A diagram of a frogs heart. A look inside the heart of a Frog looking at key valves and parts of the heart. The heart of the African clawed frog has a double-inlet and single-outlet ventricle supporting systemic and pulmonary circulations via a truncus, and a lifespan of 25-30 years. We sought to understand the unique cardiac anatomic and physiologic characteristics, with balanced circulation and low metabolic rate, by comparing the basic anatomy.
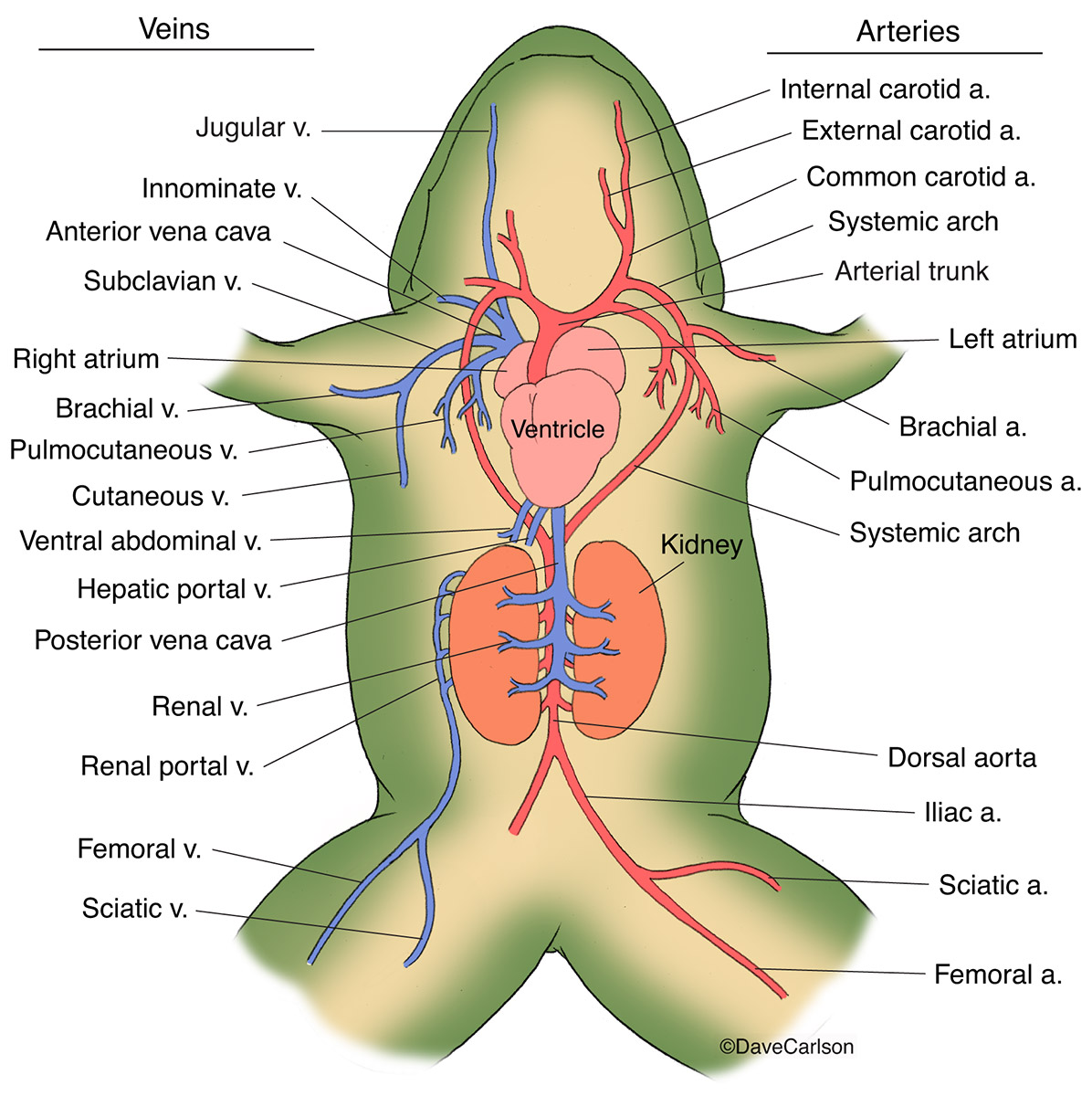
Frog Generalized Circulatory System Carlson Stock Art
Detailed Structure of Frog's Heart. Heart of frog is three chambered. It is dark red colored conical muscular organ situated mid-ventrally in the anterior part of the body cavity in between two lungs. The heart is enclosed in two membranes- an inner epicardium and outer pericardium. The space between these two layers is called pericardial cavity. I. Introduction. The heart of the frog has three chambers, one ventricle and two atria. Blood leaves the heart from the ventricle through a single truncus arteriosus which is short and soon branches into two aortic arches which loop left and right and dorsal to the heart to rejoin as a single aorta in the mid dorsal region of the body cavity. This study guide is easy to understand, yet has thorough information including a downloadable diagram of a frog's circulatory system and heart. Also covered is a full description of how the frog's three-chambered heart works. If you need to learn about this topic for a school project in science