Normal hand | Radiology Case | Radiopaedia.org Normal hand Case contributed by Andrew Murphy Diagnosis certain Share Add to Citation, DOI, disclosures and case data Presentation Patient punched a wall with both hands. x-ray Frontal Oblique Lateral Frontal Oblique Lateral Normal hand series 8 public playlists include this case A hand X-ray (radiograph) is a test that creates a picture of the inside of your hand. The picture shows the inner structure ( anatomy) of your hand in black and white. Calcium in your bones absorbs more radiation, so your bones appear white on the X-ray.

Normal hand of 13 year old, Xray Stock Image C039/3319 Science
Presentation Hand pain and a history of arthritis Patient Data Age: 55 years Gender: Female Right hand x-ray Frontal Lateral No abnormalities, no enthesopathy, no subluxation, no dislocation. Conclusion: Unremarkable appearances, if patient still presents with pain follow up with MRI. Image read by Dr Kevin Legendre. Case Discussion Phalanges Assess the cortex of each phalanx in turn, proximal to distal: pay particular attention to phalangeal tufts, shafts and ligamentous insertions if lateral or medial bony fragment, think collateral ligament avulsion if dorsal bony fragment, think extensor tendon avulsion if palmar bony fragment, think volar plate avulsion Alignment What can you see in an x ray? Normal Findings: Hand Bones/ Wrist Joint In order to read and interpret x-ray imaging of the hand, one must be familiar with the normal anatomy of the hand. Bones The human hand is comprised of many small bones and joints that are a part of the skeletal system. Overview A hand X-ray is a black and white image that shows the inner structures of your hand, such as your bones and soft tissues. This diagnostic tool can help your doctor locate and.

