Lymph Node Map | View 3D Lymph Node Anatomy Map Model | LLS Lymph Node Anatomy 3D Model 3D Model Library This model contains the following chapters. Use the buttons on the image to interact in 3D. Lymphatic Circulation - View #1 Lymphatic Circulation - View #2 Lymphatic Filtration amount USD Dedicate my donation in honor or in memory of someone Lymph nodes look like sprouting kidney beans, where the sprouts are tubes that carry lymphatic fluid around your body (lymphatic channels). Leading into each node are blood vessels. The lymph node has a protective outside layer (capsule), like a shell on the bean that divides parts of the node into rooms with a large open room in the center.

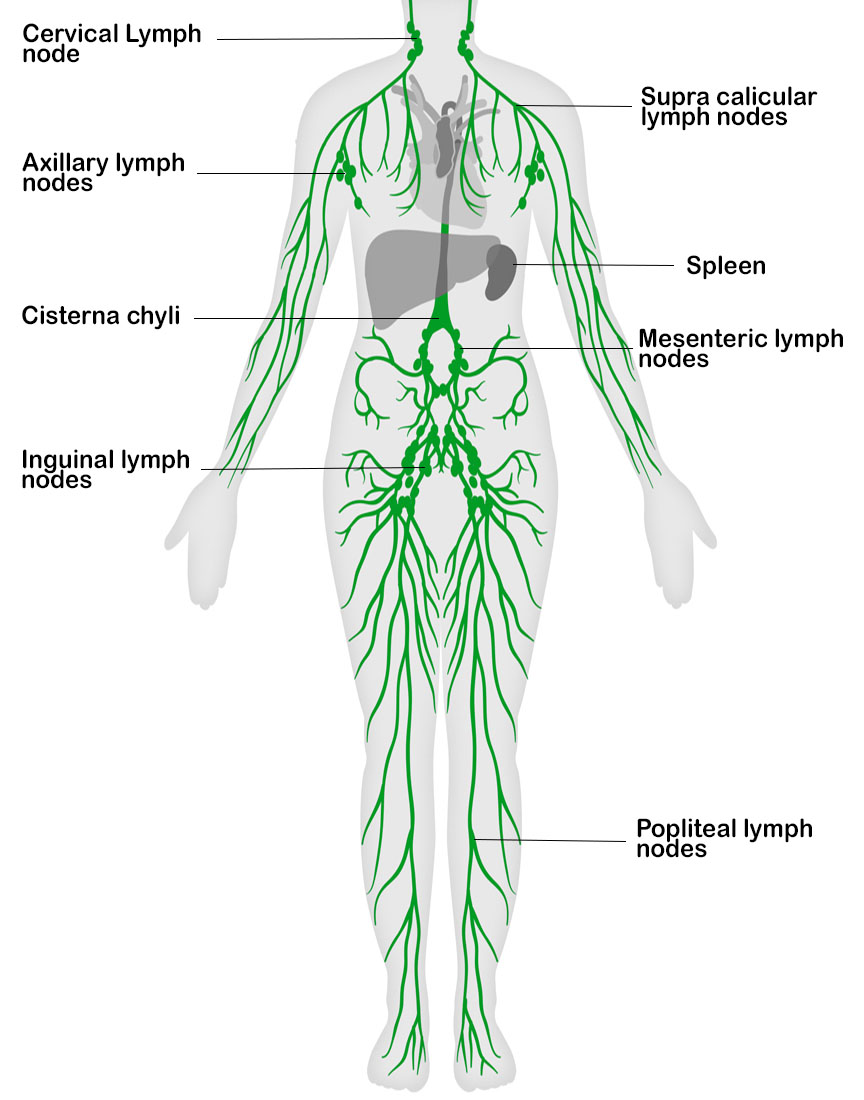
Lymph Node Locations And The Importance Of Lymphatic Drainage
Gross anatomy. Lymph nodes are bean-shaped structures about 0.1 - 2.5 cm in length. The node is enclosed in a capsule and has an indentation on one surface (along one of its long axes) known as the hilum. The hilum is the point at which arteries carrying nutrients and lymphocytes enter the lymph node and veins leave it. How they work Common conditions Lymph node cancer Contacting a doctor Summary Lymph nodes are located throughout the body. They are small, bean-shaped glands that play a crucial role in the. A lymph node, or lymph gland, [1] is a kidney -shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that include B and T cells. The head and neck, as a general anatomic region, is characterized by a large number of critical structures situated in a relatively small geographic area. It is inclusive of osseous, nervous, arterial, venous, muscular, and lymphatic structures. Lymphadenopathy is a significant clinical finding associated with acute infection, granulomatous disease, autoimmune disease, and malignancy. The.

