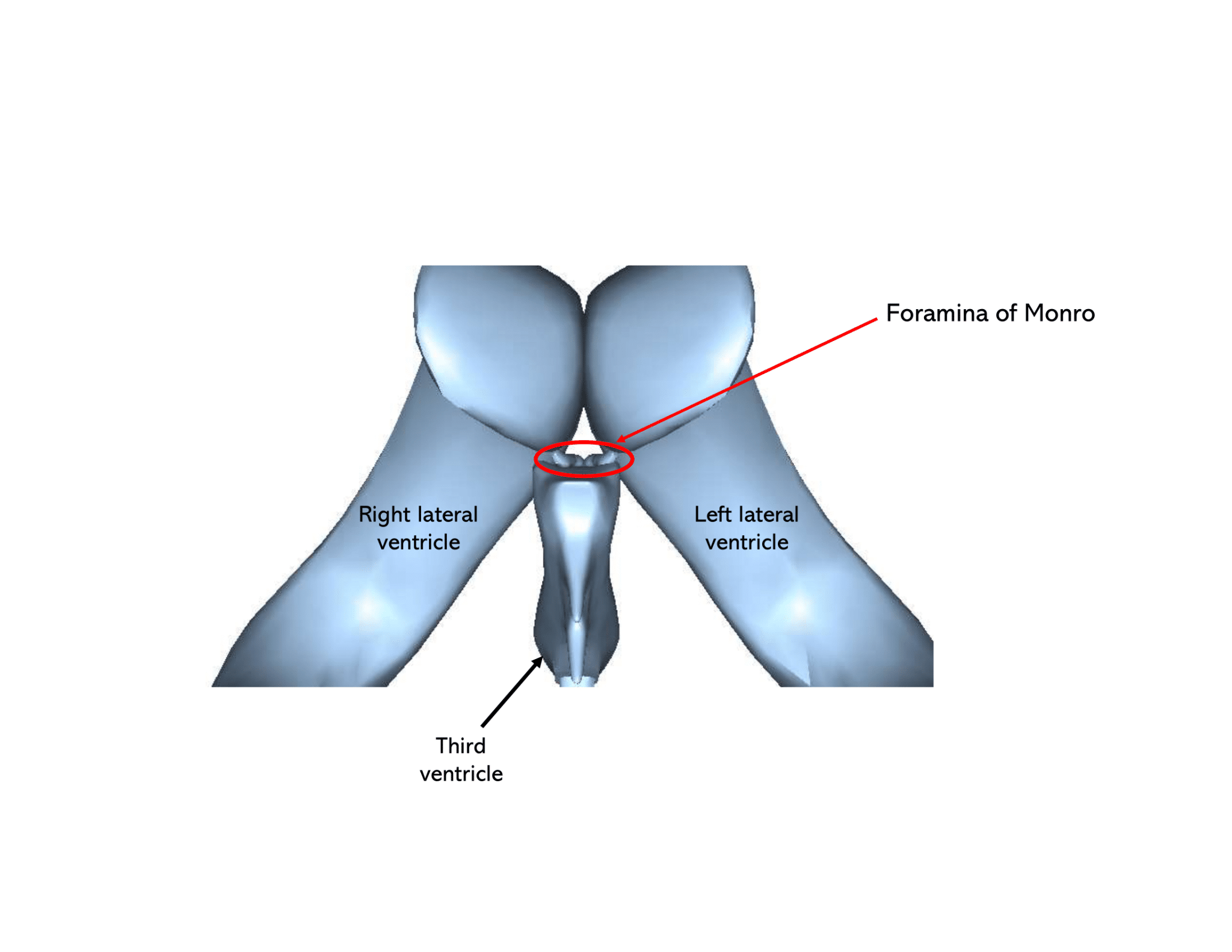
The interventricular foramen, also known as foramen of Monro , is part of the ventricular system and the connection between the third ventricle and the lateral ventricle . These paired foramina allow for the flow of cerebrospinal fluid between lateral ventricles and third ventricle s, and effacement or blockage results in non-communicating. The Foramen of Monro may be small, but it plays a significant role in brain health and function. Its involvement in cerebrospinal fluid circulation makes it a critical structure to monitor through imaging techniques like MRI and CT scans. By understanding the importance of the Foramen of Monro and its potential variations or.