or biology, or you are just interested in frogs and their anatomy, then you will value. The heart of the African clawed frog has a double-inlet and single-outlet ventricle supporting systemic and pulmonary circulations via a truncus, and a lifespan of 25-30 years. We sought to understand the unique cardiac anatomic and physiologic characteristics, with balanced circulation and low metabolic rate, by comparing the basic anatomy structures with focused echocardiography and.

Illustrations and Movies iWorx Systems Inc
Dissection and Contraction of Frog Heart Rob MacLeod and Alex Brownell (
[email protected]) March 4, 2006 1 Purpose and Background 1.1 Purpose: To examine the anatomy and basic contractile physiology of the frog heart. Frog Artery. The primary function of the heart is to pump oxygen rich blood to organs such as the brain, liver, and kidneys as well as all other tissue. The heart of the frog is different from the hearts of warm-blood animals such as humans. Although mammals have four chambers, amphibians, which are cold-blood animals, have only three. Frogs are amphibians and have a closed circulatory system. Unless there is an abnormal mutation present, frogs only have one heart to pump blood throughout the body. A frog has a three-chambered heart. The chambers include two atria and a ventricle. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the veins. Article Shared by. ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about the origin of the frog heart beat with the help of suitable diagram. By separating atria from the ventricles of excised hearts, William Harvey in 1628 had shown that the atrial rhythm was higher than the ventricular rhythm. Keith and Flack (1907) have described that from.
