A four-stroke (also four-cycle) engine is an internal combustion (IC) engine in which the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft. A stroke refers to the full travel of the piston along the cylinder, in either direction. The four separate strokes are termed: Intake: Also known as induction or suction. Spark Step 1: Intake Stroke Air and fuel enter the small engine through the carburetor. It's the job of the carburetor to supply a mixture of air and fuel that will allow for proper combustion. During the intake stroke, the intake valve between the carburetor and combustion chamber opens.
FileFour stroke engine diagram.jpg Wikimedia Commons
Physics Heat Introduction Classification Four Stroke Engine Four Stroke Engine A four-stroke engine is an internal combustion engine that utilises four distinct piston strokes (intake, compression, power, and exhaust) to complete one operating cycle. A complete operation in a four-stroke engine requires two revolutions (720 0) of the crankshaft. 1. Intake stroke Intake stroke is a process where gas (a mixture of air and fuel with a certain level) are inserted into a room inside the engine, this room called a combustion chamber. The way it works, it starts from the piston whose position is on the TDC (top dead center). The pressure volume diagram (PV diagram) that models the changes the fuel-air mixture undergoes in pressure and volume in a four stroke engine is called the Otto cycle. The changes in these will create heat, and use this heat to move the vehicle or machine (hence why it's a type of heat engine ). Diagram of four-stroke engines: The Otto cycle Nikolaus August Otto encountered the internal combustion engine built in Paris by Belgian expatriate Jean Joseph Etienne Lenoir. Lenoir successfully accomplishes the double-acting engine that works with an illuminating gas at 4% efficiency and produces only two horsepower.

1. Four stroke diesel engine Download Scientific Diagram
In a four-stroke engine, the four strokes are: 1) Intake Stroke Starting from "Top Dead Center" (TDC), and zero degrees of rotation, the piston moves down the cylinder. As the piston moves it creates a vacuum and the intake valve opens, sucking air into the cylinder. A four-stroke engine is an internal combustion engine in which the piston rotates the crankshaft four times. A stroke is the complete travel of the piston along the cylinder in each direction; four strokes are used in a four-stroke engine: Suction, Compression, Power, and Exhaust. A 4-stroke engine is an IC engine that uses four strokes of the piston to complete a working cycle. It converts the thermal energy of the fuel into useful mechanical work due to the upward and downward movement of the piston. Therefore, it belongs to the category of the reciprocating engine. Nikolaus Otto Alphonse Beau de Rochas Related Topics: four-stroke cycle, principle by which most modern automobile engines function. As illustrated by the figure, while the inlet valve is open, the piston first descends on the intake stroke.

The sequence of events in a fourstroke diesel engine involves a Stock
Speed 10 fps The four strokes of the cycle are intake, compression, power, and exhaust. Each corresponds to one full stroke of the piston; therefore, the complete cycle requires two revolutions of the crankshaft to complete. Intake During the intake stroke, the piston moves downward, drawing a fresh charge of vaporized fuel/air mixture. Four stroke engine working. To give you an idea of how fast this process occurs. A normal bike or scooter engine usually runs at around 4000 to 6000 rpm. That means 4000 to 6000 rotations of the crankshaft per minute. So in one second, the rotation of the crankshaft is. 4000/60 = 66.6 rps 4000 / 60 = 66.6 rps.
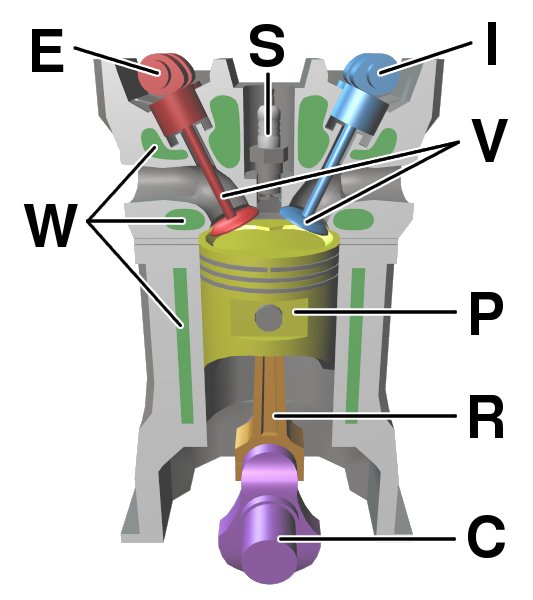
4 Stroke Combustion 4K SLOW MOTION | 33,000 FPS | Clear Engine Cylinder This videos illustrates the working of 4 stroke engine, with all the four strokes explained and also at the. An engine which completes four strokes into one power stroke or to complete one cycle is called four stroke engine. The crankshaft completes one revolution in two strokes. So it rotates two revolution in four strokes engines. Parts: 1. Piston 2.

The 4 Strokes of an Engine
Four stroke diesel engine diagram: Four stroke diesel engine working principle: The four stroke diesel engine works on the Diesel cycle. The four processes in the Diesel engine are as follows:- Process 1-2: Isentropic compression Process 2-3: Constant pressure heat addition Process 3-4: Isentropic expansion A four-stroke cycle engine is one of the most common type of small engine which is found completing five Strokes in a singly operating cycle which includes intake, compression, ignition, power, and exhaust strokes. 1. Intake Stroke: ( 4 Stroke Engine ) The intakes required whenever there is a need of air-fuel mixture inside the combustion chamber.




