Green tree python teeth are replaced throughout the snake's life, ensuring they always have sharp teeth for hunting. When they lose a tooth, a new one grows in its place. This continuous replacement is vital for the snake's survival, as damaged or worn teeth would hinder its ability to catch and eat prey. For different species of pythons such as ball pythons, they have around 150 teeth which is more in comparison to the number of teeth which green tree pythons have. Ball python's teeth have a length of about 0.4 in (1 cm) and they have a hooked shape. Green tree python teeth size is about 0.4 in (1 cm) or less and the length can be different.
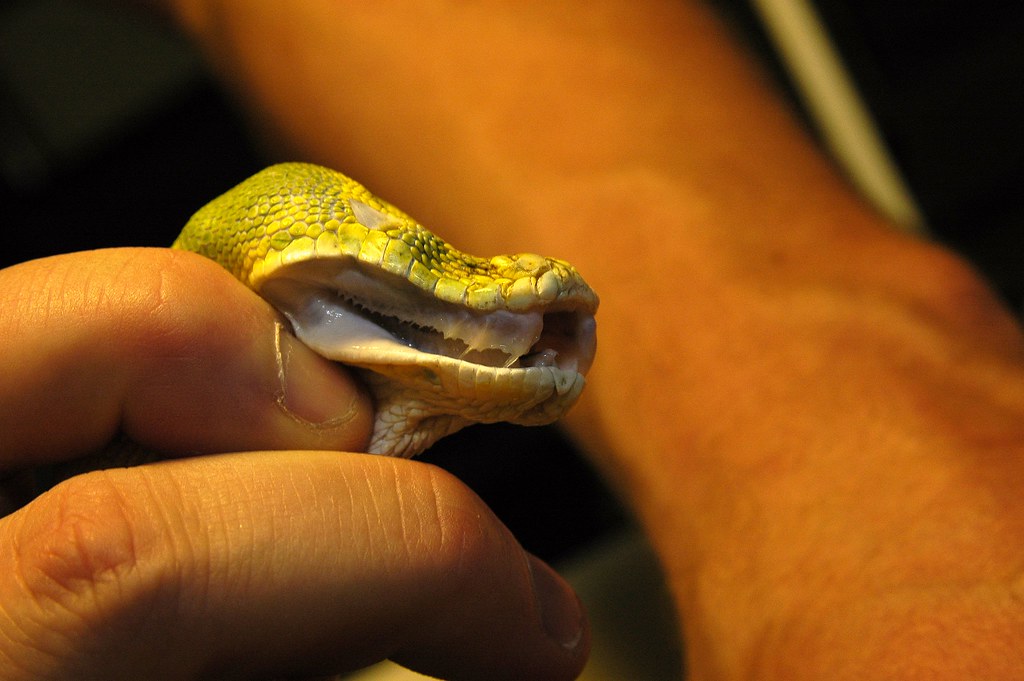
Green Tree Python Teeth The owner of the table gave me a s… Flickr
Green tree pythons are found in New Guinea, eastern Indonesia, and the northeast Cape York Peninsula of Australia. They prefer tropical rainforests with thick vegetation and high humidity. They may also inhabit secondary forests and gardens. Most of their time is spent in trees, but they also come down onto the ground, especially at night. No, green tree pythons do not have fangs. These captivating reptiles are actually non-venomous and rely on their constricting abilities to subdue prey. What they do have are rows of small, backward-curving teeth designed to grip onto their prey effectively. So while they might not be equipped with fangs for injecting venom, their teeth still. The impressive teeth help a green tree python maintain its grip while struggling prey amongst the dense rainforest branches in its natural habitat. Types. One of the major characteristics of a green tree python is a slim, triangular body, and a visible spine, with a relatively long tail accounting for approximately 14% of the reptile s total. Green tree python teeth curve backward and dig in deep to hold onto prey. They have over 100 long, curved teeth. Their bites are painful and can require medical attention. Green tree pythons detect prey using their labial pits, or heat-sensing pits. They're diet generalists, but mainly eat mammals and small reptiles. Like other python species.