Illustration showing boundaries of the right foramen of Monro as
In the brain, the interventricular foramina ( foramina of Monro) are channels that connect the paired lateral ventricles with the third ventricle at the midline of the brain. As channels, they allow cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) produced in the lateral ventricles to reach the third ventricle and then the rest of the brain's ventricular system. The differential diagnosis of masses arising from the foramen of Monro can be approached depending on the age of the patient. Pediatric choroid plexus papilloma adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma germinoma glioma Langerhans cell histiocytos. Introduction The foramen of Monro lies at the junction between the paired lateral ventricles and the third ventricle of the brain. Methods A comprehensive review of the literature was performed focusing on the foramen of Monro. Conclusions A good understanding of the anatomy of the foramen of Monro is essential for the neurosurgeon, especially with the increasing use of intraventricular endoscopy. The interventricular foramen (or foramen of Monro) is a Y-shaped channel that connect the paired lateral ventricles with the third ventricle. The third ventricle is the narrow vertical cavity of the diencephalon. It is drained by the cerebral aqueduct (of Sylvius) that conveys CSF into the fourth ventricle.
The Ventricular System Neuroanatomy CSF Geeky Medics
Its lateral wall, on either side, is indented by the hypothalamic sulcus running from the foramen of Monro to the opening of the cerebral aqueduct of Sylvius. It should also be noted that the foramen of Monro provides a passage way for the choroid plexus of the lateral ventricles to enter the third ventricle. The plexus then resides in a groove. Introduction: The foramen of Monro lies at the junction between the paired lateral ventricles and the third ventricle of the brain. Methods: A comprehensive review of the literature was performed focusing on the foramen of Monro. Conclusions: A good understanding of the anatomy of the foramen of Monro is essential for the neurosurgeon, especially with the increasing use of intraventricular. The interventricular foramen (aka Foramen of Monro) is a short passage extending from the lateral ventricle to the third ventricle, allowing for the drainage of cerebrospinal fluid from the lateral ventricles to the third ventricle. Complete Anatomy. The world's most advanced 3D anatomy platform. The foramen of Monro ( Fig. 5.1) is a short conduit connecting the paired lateral ventricles with the third ventricle of the brain. This deep structure becomes clinically significant when obstructed as this leads to obstructive (noncommunicating) hydrocephalus. Obstruction at the foramen of Monro arises from numerous etiologies, including.

Measuring the dimensions of the Foramen of Monro. In this example, the
The choroidal fissure forms a C-shape extending from the foramina of Monro to its inferior terminal point, which is termed the "inferior choroidal point." 9,15 Within the atria, there is a prominent triangular tuft called the glomus. 15 The tela choroidea is an invagination of the pia mater and ependyma, which gives rise to the choroid plexus within the choroidal fissure and along the roof. In the brain, the interventricular foramina (or foramina of Monro) are channels that connect the paired lateral ventricles with the third ventricle at the midline of the brain. As channels, they allow cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) produced in the lateral ventricles to reach the third ventricle and then the rest of the brain's ventricular system. The walls of the interventricular foramina also.
Foramina of Monro; Columns of fornix; Anterior commissure ; Lamina terminalis; Optic recess ; Optic chiasm ; Note that the foramen of Monro is located at the junction between the anterior wall and the roof of the third ventricle. When the brain is viewed from the frontal aspect, only the inferior two-thirds of the anterior wall are visible. masses at the foramen of Monro and extend into the lateral or third ventricles. Subependymoma Subependymoma (WHO grade I) is a rare slow-growing tumor most commonly occurring in the fourth ventricle of middle-aged to elderly patients [4]. Supratentorially, it favors the foramen of Monro and appears as a small (<2 cm), lobu-

Occlusion of one Monroi foramen leads to unilateral hydrocephalus
The foramen of Monro has also been referred to by the name of interventricular foramen. The structures comprising this foramen are the anterior part of the thalamus, the fornix and the choroid plexus. Findings: A sellar/suprasellar mass-like (long arrow) and rim calcifications (short arrows) impinging on the foramen of Monro causing hydrocephalus. (b): 20-year-old male with pineocytoma. Findings: A mass in the pineal gland (short arrows) with peripheral calcification (long arrow). (c): 13-year-old boy with pineal teratoma.




