculating its formal charge. So let's calculate the formal charge of H2SO4 (Sulfuric acid). Sulfuric acid is prepared industrially by the reaction of water with sulfur trioxide ( see sulfur oxide ), which in turn is made by chemical combination of sulfur dioxide and oxygen either by the contact process or the chamber process.

H2SO4 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, and Hybridization
Structural Formula. H 2 SO 4. sulfuric acid In this video we'll write the correct formula for Sulfuric acid.To write the formula for Sulfuric acid we'll use the Periodic Table, a Common Ion Table, and. Quantity Value Units Method Reference Comment; Δ r H°-132.3 ± 2.9: kJ/mol: RSC: Blanchard, Joly, et al., 1974: solvent: Sulphuric acid aqueous solution; The reaction enthalpy relies on -10.6 kJ/mol for the enthalpy of solution of EtOH(l) and on 35.1±0.1 for the enthalpy of solution of K2SO4(cr) Blanchard, Joly, et al., 1974.; MS In the H2SO4 Lewis structure, there are two double bonds and two single bonds around the sulfur atom, with four oxygen atoms attached to it, and on each. For sulfur atom, formal charge = 6 - 0 - ½ (8) = +2. For top oxygen and bottom oxygen atom, formal charge = 6 - 6 - ½ (2) = -1.

Draw the Lewis structure of sulfuric acid H2SO4 with minimized formal
How to calculate the formal charges on H2SO4 atoms? The formal charges can be calculated using the formula given below: The formal charge of an atom = [valence electrons of an atom - non-bonding electrons - ½ (bonding electrons)] The valence electrons (V.E) of an atom are the total number of electrons present in its valence shell. The acid-base strength of a molecule depends strongly on its structure. The weaker the A-H or B-H+ bond, the more likely it is to dissociate to form an H+ H + ion. In addition, any factor that stabilizes the lone pair on the conjugate base favors the dissociation of H+ H +, making the conjugate acid a stronger acid.
In the $\ce{H2SO4}$ molecule, two bonds are simple covalent ($\ce{S-OH}$ ones), and two are dative ($\ce{S-O}$ ones).. $\begingroup$ A structure with four double bonds in the sulphate ion would give the sulphur atom a formal charge of -2. This is not expected to be more stable than a configuration with two double bonds and two single bonds. Sulfuric Acid | H2SO4 or H2O4S | CID 1118 - structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological activities, safety/hazards/toxicity information, supplier lists, and more.
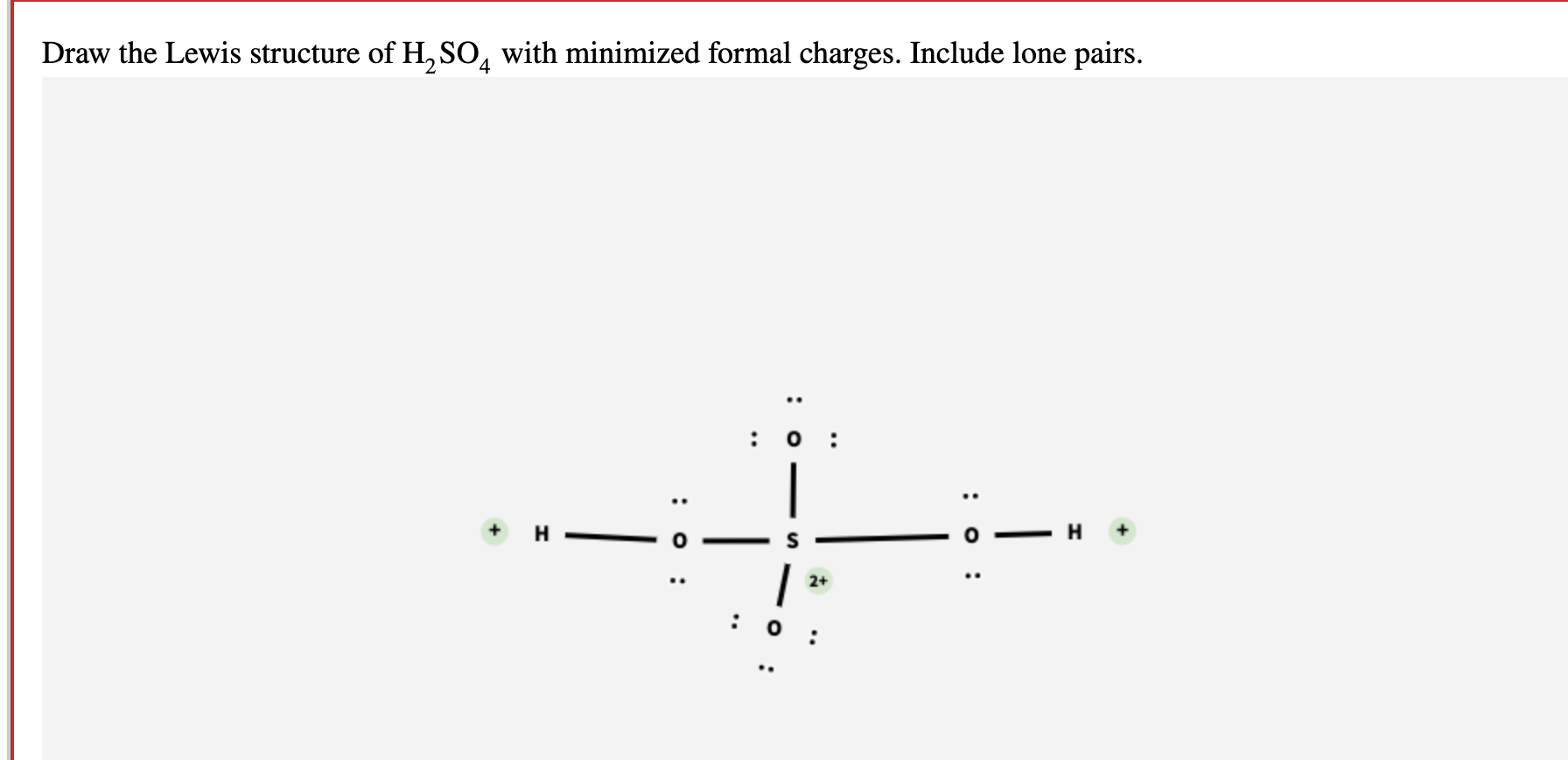
Solved Draw the Lewis structure of H2SO4 with minimized
By Biswarup Chandra Dey This article is regarding the most important acid, H2SO4 lewis structure, and its important facts. Let's start to discuss it. H2SO4 lewis structure is often known as Sulfuric acid. It is known as Oil of Vitriol. In most of the reactions in chemistry, we used sulfuric acid as a reagent. The acidity of H2SO4 is very strong. In order to calculate the formal charges for HSO4 - we'll use the equation:Formal charge = [# of valence electrons] - [nonbonding val electrons] - [bonding e.




