nephron, functional unit of the kidney, the structure that actually produces urine in the process of removing waste and excess substances from the blood. There are about 1,000,000 nephrons in each human kidney. A nephron is the basic structural and functional unit of the kidneys that regulates water and soluble substances in the blood by filtering the blood, reabsorbing what is needed, and excreting the rest as urine. Its function is vital for homeostasis of blood volume, blood pressure, and plasma osmolarity. It is regulated by the neuroendocrine.
Nephron, it's different parts and function Pharmacy Gyan
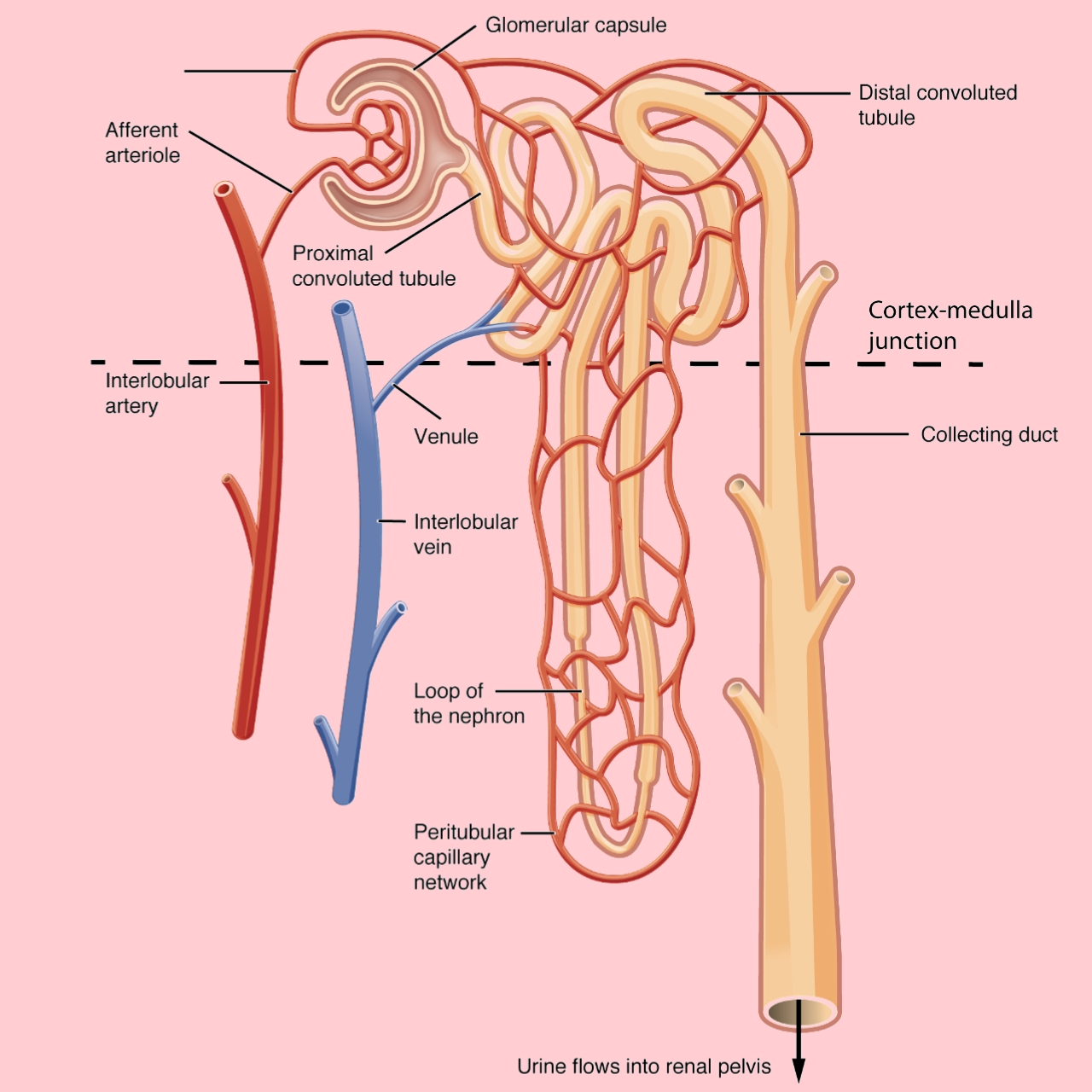
The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney. The glomerulus and convoluted tubules are located in the kidney cortex, while collecting ducts are located in the pyramids of the medulla. (credit: modification of work by NIDDK) Tubular parts of a Nephron - converts the filtrate into urine The Bowman's capsule / Glomerular capsule: A nephron is the basic unit of structure in the kidney. A nephron is used separate to water, ions and small molecules from the blood, filter out wastes and toxins, and return needed molecules to the blood. The nephron functions through ultrafiltration. Structure Fig.1) Schematic diagram of the nephron (yellow), relevant circulation (red/blue), and the four methods of altering the filtrate. The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney. [2] This means that each separate nephron is where the main work of the kidney is performed. A nephron is made of two parts: Nephrons are the "functional units" of the kidney; they cleanse the blood of toxins and balance the constituents of the circulation to homeostatic set points through the processes of filtration, reabsorption, and secretion.