Illustration of the major neck lymph node levels, with anatomical
Lymph nodes are your immune system 's first line of defense, protecting you from things like bacteria or viruses that could make you sick. You have hundreds of the small, round, or bean-shaped. Lymph Nodes. Lymph nodes are small, kidney-shaped organs of the lymphatic system. There are several hundred lymph nodes found mostly throughout the thorax and abdomen of the body with the highest concentrations in the axillary (armpit) and inguinal (groin) regions. The outside of each lymph node is made of a dense fibrous connective tissue capsule. A normal young adult body contains up to 450 lymph nodes, of which 60-70 are found in the head and neck, 100 in the thorax and as many as 250 in the abdomen and pelvis. Lymph nodes are particularly numerous in the neck, mediastinum, posterior abdominal wall, abdominal mesenteries, pelvis and proximal regions of the limbs (axillary and inguinal. Each lymph node is divided into two general regions, the capsule and the cortex. The capsule is an outer layer of connective tissue. Underlying the capsule is the cortex, a region containing mostly inactivated B and T lymphocytes plus numerous accessory cells such as dendritic cells and macrophages. The cortex is further divided into two functional areas: the outer cortex and inner cortex, or.
LYMPHATIC SYSTEM Lab Medica Healthcare
About your lymphatic mapping procedure. Lymphatic mapping is a procedure where radioactive liquid is injected under your skin near the site of the tumor. The radioactive liquid travels in your lymphatic fluid and creates a "map" of your lymphatic system. This map shows where your sentinel lymph node(s) are located. The chest wall thoracic lymph nodes receive drainage from the breasts, arms, pectoral muscles, and other muscles and skin located in the upper section of the chest. Thoracic lymph nodes are.
The lymphatic system (also called the lymphoid system) is part of the immune system. The system moves lymph, a clear fluid containing white blood cells, through your bloodstream. The lymphatic system involves many organs, including the tonsils, adenoids, spleen, and thymus. Lymph nodes filter out bacteria and cancer cells and create white blood. ISSN 2534-5079. This human anatomy module is about the lymph nodes, ganglionic areas and organs involved in oncological disease spread assessments. It was created from a scanner (computed tomography) with iodine injection of a healthy subject, covering the face, neck, thorax, abdomen and pelvis.
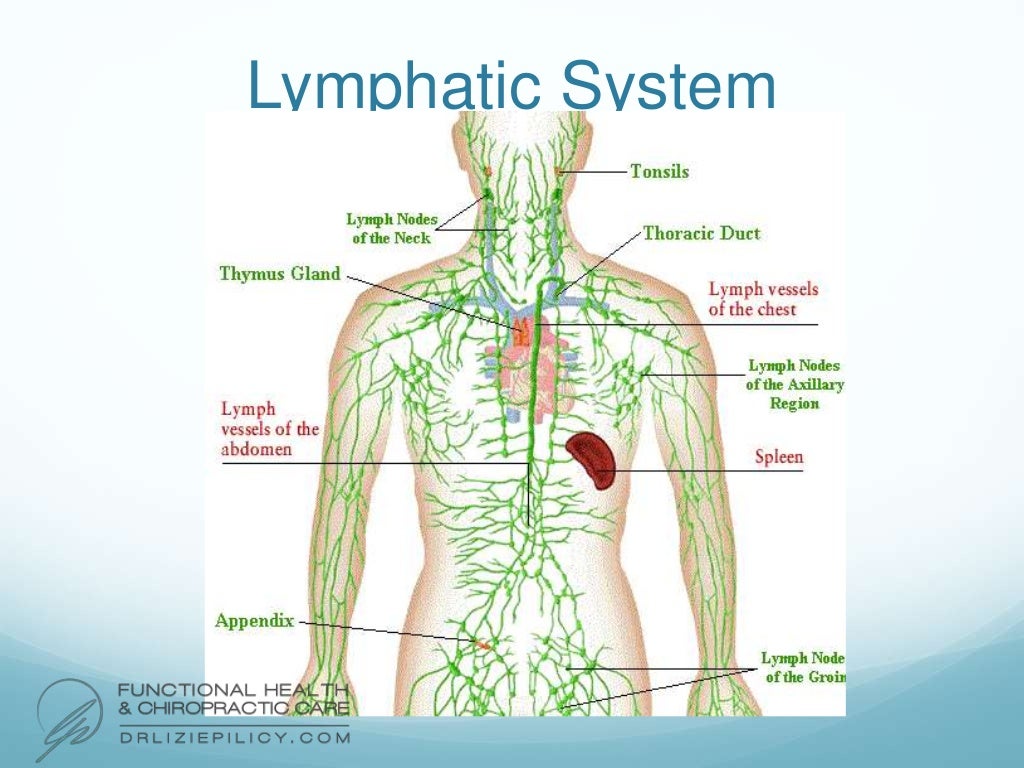
Endocrine and Lymphatic System
Lymph nodes of the head, neck and upper limb function to receive, filter and transport lymphatic fluid from surrounding tissues and viscera back into the bloodstream via the thoracic duct, right lymphatic duct and/or subclavian lymphatic trunk. Mediastinal Lymph Node Map Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Alrijne Hospital in Leiderdorp, the Netherlands Publicationdate 2010-06-08 This is an update of the 2007 article, which used the Mountain-Dresler regional lymph node classification for lung cancer staging (MD-ATS maps) (1).