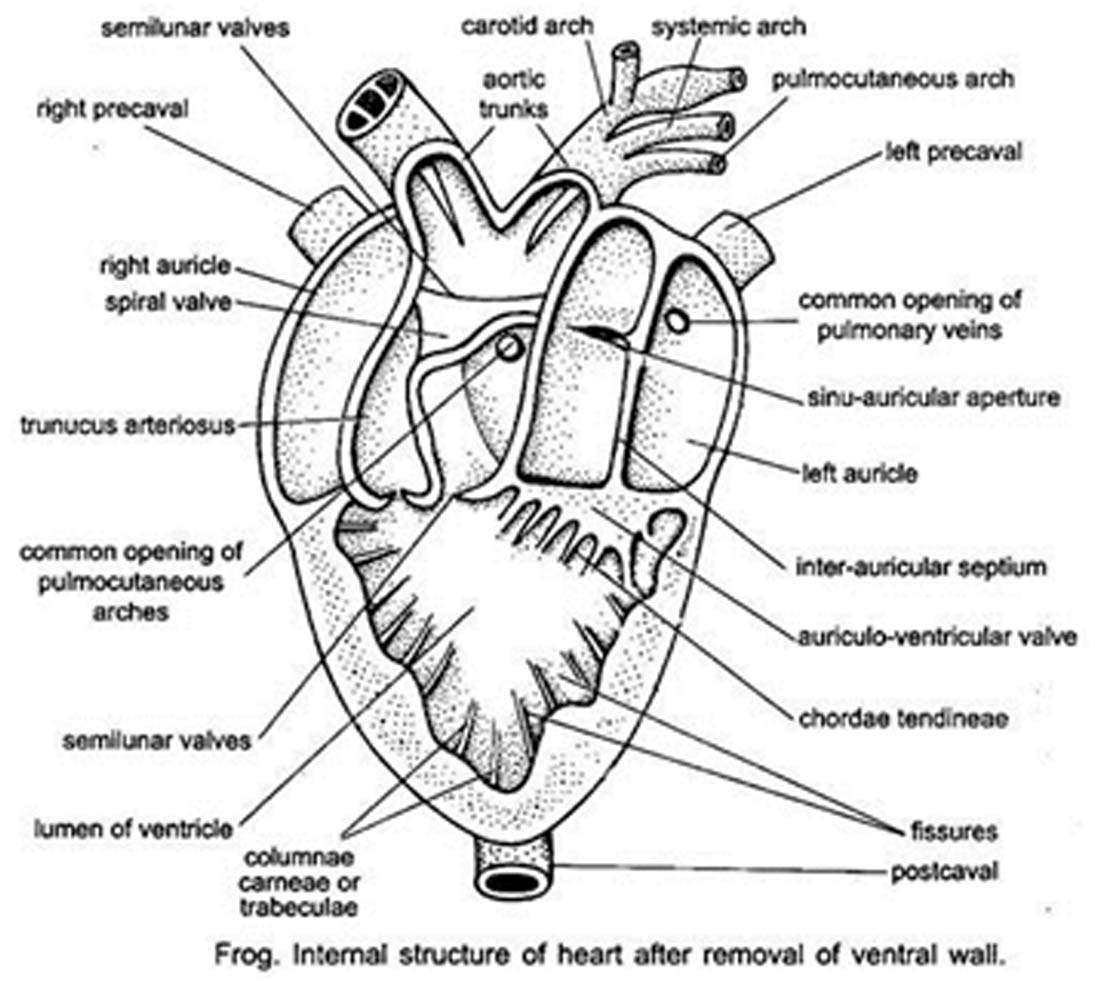
Comparative Zoology by Dr. Vidhin Kamble B. Sc I Comparative anatomy
The blood vascular system of frog is closed. It includes the heart, blood vessels, blood and lymphatic system. The prime function of this system is to distribute the digested food and oxygen to different parts of the body, in order to release energy to carry out life activities and also to bring the excretory and gaseous wastes to organs of. Human legs have two lower bones, the tibia and the fibula. In humans and frogs, the femur is the single upper leg (thigh) bone. A third division of the frog's leg consists of two elongated anklebones, or tarsals. These are the astragalus and the calcaneus. The astragalus corresponds to the human talus.
blood circulation in frog. The blood vascular or circulatory system of frog is closed. The circulatory system consists of: Heart: Arterial system. Venous system. Blood. Lymphatic system. Its main function is to transport all essential liquid and gaseous materials to the living tissues. 3. Renal portal system. The renal portal system is a specialized component of the circulatory system in frogs, playing a pivotal role in the transportation of blood to the kidneys. This system, along with other portal systems, showcases an intricate network of interconnected veins.