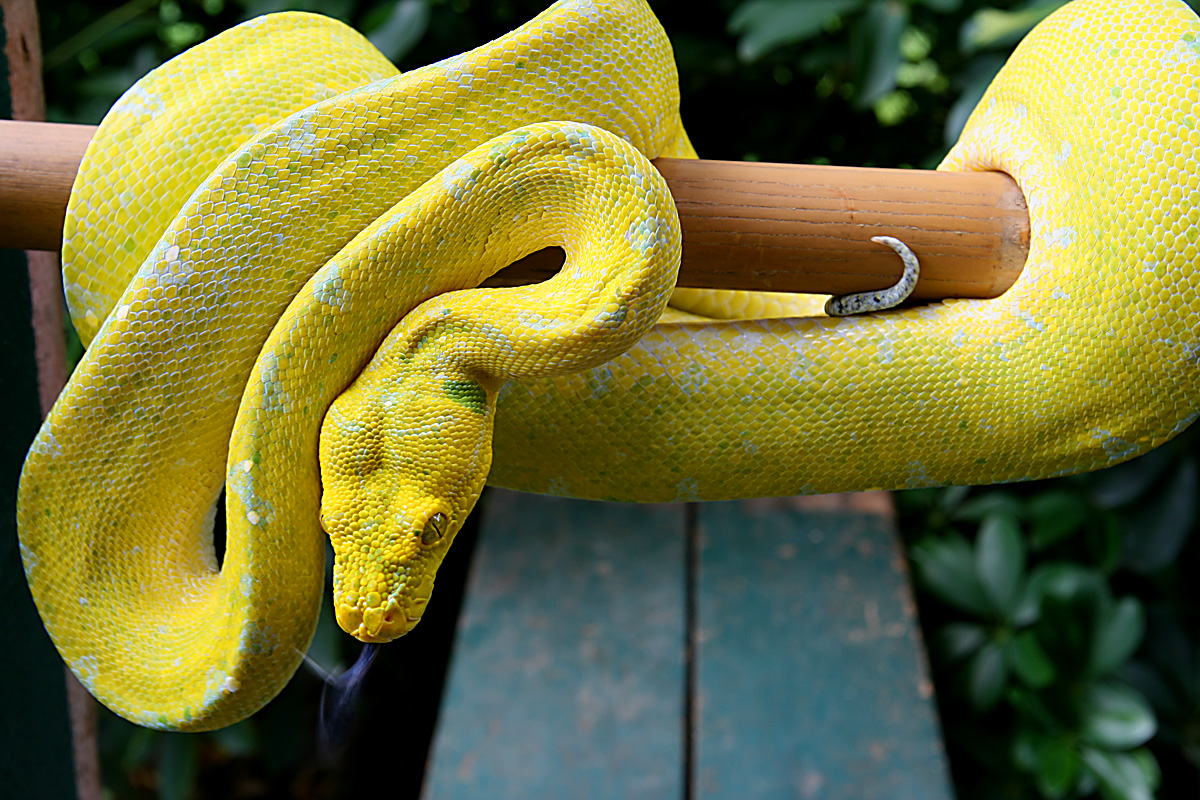

Tree Python Teeth
The green tree python (Morelia viridis), also known as the emerald green python, is a species of snake in the family Pythonidae.The species is native to New Guinea, some islands in Indonesia, and the Cape York Peninsula in Australia.First described by Hermann Schlegel in 1872, it was known for many years as Chondropython viridis.As its common name suggests, it is a bright green snake that can. Diet and Feeding Schedule. Green tree pythons are not picky eaters. A diet comprising appropriately-sized rodents will do just fine. For a juvenile python, you will want to feed them a small mouse after every few days, typically 5-7 days. If yours is an older juvenile, a feed every 7-10 days will suffice. Green tree pythons and emerald tree boas also share the same resting and hunting postures and, remarkably, both species undergo ontogenetic color change from a red or yellow juvenile to a bright green adult. This can make it quite difficult to differentiate between the two species. One of the few ways to tell them apart is the position of the. Green tree python (Morelia viridis) snake, native to New Guinea and Indonesia. Green tree pythons have over 100 long, sharp, backward-pointing teeth designed to bite into prey and hang on. Green Tree Python (Morelia viridis) coiled in a tree. Adults will grow to sizes of approximately five feet.
