The dog nose anatomy comprises external features and the structures of the nasal cavity. From the external part of a dog's nose, I will show you the features of cartilages, vomeronasal organs, and ligaments. Again, you will find the details anatomy of the nasal conchae, meatus, paranasal sinuses, and glands from the dog's nasal cavity. The dogs nose begins at the nasal planum, this is the hairless, pigmented area that is visible externally and is often referred to as the 'button' of the nose. A thick layer of keratinized epidermis covers the external dog nose and the nose is kept moist by secretions produces by the nasal glands. Nasal planum - button of the dog's nose.
The Respiratory System Veterian Key
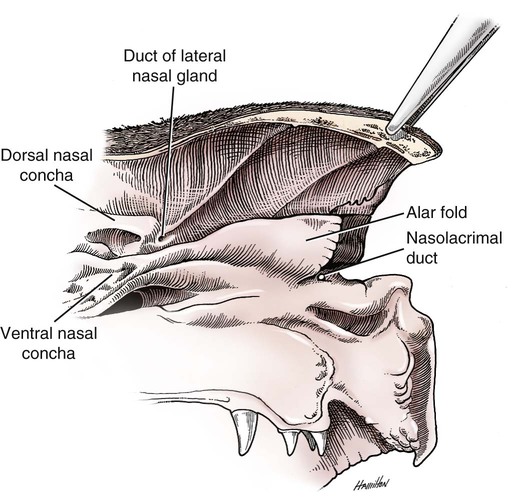
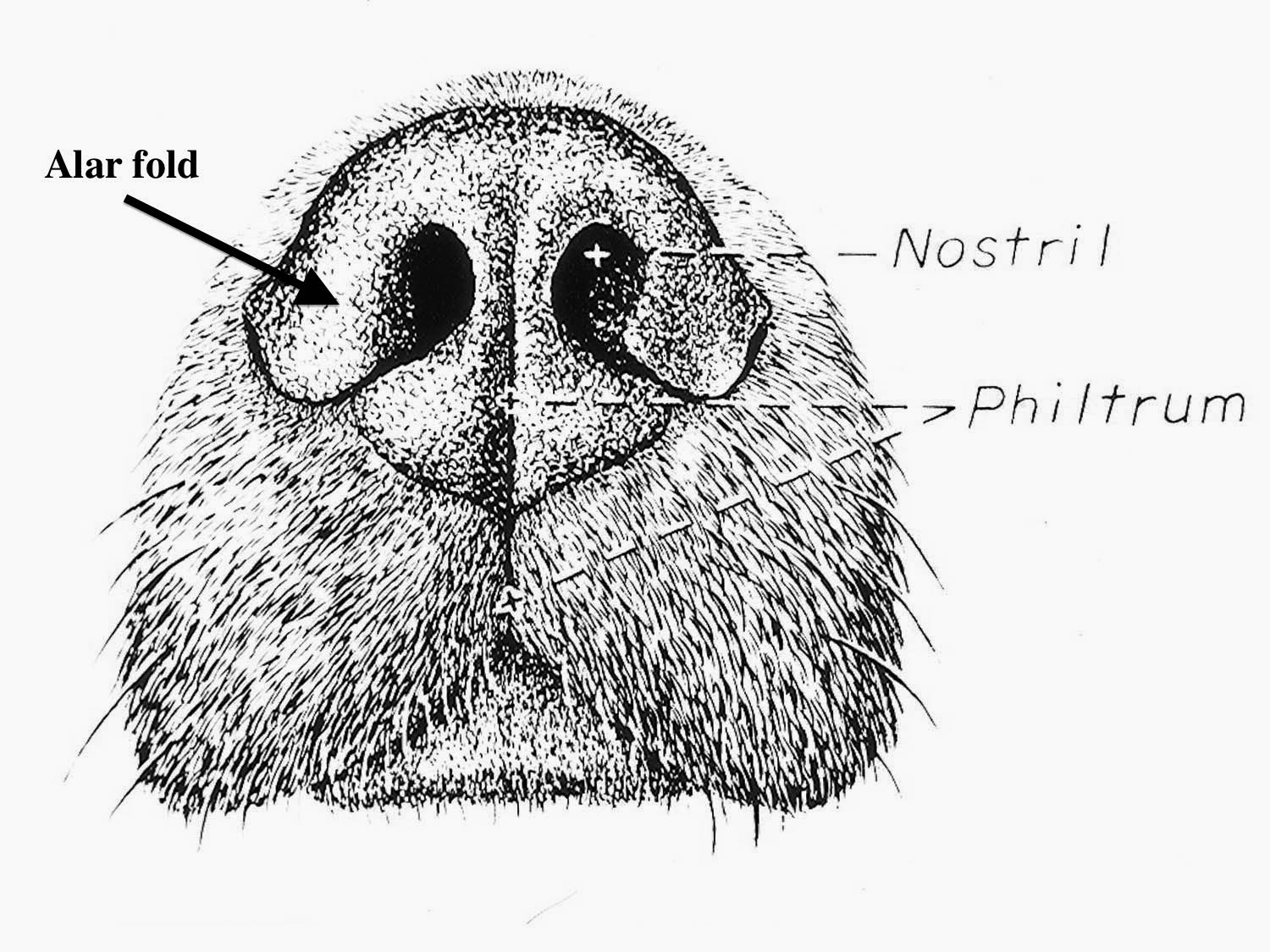
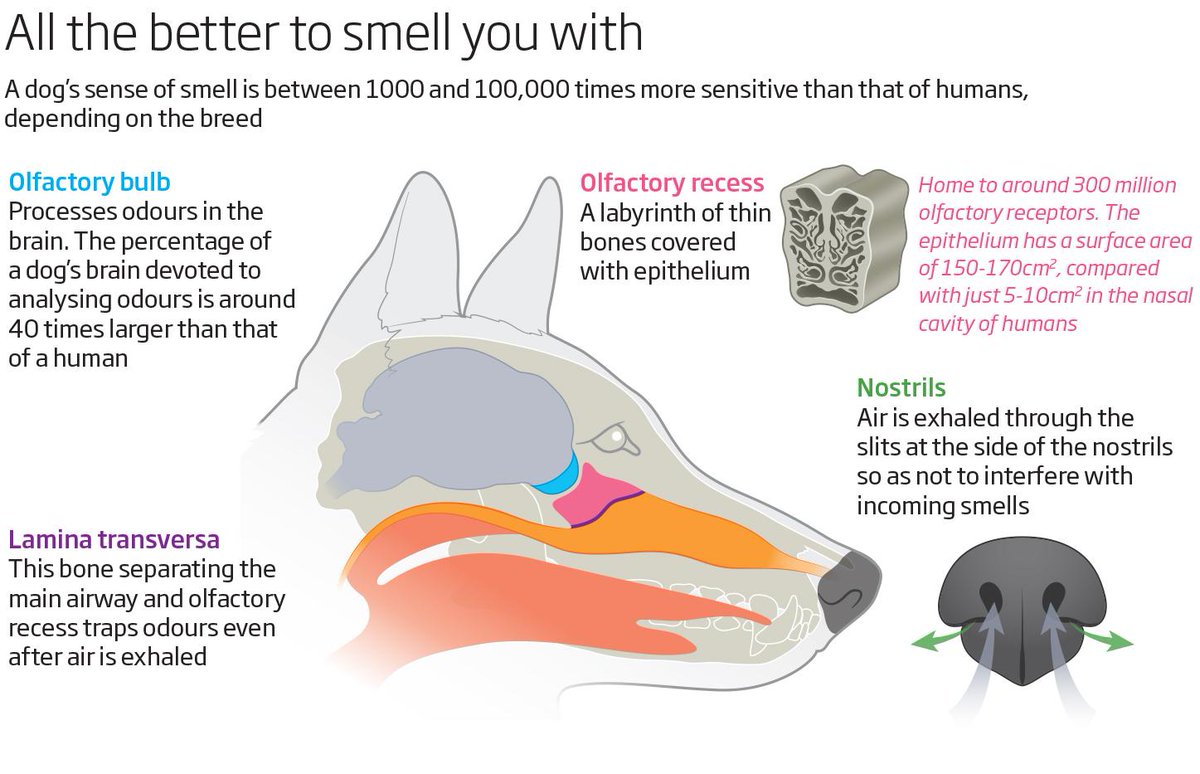
Nose The nasal cavity begins at the nostril, ends at the choanae, and is divided longitudinally by the nasal septum into two nasal fossae. The nasal planum is the pigmented, hairless, rostralmost surface of the external nose. The philtrum is the midsagittal external crease in the nasal planum. The essentials A dog's nose knows — A dog's sense of smell is incredibly powerful and is exponentially stronger than our own. This is thanks to their up to 300 million olfactory receptors, compared to a mere six million in humans. Facts About Your Dog's Nose and Amazing Sense of Smell. Here are eight more interesting facts about your dog's sense of smell that prove that canines have superior noses. 1. A dog's nose has two functions—smelling and breathing. According to Dr. Nappier, a canine's nose has the ability to separate air. Canine nose power has fascinated humans for eons. We're probably just jealous, since our noses pick up tiny fraction of what our dog's noses easily gather. Dog noses have two purposes, breathing and gathering info. All mammals have turbinates, which are bony, curly scroll-shaped plates, that air flows over in the breathing process.
