Paper is a poor conductor of electricity and heat and is therefore considered to be an insulator. We find paper being used in a number of applications such as insulation in electrical cables and also as a protective covering for food products or materials that are sensitive to heat. The conductive properties of paper can change depending on a. Paper is an insulator of both heat and electricity, meaning that it does not conduct either of them. This is because it does not allow the free flow of electrons. However, some types of paper, such as those containing metal particles, may be slightly more conductive. First, let us begin by learning about conduction.

Explain the Difference Between a Conductor and an Insulator Kendal
10 Electrical Insulators . Electric charges do not flow freely through insulators. This is an ideal quality in many cases—strong insulators are often used to coat or provide a barrier between conductors to keep electric currents under control. This can be seen in rubber-coated wires and cables. The most effective electrical insulators are: Is paper an insulator or a conductor? Let's uncover the electrifying truth! The Shocking Role of Paper as an Insulator. When it comes to conducting electricity, paper falls on the side of insulation. Similar to rubber or plastic, paper's tight molecular structure makes it a poor conductor of electrical charge. This means that electric. Paper is an insulator when dry because electrical insulation is good with paper in that state and when the voltage is not crack via the holes in the paper. If the liquidity is high, the paper loses electrical and thermal insulation capability. If the temperature reaches 200°C then the paper can decline or liable to ultraviolet from a sun. Examples of Conductors and Insulators. Examples of conductors include metals, aqueous solutions of salts (i.e., ionic compounds dissolved in water), graphite, and the human body. Examples of insulators include plastics, Styrofoam, paper, rubber, glass and dry air. The division of materials into the categories of conductors and insulators is a.

Is Paper a Conductor or Insulator
The flow of electricity is called current. Metals are generally very good conductors, meaning they let current flow easily. Materials that do not let current flow easily are called insulators. Define conductor and insulator, explain the difference, and give examples of each.. Thus a positively charged glass rod attracts neutral pieces of paper, as will a negatively charged rubber rod. Some molecules, like water, are polar molecules. Polar molecules have a natural or inherent separation of charge, although they are neutral overall.. Electrons and ions in insulators are bound in the structure and cannot move easily—as much as 1023 10 23 times more slowly than in conductors. Pure water and dry table salt are insulators, for example, whereas molten salt and salty water are conductors. Figure 18.11 An electroscope is a favorite instrument in physics demonstrations and. A conductor is a material that allows electrons to flow freely through it, making it useful for carrying electric current. An insulatoris a material that resists the flow of electrons, so it does not allow electric current to pass through it. Learn about how conductors and insulators work and how they are effected by changes in electrical current.