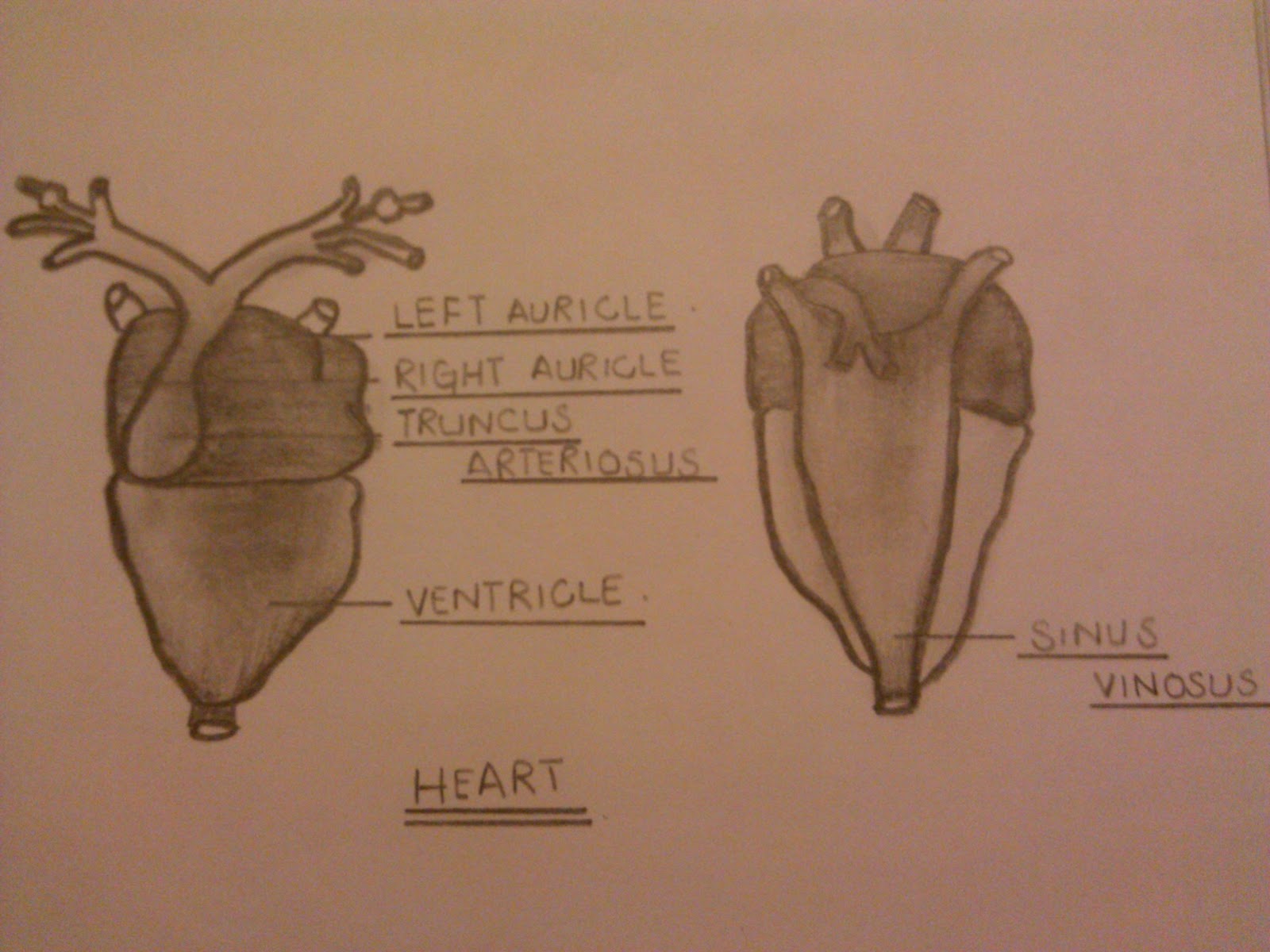
Isolated System Observation of heart of frog.
Frogs are a type of amphibians with a closed circulatory system.Hence, its blood only circulates through the blood vessels and heart. The circulatory system of frogs composes of two parts: the cardiovascular system and the lymphatic system.The main function of the cardiovascular system is to supply oxygen and nutrients to the tissues and to aid in the elimination of metabolic wastes while the. A frog's digestive system starts with their long, sticky tongues that they use to catch their prey. Inside their mouth, frogs also have small teeth, and a set of two larger teeth. These are not really used to chew since frogs swallow their prey alive and whole. Their teeth are used mostly to keep back their prey.