Veterinary Key Points Surgical Correction of Stenotic Nares Or how to
A dog's nasal cavity is divided into two separate chambers and opens into two nostrils, or nares, that can wiggle independently and that can take in smells separately. As a dog sniffs, particles and compounds are trapped in the nasal cavity by mucus while scent receptors process them. The dog's nose is kept moist by lacrimal (tear) and nasal gland secretions. The moist nose allows the dog to inhale a larger number of scent molecules. Once the scent is captured, it is dissolved and transported to the olfactory (scent) region inside the nose. The olfactory receptor cells are located in this region. The dog has two nostrils (nares) divided by a cartilaginous and bony septum. The tip of the dog's nose - rhinarium - is typically moist and cool to touch. When a dog flares its nostrils to sniff, the shape of the nostril openings change thus allowing redirection of air into the upper part of the snout and more direct airflow to the olfactory area. Adams and Hotchkiss (1983) described the nasal mucosa of the dog. The nasolacrimal duct (ductus nasolacrimalis) carries the serous secretion from the conjunctival sac to the nasal vestibule (Fig. 8-4). A characteristic of a healthy dog is a moist nose, which is maintained in part by the combined secretions of the lacrimal and lateral nasal glands.
Part 5 Understanding Your Dog's Senses Woofalicious Tales
Quick idea: in this article, you will learn the location of different organs from the different systems (like skeletal, digestive, respiratory, urinary, cardiovascular, endocrine, nervous, and special sense) of a dog with their important anatomical features. Dog anatomy comprises the anatomical studies of the visible parts of the body of a domestic dog.Details of structures vary tremendously from breed to breed, more than in any other animal species, wild or domesticated, as dogs are highly variable in height and weight. The smallest known adult dog was a Yorkshire Terrier that stood only 6.3 cm (2.5 in) at the shoulder, 9.5 cm (3.7 in) in length.
Nasal cavity The nasal cavity is essentially a tube with a wall established by several bones of the skull. The borders of the nasal cavity are as follows: Caudal: The cribrifrom plate of the ethmoid bone . Ventral: Continuous with the nasopharynx. Dorsal: The maxilla and the palatine processes of the incisive bone . A dog's nose knows In the dog the sense of smelling, the olfactory system, is the main special sense and it is extremely sensitive and efficient. Possibly 30% of their brain is dedicated to analysing odour. It is estimated that the percentage of a dog's brain devoted to analysing odours is 40 times larger than that of a human. [1]

Dog Throat Anatomy With Diagram Pharynx And Larynx Anatomylearner
The nose is positioned in the center of the face. The structure and length of the nose varies greatly in dogs. In dolichocephalic breeds of dogs (e.g. collie, Doberman pinscher, German shepherd dog), the nose is quite long and prominent. In brachycephalic breeds of dogs (e.g. pug, Pekingese, Lhasa apso, bulldog), the nose is quite short and. This modules of vet-Anatomy provides a basic foundation in animal anatomy for students of veterinary medicine. This veterinary anatomical atlas includes selected labeling structures to help student to understand and discover animal anatomy (skeleton, bones, muscles, joints, viscera, respiratory system, cardiovascular system).