Conductor Or Insulator? Science Experiment For Kids YouTube
Make a list of all of the objects that you can see in the room. Separate these objects into conductors and insulators. Explain how you know if a material is a conductor or an insulator. Electrical insulation papers are paper types that are used as electrical insulation in many applications due to pure cellulose having outstanding electrical properties. Cellulose is a good insulator and is also polar, [clarification needed] having a dielectric constant significantly greater than one. Electrical paper products are classified by their thickness, with tissue considered papers.
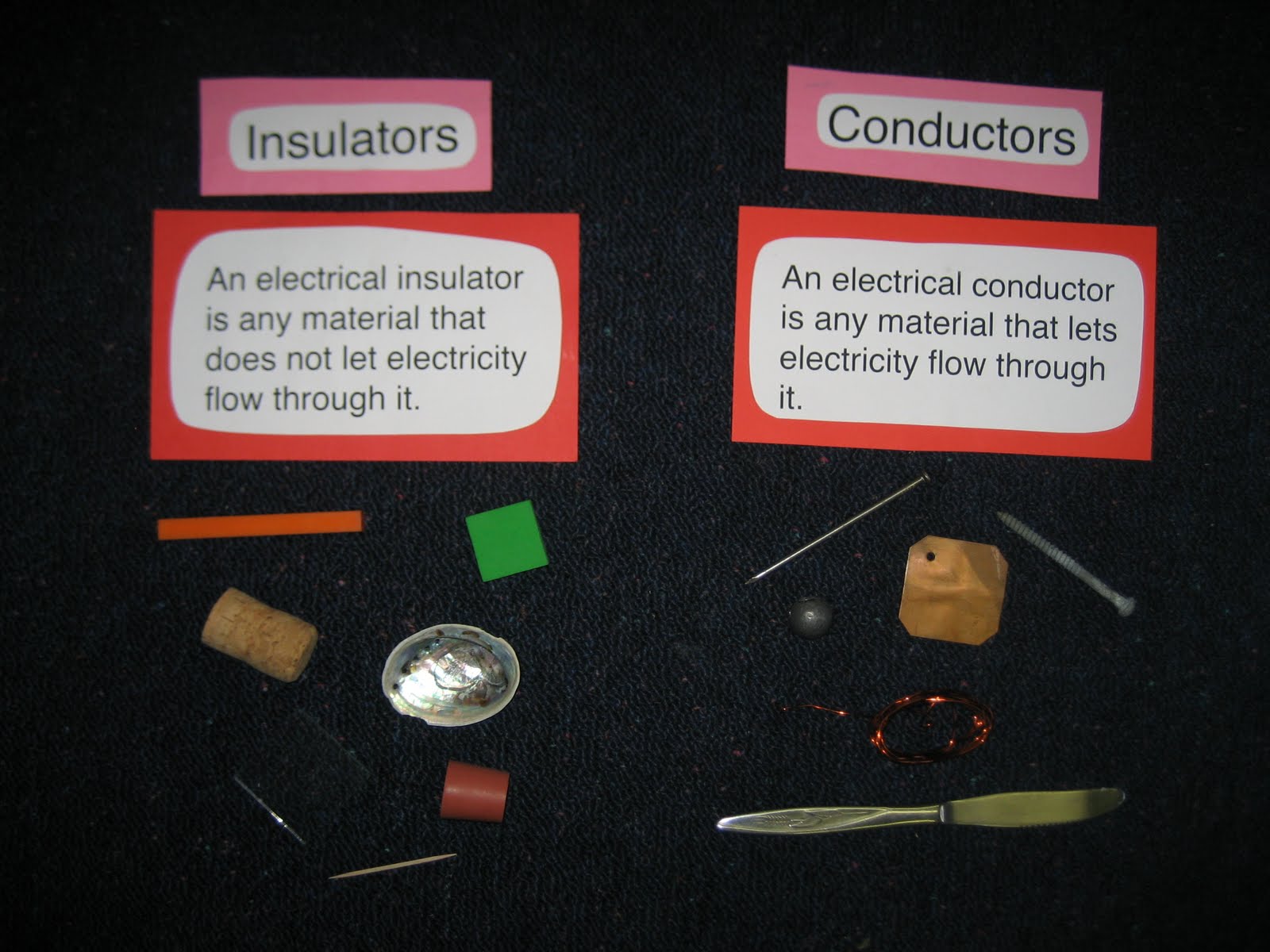
After defining a conductor and an insulator, complete the chart by listing which test items are conductors and which are insulators (poor or non-conducting objects). Math extension: Cut two of the same-size circles out of two sheets of different color construction paper (cut at the same time so they are exactly the same size). These are called insulators. Electrons and ions in insulators are bound in the structure and cannot move easily—as much as 10 23 times more slowly than in conductors. Pure water and dry table salt are insulators, for example, whereas molten salt and salty water are conductors.
ScienceEHS Conductors and Insulators
Is paper an insulator? Question: Is paper an insulator? Material Classification: We classify various kinds of materials that react differently with heat and electricity as insulators and conductors. These two categories each have their own characteristics that carry out different functions to our everyday lives. Answer and Explanation: Comparing Materials. Glass is far inferior to paper, plastic and Styrofoam in terms of insulation. Thermal conductivity in terms of BTU/ (feet - hour - degrees F) is 1.82 for glass, 0.09 for paper, 0.06 for Styrofoam. The conductivity of plastics varies depending on the materials: for polypropylene and polycarbonate, the thermal conductivity.



