A step-by-step explanation of how to draw the HCO3- Lewis Dot Structure (Hydrogen Carbonate or Bicarbonate Ion).For the HCO3- structure use the periodic tabl. Bicarbonate (HCO3-) Ion Lewis Structure Iodate ion (HCO 3-) Ion Lewis Structure Bicarbonate ion contains one carbon atom, three oxygen atoms and one hydrogen atom. Lewis structure of carbonate ion (HCO 3-) contains one C=O bond, two C-O bonds and one O-H bond. There is -1 charge on one oxygen atom in HCO 3- lewis structure. HCO 3- lewis structure
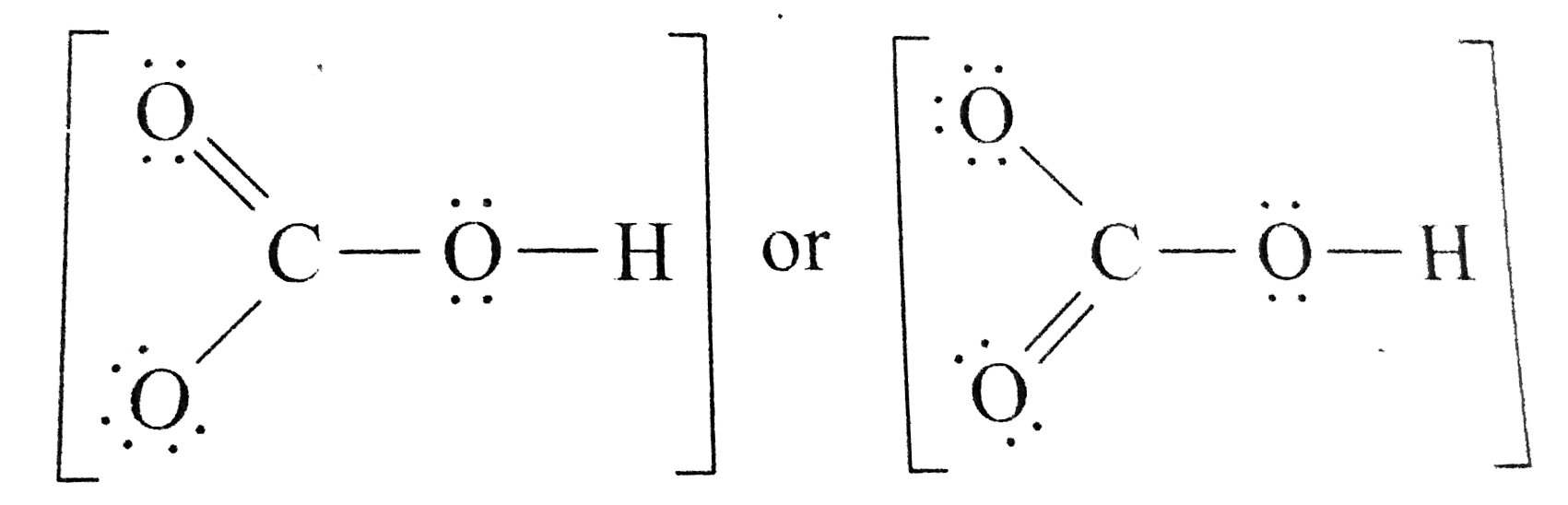
Draw a Lewis structure for the bicarbonate ion, HCO3^().
HCO3- Molecular Geometry / Shape and Bond Angles Wayne Breslyn 725K subscribers Join Subscribe Subscribed 29K views 10 years ago A quick explanation of the molecular geometry of HCO3- including. Lewis structure of HCO3- (Bicarbonate ion) contains one double bond between the Carbon atom (C) & one Oxygen atom (O) and the rest other atoms are single bonded with each other. The Carbon atom is at the center and it is surrounded by 2 Oxygen atoms and one O-H bond. The single bonded Oxygen atom has -1 formal charge. Check me out: http://www.chemistnate.com HCO3- Lewis structure November 7, 2023 by Deep The information on this page is fact-checked. HCO 3- Lewis structure HCO 3- (bicarbonate) has one hydrogen atom, one carbon atom, and three oxygen atoms. In the HCO 3- Lewis structure, there is one double bond and two single bonds around the carbon atom, with three oxygen atoms attached to it.

