House's Path Goal Theory The theory was developed by Robert House and has its roots in the expectancy theory of motivation. The theory is based on the premise that an employee's perception of expectancies between his effort and performance is greatly affected by a leader's behavior. The path-goal theory, also known as the path-goal theory of leader effectiveness or the path-goal model, is a leadership theory developed by Robert House, an Ohio State University graduate, in 1971 and revised in 1996.
PPT Leadership and Organizational PowerPoint Presentation, free
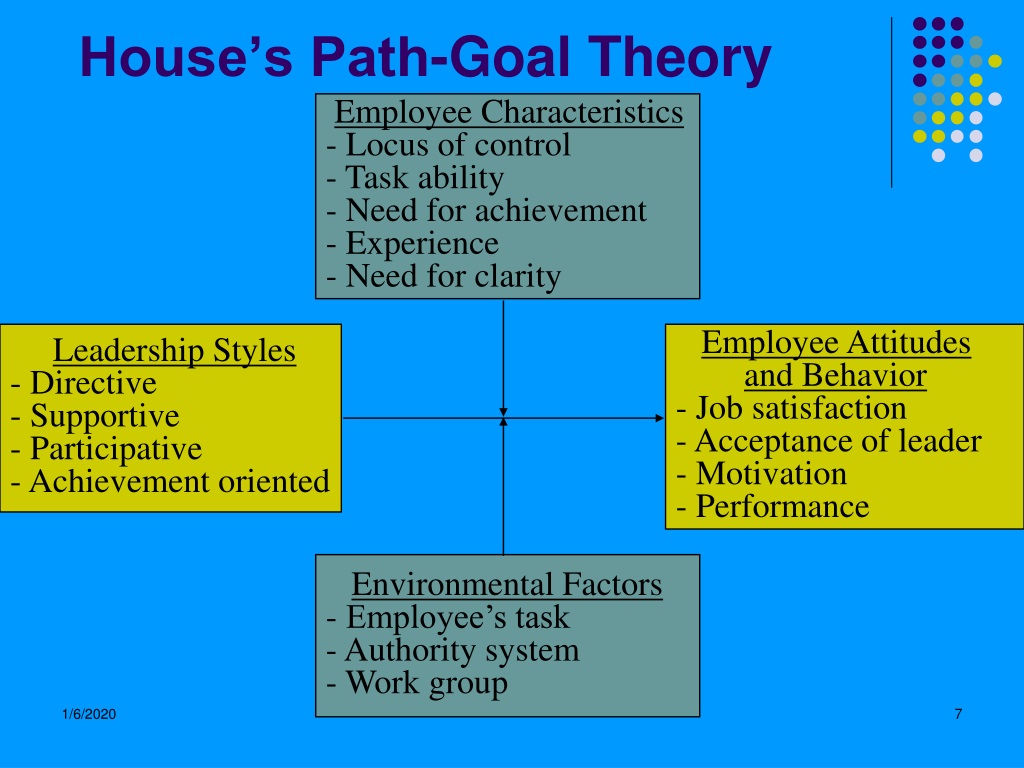
Psychologist, Robert House, developed Path-Goal Theory in 1971, and then redefined and updated it in a 1996 article in The Leadership Quarterly. Let's look at some of the elements of the theory. Leadership Responsibilities According to it, if you want your people to achieve their goals, you need to help, support, and motivate them. What is House's Path-Goal Theory? Path-Goal Model of leadership was proposed by Robert House. It concerns the relationship between leadership styles and situations. More specifically, it explores which leadership styles are more effective in any given situation. House's Path Goal Theory (Situational Leadership) Path-goal Theory by Robert House concentrates on an array of situational factors (task ambiguity, characteristics of followers, and the work environment) and suggests a situation-sensitive use of either directive, supportive, participative, or achievement oriented leadership styles in order to clarify for subordinates the path between performanc. Robert House's path-goal theory provides a framework for understanding how leaders can influence and motivate their teams. This theory suggests that leaders can enhance motivation and performance by clarifying goals, removing obstacles and providing support to their team members.

PPT Chapter 10 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6520467
Robert J. House's 1971 path-goal theory of leadership extended the work of Martin G. Evans and used expectancy theory to describe the interactions between leaders and their followers to answer the question: "How do leaders motivate followers?" There are four leadership styles for the path-goal theory: 1. Directive: In this approach, leaders inform subordinates about expectations and guide them through completion. This gives the team members a sense of direction and belonging and helps clarify goals. 2. Achievement-oriented: Achievement-oriented leadership is a hands-off approach. These notions were further elaborated in the original statement of path-goal theory (House, 1971, p. 326). Substitutes theory is an extension of path-goal theory in that it elaborates in substantial detail many of the moderating variables suggested by path-goal theory. The evidence relative to substitutes theory is mixed (Podsakoff, Mackenzie. The path-goal theory of leadership has fulfilled that criterion well. From the initial development by Evans in 1968, the theory has developed into a contingency form (House, 1971) and into a general diagnostic model (Kerr & Jermier, 1978). Once path-goal theory had focused upon transactional calculative forms of leadership (the impact on.

PPT Leadership PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3121081
Path-Goal theory argues that leaders should vary behaviour according to the situation and the problems or opportunities it presents, encouraging a leader to vary his mind-set and behaviour as needed. House, Robert J. (1996). Path-Goal Theory Of Leadership: Lessons, Legacy, And A Reformulated Theory. The Leadership Quarterly 7.3 (1996): 323-352. Examines R. J. House's (1971) path-goal leadership theory suggesting that it is time to reexamine the level of support for the theory. In light of the absence of studies testing the critical motivational hypotheses of the theory it is hard to argue that the theory has undergone reasonable testing.
Technical Details. Name(s): Path-Goal Theory Author: Robert House Classification: Contingency or Transactional Leadership Theory Year: 1971, revised in 1996 Pro's. In a situation where something needs to be done in a short time - such as emergencies and complicated situations in which there is a time constraint, this method may be preferable. Path-goal theory identifies four key types of leadership behavior: 1. Achievement-oriented With this type of leadership style, the leader focuses on encouraging excellence by setting challenging goals. Leaders encourage employees to pursue their highest level of performance and the leader trusts their ability to handle this.

😱 Robert house path goal theory. What is Robert House's Path. 20221101
Here the Participative leader strengthens the path-goal connection in three ways: First, aligning followers' values and concerns with the aims. Second, ensuring followers are happy with how they are to achieve the goals. Third, giving followers a strong sense of autonomy and satisfaction, so improving motivation to achieve the goal. Robert House's Path-Goal Theory is a leadership theory that is based on specifying the style of behavior of the leader that best fits their direct reports and their work environment. This allows the style of leadership to be able to achieve a specific goal. There are several goals that can be pursued when implementing this theory.




