Definition A disposition is a general, relatively stable inclination to approach new learning tasks and situations in a particular way. Researchers have identified a variety of dispositions that have an impact on learning and performance, sometimes for the better and sometimes for the worse. Dispositions are a complex interplay of behaviours, not a singular attribute or response. Learning as a highly complex act will comprise a combination of dispositions and each disposition such as creativity will demand multiple individual skills harnessed for a common goal.
Learning Dispositions in Early Childhood Blog
Dispositions some dispositions can be positive less helpful or negative than others - Dispositions children's learning encouraged and are not strengthened, development. can be over time. Learning dispositions can be understood as enduring habits of mind and actions that affect how students approach learning. The EYLF goes on to explain dispositions as "tendencies to respond in characteristic ways to situations, for example, maintaining an optimistic outlook, being willing to persevere, approaching new experiences with confidence." A child's disposition to learning affects the attitude with which they learn. This, in turn, directly affects the effort that they are willing to put in. In this way, having positive learning dispositions goes a long way to creating positive learning outcomes. Encouraging Positive Learning Dispositions in Students The term 'learning dispositions', sometimes called 'habits of mind' or 'dispositions to learning', refer to the way in which learners engage in and relate to the learning process. Learning dispositions affect how students approach learning and therefore the outcomes of their learning.
Learning Dispositions ELDERSLIE PUBLIC SCHOOL VISIBLE LEARNING
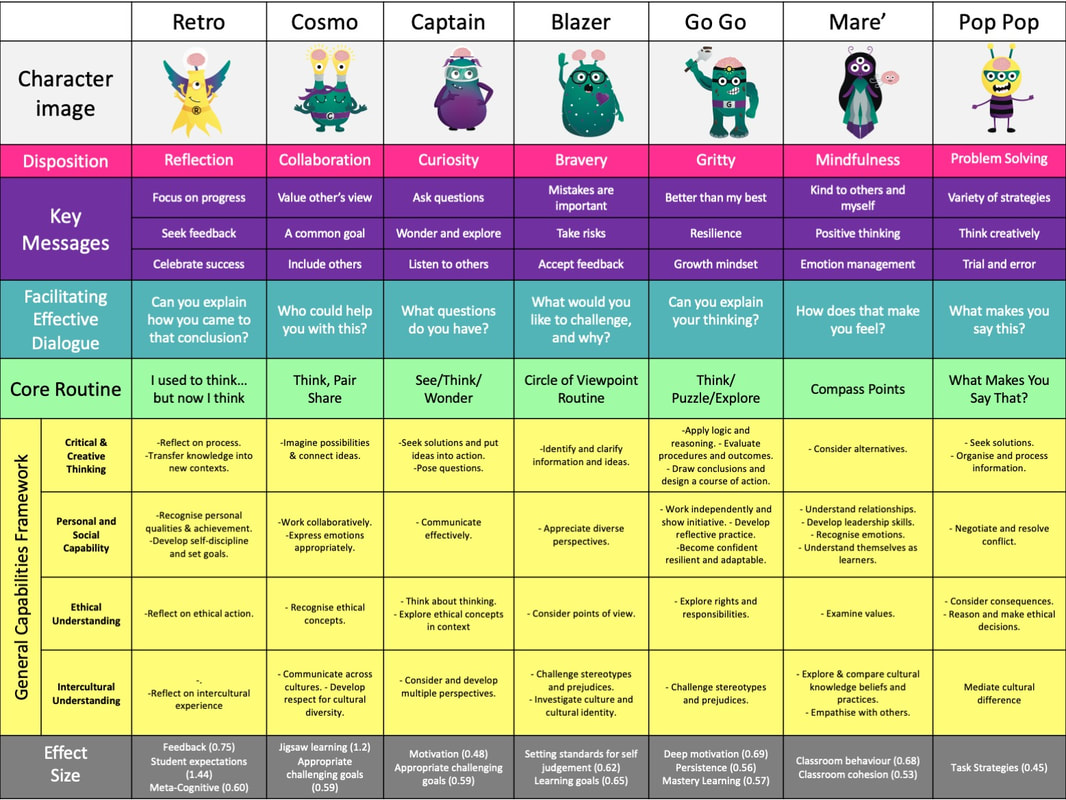
The Learning Disposition Wheel is based on extensive research in psychology and education and informed by Self-Determination Theory. It is a coherence maker or schema that identifies the dispositions needed for deeper, self-regulated and transferable learning. These dispositions can be learnt and taught through mindfully selected pedagogical. For the purpose of my research, a disposition was defined as a prevailing cognitive and emotional state towards the content being learned and toward the learning process. It assumed that a disposition was not a fixed trait. Rather, a disposition could be learned or acquired and was dynamic and flexible. Dispositions as an aspect of the mind more so than environment are referred to variously as intellectual habits, mindsets, habits of mind, thinking dispositions, learning dispositions, ways of knowing, key competencies, and learning power, according to Carr, et al. 2009. Although to be useful for learning, dispositions must be acted on within a. This article describes an emerging theoretical framework for examining relationships between learning dispositions and learning architecture. Three domains of learning dispositions — resilience, reciprocity and imagination — are discussed in relation to the structures and processes of early childhood education settings and new entrant classrooms.

Fostering Positive Learning Dispositions In the Classroom Teach Starter
Learning dispositions refer to cognitive and emotional habits that an individual has formed in relation to learning (e.g., curiosity, resilience, etc) Learning techniques are the actions that students take during, in preparation for, or following, learning (e.g., note taking, retrieval practice, meditation, learning journals) The relationship. Dispositions of effective learners include independence, confidence, curiosity and persistence. Other dispositions for learning are self-control, optimism, self-motivation, resilience, problem-solving and, in some cases, courage and risk-taking. All these habits of the mind are important for lifelong learning. Dispositions affect how children.
Print Why Children's Dispositions Should Matter to All Teachers This article explores the link between effective learning and children's dispositions and habits. The authors provide examples that teachers may use to help strengthen children's independence, creativity, motivation, and resilience. Last updated: 29-Mar-2023 Explore the evidence and practices that promote and nurture development of positive dispositions for learning in literacy and numeracy.

Fostering Positive Learning Dispositions In the Classroom Singapore
Positive dispositions like curiosity, cooperation, creativity, persistence and enthusiasm help children to learn and grow. We explore how to encourage these dispositions and why they are important. Learning dispositions refer to how children engage in and relate to the learning process. Learning dispositions give us one set of tools to develop a good foundation of learning skills in the early years. What are learning dispositions? The following are the most common learning dispositions that parents will encounter in early learning centres in New Zealand: courage and curiosity trust and playfulness