Hco3lewis Structure
By Sarnali Mukherjee HCO3- Lewis structure is reliable in denoting considerable chemical and physical properties of Bicarbonate. As Lewis structure brings forth a fundamental sketch of HCO3-, it is effective in highlighting the electronic fact about the compound. How to Draw the Lewis Structure of Bicarbonate (HCO3-) | Channels for Pearson+ with Jules Exam Prep Explore Next video General Chemistry 11. Bonding & Molecular Structure Lewis Dot Structures: Acids 4m How to Draw the Lewis Structure of Bicarbonate (HCO3-) chemistNATE 888 Was this helpful? 0 Previous video Next video Comments (0) Related Videos HCO3- lewis structure has a Carbon atom (C) at the center which is surrounded by two Oxygen atoms (O) and one O-H group. There is 1 double bond between the Carbon atom (C) & Oxygen atom (O) and the rest other atoms have a single bond. There is a -1 formal charge on the single bonded Oxygen atom (O). You should put the H CO 3- Lewis structure in brackets with as 1- on the outside to show that it is an ion with a negative one charge. There are a total of 24 valence electrons in H CO 3-. HCO3- Lewis Structure: How to Draw the Lewis Structure for HCO3- Watch on See the Big List of Lewis Structures
Lewis dot structure for hco3 examquiz
Chemistry 101A Topic F: Molecular Structure 9: Basic Concepts of Covalent Bonding 9.3: Drawing Lewis Structures How to draw lewis structure of HCO3-? The bicarbonate (HCO3-) ion comprises a carbon (C) atom at the center. It is double-covalently bonded to an oxygen (O) atom at one side and to another O-atom and an OH functional group vis single covalent bonds at the other two sides. There is no lone pair of electrons on the central C-atom.
Lewis Structures. Page ID. A Lewis Structure is a very simplified representation of the valence shell electrons in a molecule. It is used to show how the electrons are arranged around individual atoms in a molecule. Electrons are shown as "dots" or for bonding electrons as a line between the two atoms. The goal is to obtain the "best" electron. Lewis Structure of Carbonic Acid (H2CO3) The formula of carbonic acid is H2CO3. It has two H atoms, one C atom, and three O atoms. To understand the molecular formula of H2CO3, we have to observe the electronic configuration of the participating atoms and how many atoms they have in the outer shell.

Bicarbonate anion hco3 structural chemical Vector Image
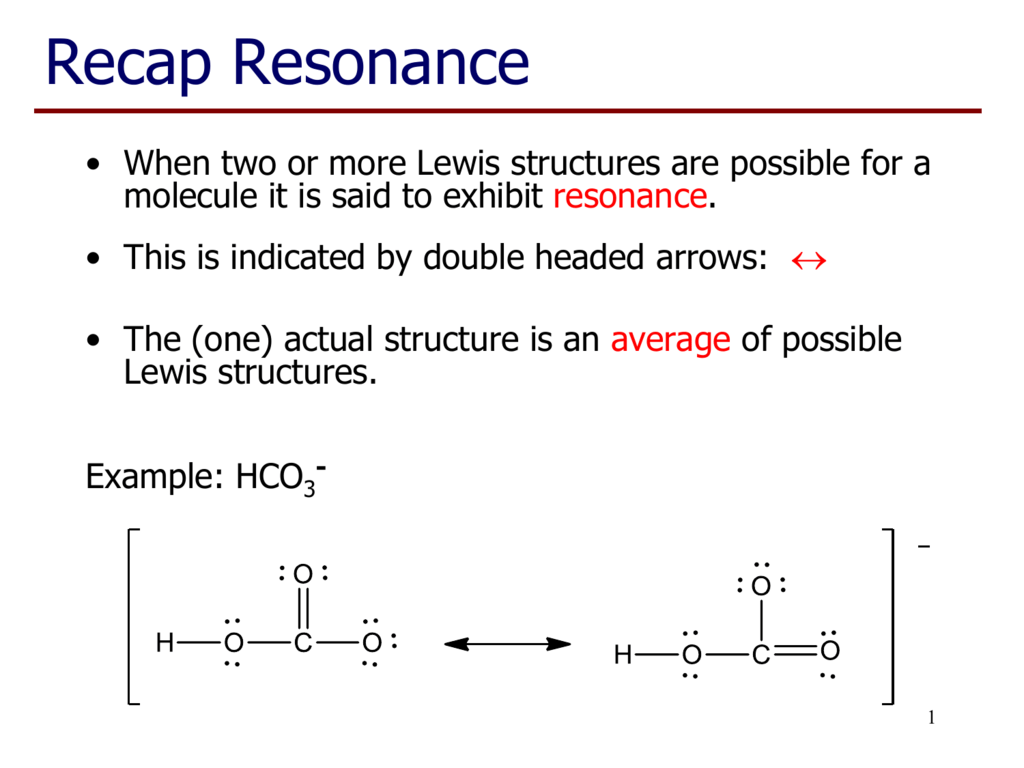
There are two resonance structures HCO3 - (Bicarbonate ion). We start with a valid Lewis structure and then follow these general rules. For the HCO3 - reson. Frequency calculation at the HF/6-31G*//HF/6-31G* level showed that the structure 8 is not a minimum, as it contains two imaginary frequencies. $\ce{H3CO3+}$ shares structural similarities with its triaza-analog, the guanidinium ion, as both are possessing resonance stabilization via their onium forms [3, p. 60]. References