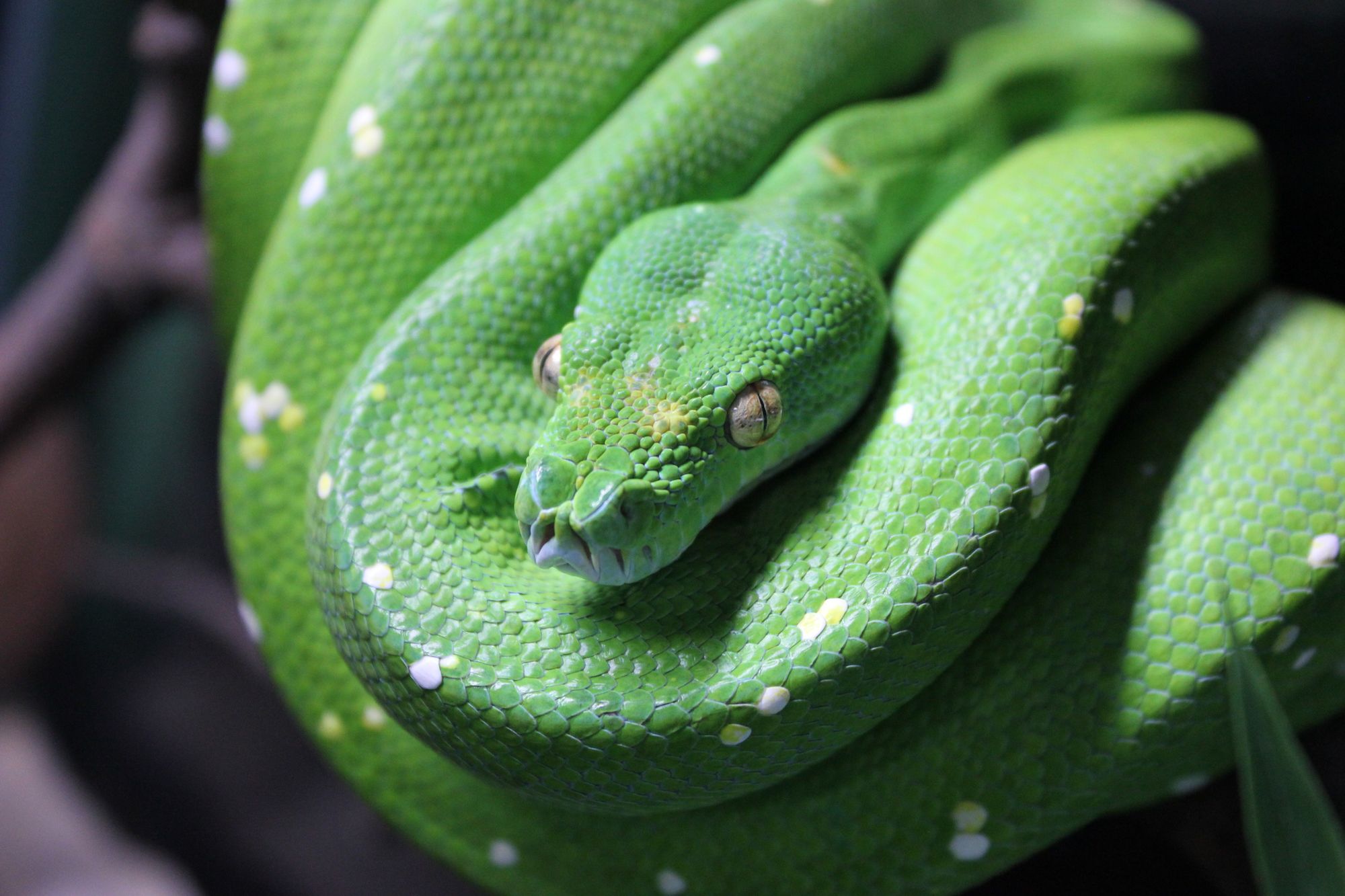

Green Tree Python
What is bright green, lives high up in the trees, and has over 100 teeth? A Green Tree Python! These arboreal snakes are born yellow or brick-red and turn bright green as they mature. Their vivid color, with a pattern of spots and stripes, provides a perfect camouflage. They can be virtually invisible in the tropical rainforests of New Guinea. Imported green tree pythons are aggressive and bite handlers. Due to it being an arboreal constrictor snake, its 100+ teeth create deep cuts and tears in the skin. A bite from green tree python teeth is a painful one that can require medical intervention. The green tree python is not a snake for frequent handling, it is shy and mostly nocturnal.