Associate Degree Nursing Physiology Review Human anatomy and
2. The "Bowman's capsule" is the part of a nephron which receives the filtrate. It is a part of a nephron, and only delivers filtrate to a single nephron. The afferent artery and efferent artery are not nephrons, they are arteries outside the nephron that run around the kidney (the red lines that run around the large kidney diagram to the right. 1/4 Synonyms: Cortex renalis The kidneys are paired retroperitoneal organs of the urinary system. Their function is to filter blood and produce urine. Each kidney consists of a cortex, medulla and calyces. The nephron is the main functional unit of the kidney, in charge of removing metabolic waste and excess water from the blood. The left kidney is located at about the T12 to L3 vertebrae, whereas the right is lower due to slight displacement by the liver. Upper portions of the kidneys are somewhat protected by the eleventh and twelfth ribs ( Figure 25.7 ). Each kidney weighs about 125-175 g in males and 115-155 g in females. They are about 11-14 cm in length, 6. Nephron (overview) Ultrastructurally, the nephron is the functional representative of the kidney. Each nephron contains arenal corpuscle, which is the initial component that filters the blood, and a renal tubule that processes and carries the filtered fluid to the system of calyces. The renal corpuscle has two components: the glomerular (Bowman.

Diagram of the nephron segments and its juxtaglomerular apparatus
Label a Nephron by ninalahoti 129,291 plays 16 questions ~40 sec English 16p 72 4.36 (you: not rated) Tries Unlimited [?] Last Played December 5, 2023 - 02:42 PM There is a printable worksheet available for download here so you can take the quiz with pen and paper. From the quiz author This is a nephron. Label it. Remaining 0 Correct 0 Wrong 0 April 5, 2021 in Anatomy, Worksheets by Shannan Muskopf anatomy, kidney, label, learn, nephron, practice, urinary Students practice labeling the urinary system with this drag and drop activity. Three slides have detailed images of the kidneys, ureters, and nephrons.
Description. Image of a close up nephron and its place in the kidney. Labels on the kidney cross section show where unfiltered blood enters, filtered blood leaves, and urine exits. On the nephron, the glomerulus, tubule, and collecting duct are labeled along with where unfiltered blood enters, filtered blood exits, and urine exits. Practice labeling the nephron with this reinforcement activity. Students can also color the image to identify the major structures of the nephron: glomerulus, bowman's capsule, proximal and distal tubules, loop of Henle, collecting duct and capillaries.

Nephron Definition, Structure, Physiology, Functions
The nephron has three major parts: the glomerulus, the Bowman's Capsule, and the tubules, which consist of the promimal and distal tubule and the Loop of Henle. Blood enters the kidney from the renal artery and moves into the glomerulus, where filtration occurs. Filtration is the process by which water and dissolved particles are pulled out of. A nephron is the unit of structure and function in the kidney. Each nephron is a coiled tube held together by a tough fibrous connective tissue. In humans, a healthy adult has 1 to 1.5 million nephrons in each kidney, functioning together to filter blood from all its impurities.