X Ray Hand Bones
Bones of the hand - Normal X-ray (PA) Finger bones articulate at the metacarpophalangeal joints ( MCPJ ), the proximal interphalangeal joints ( PIPJ) and the distal interphalangeal joints ( DIPJ) Normal AP view of the hand demonstrating the normal configuration of epiphyses in an 8-year-old boy. Ultrasound The advent of high-frequency ultrasound probes has revolutionized soft tissue imaging of the hand and wrist. This test is an x-ray of one or both hands. Alternative Names. X-ray - hand. How the Test is Performed. A hand x-ray is taken in a hospital radiology department or your health care provider's office by an x-ray technician. You will be asked to place your hand on the x-ray table, and keep it very still as the picture is being taken. Hand Checklists 1 Radiographic examination PA Pronation oblique Lateral 2 Common sites of injury in adults Fractures Phalanges (55% of hand injuries) Distal (50+% of fractures of the phalanx) Ungual tuft, base, shaft, baseball finger avulsion Proximal (15% of fractures of the phalanx) Shaft, base, condyles, volar plate avulsion
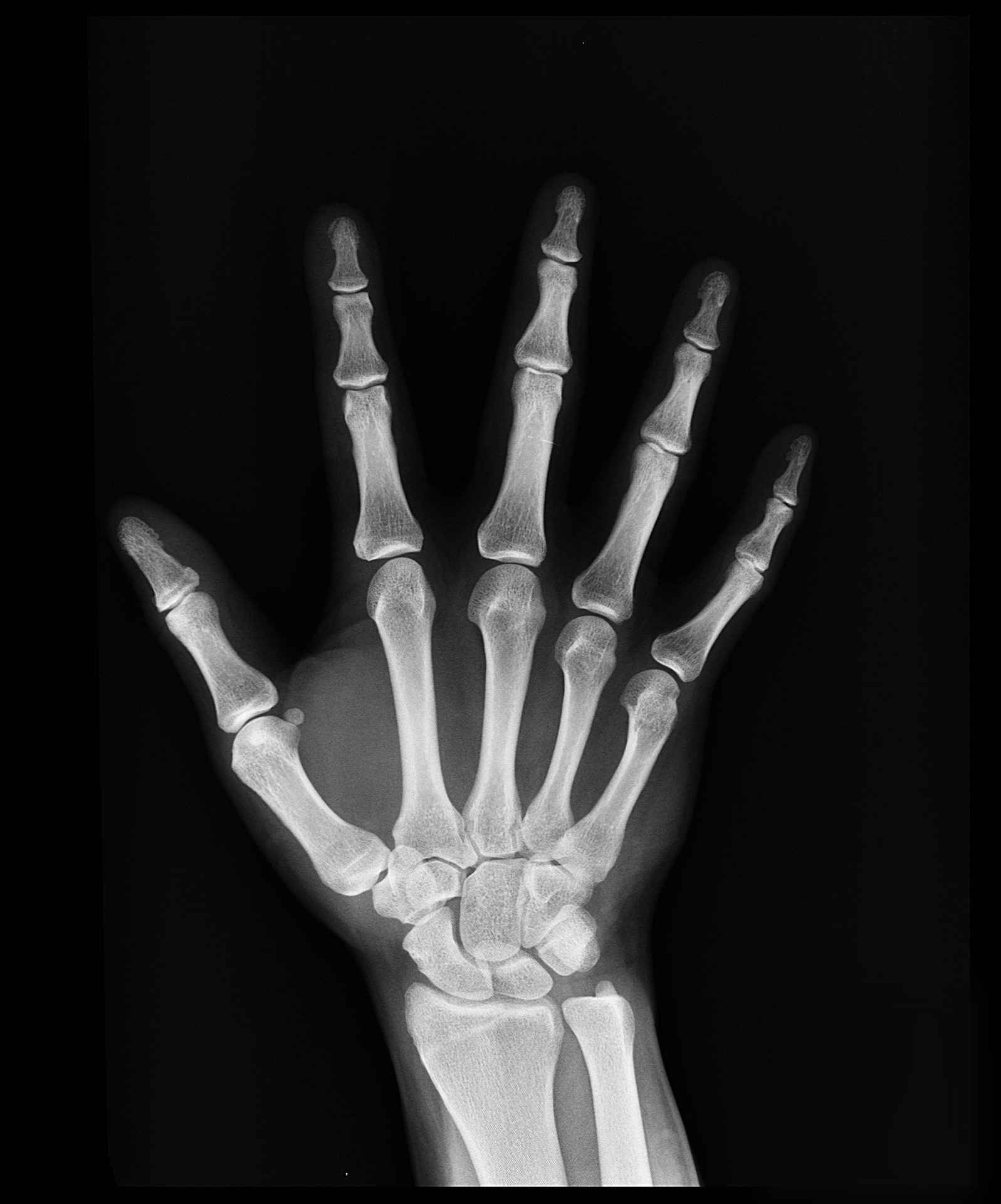
Normal Hand X Ray Colorvir Xray photo of normal right hand Stock
lateral view projection 90° to the PA view demonstrates multiple carpal bones overlapping, often used to determine fracture displacement used to localize foreign bodies Additional projections lateral fan view: offers a view of the individual middle and distal phalanges, avoiding overlap lateral flexion view Approximately 30% of scaphoid fractures are not visible on initial X-rays - appropriate treatment and follow up are required even if the X-rays are normal. The standard wrist views are Posterior-Anterior (PA) and Lateral. In certain circumstances further views are helpful so that the 8 overlapping bones are more easily seen.
Approach to Hand X-Rays X-Ray Interpretation Hand radiographs are typically done in 3 views. The ABCDs approach to interpretation is described below. POSTERIOR-ANTERIOR VIEW This is the most commonly used view for interpretation. Immobilization techniques Children will find it difficult to keep their hand still; particularly if the limb is injured. One option is to have a parent or radiographer hold the child's hand in place; however, the parent's hand may appear on the radiograph and obscure the child's anatomy.

Normal Hand X Ray Colorvir Xray photo of normal right hand Stock
Hand: When acquiring hand radiographs, the patient is typically seated at the end of the table with the elbow in flexion. The technologist should align the long axis of the hand, generally parallel to the image receptor.. The Grashey view is obtained with the patient rotated 35-45 degrees, so the x-ray beam is parallel to the articular. normal hand x-ray Moderate hand arthritis on x-ray Severe hand arthritis on x-ray Arthritis is typically diagnosed on x-rays. Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis and is related to wear-and-tear processes, genetics, injuries, and it is a normal part of the aging process.




