Simply put, the difference between these theories is that monetarist economics involves the control of money in the economy, while Keynesian economics involves government expenditures.. The primary difference between Monetarism and Keynesianism stems from the widely different views on the authority and means for maintaining economic stability in a nation. Monetarism revolves around the inflow of money into the economy, while Keynesianism advocates control over the demand for goods and services.

What are the key Differences between Keynesian vs Economics
The distinction between Keynesian and monetarists positions is a bit more blurred. For example, many 'Keynesian' economists have taken on board ideas of a natural rate of unemployment, in addition to demand deficient unemployment. 'New Classical' economists are more likely to accept ideas of rigidities in prices and wages. Related The key difference at the core of both theories is that Monetarists do not think that government spending is the best path to economic stability. Instead, they emphasize inflation. Keynesian and. Monetarism is a branch of Keynesian economics that emphasizes the use of monetary policy over fiscal policy to manage aggregate demand, contrary to most Keynesians. 12 - Keynesians versus monetarists Published online by Cambridge University Press: 10 December 2009 Mark Blaug Chapter Get access Cite Summary Fruitless debate? In taking up this topic, we go to the heart of the furious controversies that have surrounded questions of macroeconomic policy in recent years.
PPT Benefits of a Common Currency PowerPoint Presentation, free
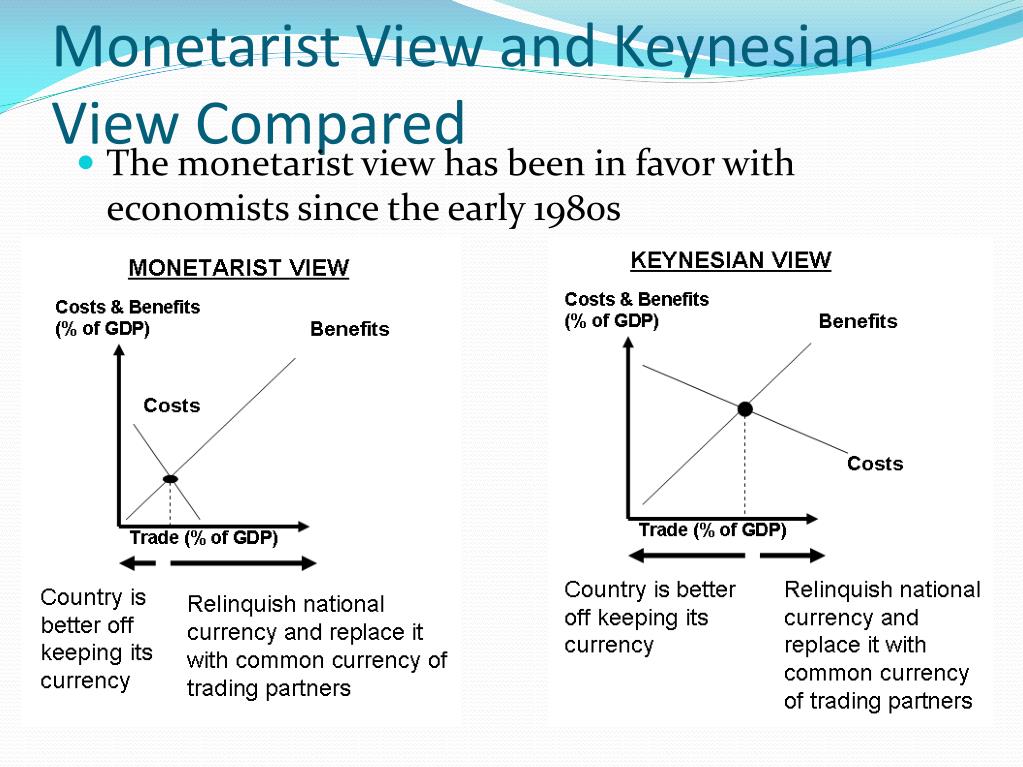
Learn about the comparison between Monetarism and Keynesian Approaches. In essence, monetarists say, "only money matters for aggregate demand"; Keynesians reply, "Money matters but so does fiscal policy". See Fig. 14.2, which is self-explanatory. A second difference revolves around aggregate supply. Keynesian economics stresses that the AS curve is relatively flat. If prices and wages are. The article analyzes two approaches to developing economic policy, Keynesian and monetarist. The main ideas of J. Keynes and M. Friedman and their applicability as the basis for designing an anticrisis economic policy are considered in a historical context. In short, Keynes, the Keynesians and Monetarism contends that monetarism defeated Keynesianism in the battle of ideas in the 1970s and 1980s. The achievement of greater macroeconomic stability in the last 15 years is largely due to the impact of monetarist thinking on policy-making. By Nick K. Lioudis Updated Mar 20, 2019 Monetarist economics is Milton Friedman 's direct criticism of Keynesian economics theory, formulated by John Maynard Keynes. Simply put, the difference between these theories is that monetarist economics involves the control of money in the economy, while Keynesian economics involves government expenditures.

keynesianism vs
The Monetarists versus the Keynesians: There are conflicting views on the mechanism as to how money supply affects the general economic activities or income level. On the one hand, some theorists put the emphasis on a direct relation between the money supply and expenditure. Whereas Keynesians naively believe that government spending is a source of economic growth, monetarists in a similarly naïve way believe that money creation for the sake of it boosts the economy.
Currently, Keynesians are supposed to be the advocates of lax monetary policy, while Monetarists propagate a return to normality. The controversy between Keynesianism and Monetarism, however, is a counter-productive frame for the current debate. Keynesian economics is an economic theory of total spending in the economy and its effects on output and inflation . Keynesian economics was developed by the British economist John Maynard Keynes.

and Keynesian comparison part 1 theory upsc
Nominal GDP rose only 0.3 percent in the first quarter. Since money growth plus velocity growth equals nominal GDP growth, M2 velocity must have declined by 6.6 percent. So a 6.9 percent growth in. Keynesians argue greater emphasis on the role of aggregate demand in causing and overcoming a recession. 2. Demand deficient unemployment Because of the different opinions about the shape of the aggregate supply and the role of aggregate demand in influencing economic growth, there are different views about the cause of unemployment