The green tree python is arboreal, meaning that it spends the majority of its time in trees. It has pit organs around the lips that can detect any object radiating heat. These pits help the snake find prey. The green tree python feeds upon birds and small mammals, including bats. The snake coils around a branch and remains motionless, waiting. Green Tree Pythons have razor-sharp teeth - up to 90 of them. This makes it easier for them to grip their prey and restraint them with their coils. Their Green Coloration Isn't Always Green: Don't be alarmed if you come across a Green Tree Python that isn't green. At different times of the day and during different life cycles, their.
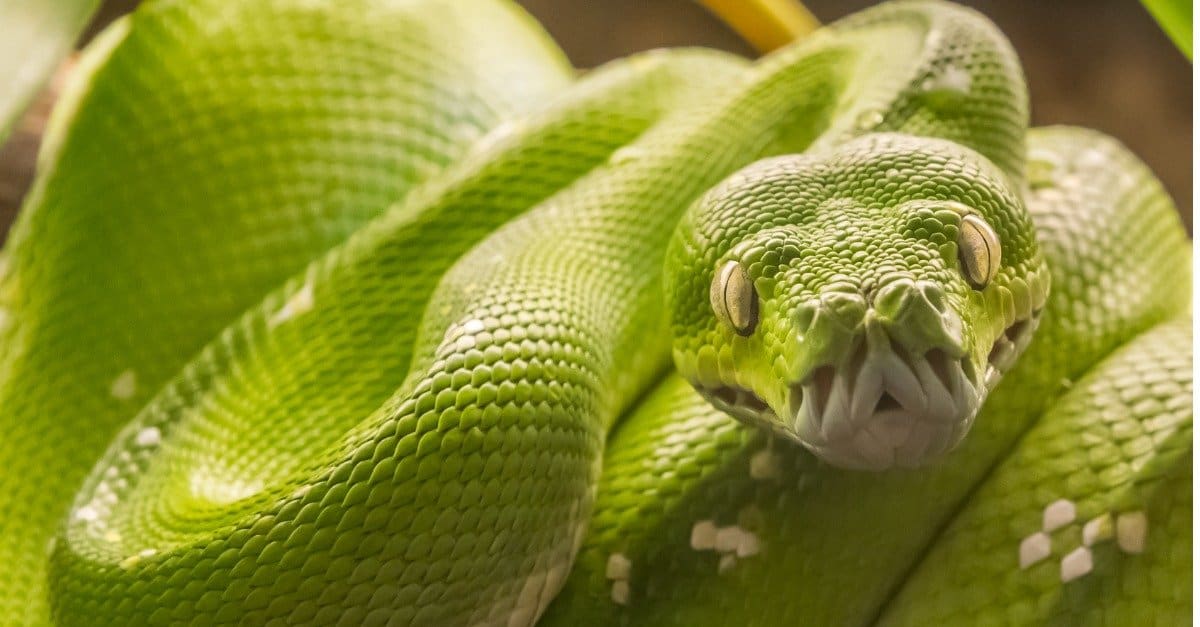

Green Tree Python Animal Facts Morelia viridis Wiki Point
The Green Tree Python has sharp and elongated teeth that are ideal for capturing and holding onto its prey. Once its teeth sink into the prey's flesh, the python uses its powerful muscles to constrict and suffocate its victim, ensuring a successful kill. The green tree python is an exotic, non-venomous snake with a prehensile tail. It's commonly found in New Guinea, Indonesia, and Australia. Though they're non-venomous, green tree pythons are known to have plenty of teeth-typically more than 100-and inflict painful, aggressive bites when provoked.




